
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
This article is a draft. FairMormon editors are currently editing it. We welcome your suggestions on improving the content.
| Answers portal |
| The Book of Abraham |
 |
|
FAQ:
Book of Abraham content: Production: |
|
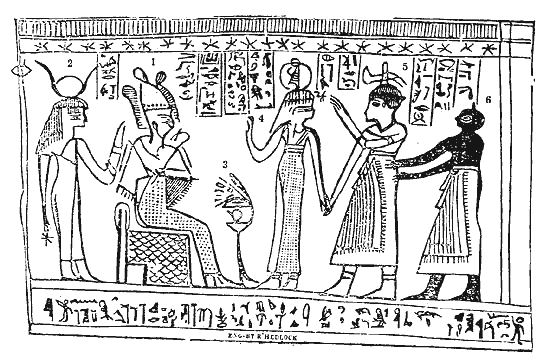
== The following are common criticisms associated with Facsimile 3:
To see citations to the critical sources for these claims, click here
====
According to Michael D. Rhodes in the Encyclopedia of Mormonism,
Facsimile 3 presents a constantly recurring scene in Egyptian literature, best known from the 125th chapter of the Book of the Dead. It represents the judgment of the dead before the throne of Osiris. It is likely that it came at the end of the Book of Breathings text, of which Facsimile 1 formed the beginning, since other examples contain vignettes similar to this. Moreover, the name of Hor, owner of the papyrus, appears in the hieroglyphs at the bottom of this facsimile.
Joseph Smith explained that Facsimile 3 represents Abraham sitting on the pharaoh's throne teaching principles of astronomy to the Egyptian court. Critics have pointed out that the second figure, which Joseph Smith says is the king, is the goddess Hathor (or Isis). There are, however, examples in other papyri, not in the possession of Joseph Smith, in which the pharaoh is portrayed as Hathor. In fact, the whole scene is typical of Egyptian ritual drama in which costumed actors played the parts of various gods and goddesses.
In summary, Facsimile 1 formed the beginning, and Facsimile 3 the end of a document known as the Book of Breathings, an Egyptian religious text dated paleographically to the time of Jesus. Facsimile 2, the hypocephalus, is also a late Egyptian religious text. The association of these facsimiles with the book of Abraham might be explained as Joseph Smith's attempt to find illustrations from the papyri he owned that most closely matched what he had received in revelation when translating the Book of Abraham. Moreover, the Prophet's explanations of each of the facsimiles accord with present understanding of Egyptian religious practices. [1]
Robert K. Ritner, Professor of Egyptology at the University of Chicago, states that "Smith’s hopeless translation also turns the goddess Maat into a male prince, the papyrus owner into a waiter, and the black jackal Anubis into a Negro slave."[2]
Larry E. Morris notes the following in response to criticism leveled by Professor Ritner at the Book of Abraham,
Furthermore, Ritner does not inform his readers that certain elements of the Book of Abraham also appear in ancient or medieval texts. Take, for example, Facsimile 3, which depicts, as Ritner puts it, "enthroned Abraham lecturing the male Pharaoh (actually enthroned Osiris with the female Isis)" (JNES, p. 162). In what Ritner describes as nonsense, Joseph Smith claimed that Abraham is "sitting upon Pharoah's throne . . . reasoning upon the principles of Astronomy" (Facsimile 3, explanation).
Clearly, Joseph Smith's interpretation did not come from Genesis (where there is no discussion of Abraham doing such a thing). From Ritner's point of view, therefore, this must qualify as one of Joseph's "uninspired fantasies." But going a layer deeper reveals interesting complexities. A number of ancient texts, for example, state that Abraham taught astronomy to the Egyptians. Citing the Jewish writer Artapanus (who lived prior to the first century BC), a fourth-century bishop of Caesarea, Eusebius, states: "They were called Hebrews after Abraham. [Artapanus] says that the latter came to Egypt with all his household to the Egyptian king Pharethothes, and taught him astrology, that he remained there twenty years and then departed again for the regions of Syria."22
As for Abraham sitting on a king's throne—another detail not mentioned in Genesis—note this example from Qisas al-Anbiya' (Stories of the Prophets), an Islamic text compiled in AD 1310: "The chamberlain brought Abraham to the king. The king looked at Abraham; he was good looking and handsome. The king honoured Abraham and seated him at his side."23 [3]
Morris concludes,
Ritner may counter that such parallels do not establish the authenticity of the Book of Abraham. That is true, but certainly they deserve some mention. At the very least, these parallels show that "all of this nonsense" is not really an appropriate description of Joseph Smith's interpretation. Fairness demands that Ritner, in his dismissal of the content of the Book of Abraham, at least mention similarities between it and other texts about Abraham and point readers to other sources of information. [4]
For a detailed response, see: Book of Abraham/Parallels with ancients texts
Critics focus on three specific interpretations which reference an interpretation of characters in the facsimile. Joseph Smith provides the following identifications for three of the figures in the facsimile:
What is notable in these particular identifications is that Joseph isn't simply assigning an identify to each figure, but is indicating that characters located near each figure confirm the assignments. Egyptologists note that the characters have an entirely different meaning.
| This section of the article is still under construction. We welcome your suggestions for improving the content of this FairMormon Answers article. |
Figure 2, identified by Joseph as "King Pharaoh" and figure 4, identified by Joseph as "Prince of Pharaoh" are obviously drawn as female figures. The fact that they are drawn as females is so obvious, in fact, that critics take this as evidence of Joseph's lack of ability to interpret the facsimiles in any fashion whatsoever. Since the figures would obviously have appeared as females even to Joseph's eye, why then are they interpreted as two of the primary male figures?
For a detailed response, see: Identification of female figures in Facsimile 3
| This section of the article is still under construction. We welcome your suggestions for improving the content of this FairMormon Answers article. |

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now