
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
< Criticism of Mormonism | Websites | MormonThink
| Joseph Running with the Plates | A FAIR Analysis of: MormonThink, a work by author: Anonymous
|
Blacks and the Priesthood |
| Claim Evaluation |
| MormonThink |
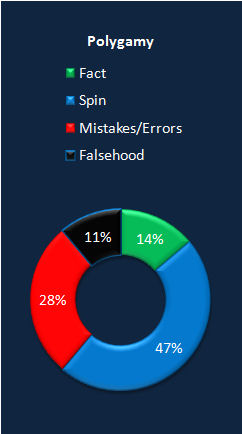
|
The reasons most commonly given by members (even if not published in church lesson manuals) to justify polygamy are: There were more women than men in the 1800s and polygamy provided a way for women, particularly widows to have the benefits of a husband
The reasons most commonly given by members (even if not published in church lesson manuals) to justify polygamy are:...Polygamy was not practiced until after the Saints started immigrating to Utah, and done so that women, whose husbands had died from the exertions of the trek, could be taken care of.
Member beliefs....Polygamy was not illegal in the 1800s and was not in violation of U.S. law or against the 12th article of faith, which supports obeying the laws of the land.
....
Polygamy was always illegal whenever and wherever the Mormons practiced it. It was even illegal in Canada and Mexico as they only recognize marriages that are legal in the person's home country.
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
The reasons most commonly given by members (even if not published in church lesson manuals) to justify polygamy are:...Polygamy was an acceptable way to rapidly increase the Church membership.
For example Brigham Young reportedly had 55 children by some 29 child-bearing capable wives but had those women had their own husbands they may have had 150 or more children in total. This reasoning only makes sense if there was a shortage of men but as shown above this was not the case.
The first edition of the Doctrine and Covenants (1835) included a section denying any practice of polygamy: "Inasmuch as this Church of Christ has been reproached with the crime of fornication and polygamy, we declare that we believe that one man should have one wife, and one woman but one husband, except in the case of death, when either is at liberty to marry again." (History of the Church, Vol. 2, p. 247)
The Article on Marriage was printed in the 1835 D&C as section 101 and in the 1844 D&C as section 109. The portion of the Article on Marriage relevant to polygamy states:
Inasmuch as this church of Christ has been reproached with the crime of fornication, and polygamy: we declare that we believe, that one man should have one wife; and one woman, but one husband, except in case of death, when either is at liberty to marry again. [1]
This was true—the Church membership generally was not being taught plural marriage, and were not living it at that time.
In fact, the statement remained in the D&C until the 1876 edition, even though plural marriage had been taught to specific individuals since at least 1831, practiced in secret since 1836, and practiced openly since 1852. The matter of not removing it in 1852 was simply due to the fact that a new edition of the D&C was not published until 1876.
While some have suggested that the article was published against Joseph's wishes or without his knowledge, the available evidence suggests that he supported its publication. It was likely included to counter the perception that the Mormon's practice of communal property (the "law of consecration") included a community of wives.
This statement was not a revelation given to Joseph Smith—it was written by Oliver Cowdery and introduced to a conference of the priesthood at Kirtland on 17 August 1835. Cowdery also wrote a statement of belief on government that has been retained in our current edition of the D&C as section 134. Both were sustained at the conference and included in the 1835 D&C, which was already at the press and ready to be published. Joseph Smith was preaching in Michigan at the time Oliver and W.W. Phelps introduced these two articles to the conference; it is not known if he approved of their addition to the D&C at the time, although he did retain them in the 1844 Nauvoo edition, which argues that he was not opposed to them. (Phelps read the article on marriage, while Cowdery read the one on government.) [2]
Some have suggested that the manner in which the conference was called suggests that Joseph was not the instigator of it, since it seems to have been done quite quickly, with relatively few high church leaders in attendance:
The General Assembly, which may have been announced on only twenty-four hours' notice, was held Monday, August 17[, 1835]. Its spur-of-the-moment nature is demonstrated by observing that a puzzling majority of Church leaders were absent. Missing from the meeting were all of the Twelve Apostles, eight of the twelve Kirtland High Council members nine of the twelve Missouri High Council members, three of the seven Presidents of the Quorum of Seventy, Presiding Bishop Partridge, and...two of the three members of the First Presidency. [3]
However, there is also some evidence that an article on marriage was already anticipated, and cited four times in the new D&C's index, which was prepared under Joseph's direction and probably available prior to his departure. Thus, "if a disagreement existed, it was resolved before the Prophet left for Pontiac." [4]
On July 7, 1878, Joseph F. Smith discussed Oliver's awareness of polygamy at the time of this publication:
To put this matter more correctly before you, I here declare that the principle of plural marriage was not first revealed on the 12th day of July, 1843. It was written for the first time on that date, but it had been revealed to the Prophet many years before that, perhaps as early as 1832. About this time, or subsequently, Joseph, the Prophet, intrusted this fact to Oliver Cowdery; he abused the confidence imposed in him, and brought reproach upon himself, and thereby upon the church by "running before he was sent," and "taking liberties without license," so to speak, hence the publication, by O. Cowdery, about this time, of an article on marriage, which was carefully worded, and afterwards found its way into the Doctrine and Covenants without authority. This article explains itself to those who understand the facts, and is an indisputable evidence of the early existence of the knowledge of the principle of patriarchal marriage by the Prophet Joseph, and also by Oliver Cowdery. [5]
However, there continues to be debate about whether Oliver Cowdery knew about--or prematurely practiced--plural marriage in the 1830s. [6] Oliver would learn about the Fanny Alger marriage, but his reaction at the time seems to have been wholly negative.
The original D&C 101 article outlined the general practice of performing a Latter-day Saint wedding, explained LDS beliefs about the marriage relationship, and denied that the Saints were practicing polygamy.
Some have argued that rumors of "polygamy" may already have been circulating as a result of the Prophet teaching the concept to some of his close associates. However, Brian Hales has argued that there are few if any extant attacks on Joseph or the Saints about polygamy prior to the 1840s:
...if the article was designed to neutralize reports about Joseph Smith and his alleged "crimes," polygamy would not have been included because that allegation was not made then nor at any other time during the Kirtland period according to any documentation currently available. In other words, assuming that the denial of polygamy in the "Marriage" article [of D&C 101] was specifically tied to rumors of Joseph Smith's behavior is problematic, unless other corroborating evidence can be located. [7]
On the other hand, charges of polygamy or "free love" or having wives in common were often made against new or little-known religious or social groups. As Hales reports:
Some [nineteenth-century utopian societies] experimented with novel marital and sexual practices, which focused suspicion on all the groups....Accordingly, early Latter-day Saint efforts to live the law of consecration, even though it sustained traditional monogamy, were instantly misunderstood....
John L. Brooke...wrote: "Among the non-Mormons in Ohio there were suspicions that the community of property dictated in the 'Law of Consecration' included wives."...
It seems plausible, even likely, that beginning in 1831, some uninformed individuals assumed that the law of consecration included a community of wives as one of its tenets, even publishing such claims, although there is no indication that this is how the Mormons themselves interpreted the law of consecration. Understandably, Church leaders would actively seek to deny such untrue allegations in a document on marriage to be included in the 1835 Doctrine and Covenants. [8]
Gilbert Scharffs notes:
The original Section 101 (never claimed as a revelation but approved as a statement of belief) did state that monogamy was the practice of the Church at that time. The section was not written by Joseph Smith and was voted upon by members in his absence. Perhaps the section was intended to prevent members from getting involved with plural marriage until such a time as the practice would be authorized by the Lord Church-wide. When that became the fact, the current Section 132 replaced the old Section 101. [9]
Wiki links |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Notes
The Article on Marriage was printed in the 1835 D&C as section 101 and in the 1844 D&C as section 109. The portion of the Article on Marriage relevant to polygamy states:
Inasmuch as this church of Christ has been reproached with the crime of fornication, and polygamy: we declare that we believe, that one man should have one wife; and one woman, but one husband, except in case of death, when either is at liberty to marry again. [1]
This was true—the Church membership generally was not being taught plural marriage, and were not living it at that time.
In fact, the statement remained in the D&C until the 1876 edition, even though plural marriage had been taught to specific individuals since at least 1831, practiced in secret since 1836, and practiced openly since 1852. The matter of not removing it in 1852 was simply due to the fact that a new edition of the D&C was not published until 1876.
While some have suggested that the article was published against Joseph's wishes or without his knowledge, the available evidence suggests that he supported its publication. It was likely included to counter the perception that the Mormon's practice of communal property (the "law of consecration") included a community of wives.
This statement was not a revelation given to Joseph Smith—it was written by Oliver Cowdery and introduced to a conference of the priesthood at Kirtland on 17 August 1835. Cowdery also wrote a statement of belief on government that has been retained in our current edition of the D&C as section 134. Both were sustained at the conference and included in the 1835 D&C, which was already at the press and ready to be published. Joseph Smith was preaching in Michigan at the time Oliver and W.W. Phelps introduced these two articles to the conference; it is not known if he approved of their addition to the D&C at the time, although he did retain them in the 1844 Nauvoo edition, which argues that he was not opposed to them. (Phelps read the article on marriage, while Cowdery read the one on government.) [2]
Some have suggested that the manner in which the conference was called suggests that Joseph was not the instigator of it, since it seems to have been done quite quickly, with relatively few high church leaders in attendance:
The General Assembly, which may have been announced on only twenty-four hours' notice, was held Monday, August 17[, 1835]. Its spur-of-the-moment nature is demonstrated by observing that a puzzling majority of Church leaders were absent. Missing from the meeting were all of the Twelve Apostles, eight of the twelve Kirtland High Council members nine of the twelve Missouri High Council members, three of the seven Presidents of the Quorum of Seventy, Presiding Bishop Partridge, and...two of the three members of the First Presidency. [3]
However, there is also some evidence that an article on marriage was already anticipated, and cited four times in the new D&C's index, which was prepared under Joseph's direction and probably available prior to his departure. Thus, "if a disagreement existed, it was resolved before the Prophet left for Pontiac." [4]
On July 7, 1878, Joseph F. Smith discussed Oliver's awareness of polygamy at the time of this publication:
To put this matter more correctly before you, I here declare that the principle of plural marriage was not first revealed on the 12th day of July, 1843. It was written for the first time on that date, but it had been revealed to the Prophet many years before that, perhaps as early as 1832. About this time, or subsequently, Joseph, the Prophet, intrusted this fact to Oliver Cowdery; he abused the confidence imposed in him, and brought reproach upon himself, and thereby upon the church by "running before he was sent," and "taking liberties without license," so to speak, hence the publication, by O. Cowdery, about this time, of an article on marriage, which was carefully worded, and afterwards found its way into the Doctrine and Covenants without authority. This article explains itself to those who understand the facts, and is an indisputable evidence of the early existence of the knowledge of the principle of patriarchal marriage by the Prophet Joseph, and also by Oliver Cowdery. [5]
However, there continues to be debate about whether Oliver Cowdery knew about--or prematurely practiced--plural marriage in the 1830s. [6] Oliver would learn about the Fanny Alger marriage, but his reaction at the time seems to have been wholly negative.
The original D&C 101 article outlined the general practice of performing a Latter-day Saint wedding, explained LDS beliefs about the marriage relationship, and denied that the Saints were practicing polygamy.
Some have argued that rumors of "polygamy" may already have been circulating as a result of the Prophet teaching the concept to some of his close associates. However, Brian Hales has argued that there are few if any extant attacks on Joseph or the Saints about polygamy prior to the 1840s:
...if the article was designed to neutralize reports about Joseph Smith and his alleged "crimes," polygamy would not have been included because that allegation was not made then nor at any other time during the Kirtland period according to any documentation currently available. In other words, assuming that the denial of polygamy in the "Marriage" article [of D&C 101] was specifically tied to rumors of Joseph Smith's behavior is problematic, unless other corroborating evidence can be located. [7]
On the other hand, charges of polygamy or "free love" or having wives in common were often made against new or little-known religious or social groups. As Hales reports:
Some [nineteenth-century utopian societies] experimented with novel marital and sexual practices, which focused suspicion on all the groups....Accordingly, early Latter-day Saint efforts to live the law of consecration, even though it sustained traditional monogamy, were instantly misunderstood....
John L. Brooke...wrote: "Among the non-Mormons in Ohio there were suspicions that the community of property dictated in the 'Law of Consecration' included wives."...
It seems plausible, even likely, that beginning in 1831, some uninformed individuals assumed that the law of consecration included a community of wives as one of its tenets, even publishing such claims, although there is no indication that this is how the Mormons themselves interpreted the law of consecration. Understandably, Church leaders would actively seek to deny such untrue allegations in a document on marriage to be included in the 1835 Doctrine and Covenants. [8]
Gilbert Scharffs notes:
The original Section 101 (never claimed as a revelation but approved as a statement of belief) did state that monogamy was the practice of the Church at that time. The section was not written by Joseph Smith and was voted upon by members in his absence. Perhaps the section was intended to prevent members from getting involved with plural marriage until such a time as the practice would be authorized by the Lord Church-wide. When that became the fact, the current Section 132 replaced the old Section 101. [9]
Wiki links |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Notes
The Article on Marriage was printed in the 1835 D&C as section 101 and in the 1844 D&C as section 109. The portion of the Article on Marriage relevant to polygamy states:
Inasmuch as this church of Christ has been reproached with the crime of fornication, and polygamy: we declare that we believe, that one man should have one wife; and one woman, but one husband, except in case of death, when either is at liberty to marry again. [1]
This was true—the Church membership generally was not being taught plural marriage, and were not living it at that time.
In fact, the statement remained in the D&C until the 1876 edition, even though plural marriage had been taught to specific individuals since at least 1831, practiced in secret since 1836, and practiced openly since 1852. The matter of not removing it in 1852 was simply due to the fact that a new edition of the D&C was not published until 1876.
While some have suggested that the article was published against Joseph's wishes or without his knowledge, the available evidence suggests that he supported its publication. It was likely included to counter the perception that the Mormon's practice of communal property (the "law of consecration") included a community of wives.
This statement was not a revelation given to Joseph Smith—it was written by Oliver Cowdery and introduced to a conference of the priesthood at Kirtland on 17 August 1835. Cowdery also wrote a statement of belief on government that has been retained in our current edition of the D&C as section 134. Both were sustained at the conference and included in the 1835 D&C, which was already at the press and ready to be published. Joseph Smith was preaching in Michigan at the time Oliver and W.W. Phelps introduced these two articles to the conference; it is not known if he approved of their addition to the D&C at the time, although he did retain them in the 1844 Nauvoo edition, which argues that he was not opposed to them. (Phelps read the article on marriage, while Cowdery read the one on government.) [2]
Some have suggested that the manner in which the conference was called suggests that Joseph was not the instigator of it, since it seems to have been done quite quickly, with relatively few high church leaders in attendance:
The General Assembly, which may have been announced on only twenty-four hours' notice, was held Monday, August 17[, 1835]. Its spur-of-the-moment nature is demonstrated by observing that a puzzling majority of Church leaders were absent. Missing from the meeting were all of the Twelve Apostles, eight of the twelve Kirtland High Council members nine of the twelve Missouri High Council members, three of the seven Presidents of the Quorum of Seventy, Presiding Bishop Partridge, and...two of the three members of the First Presidency. [3]
However, there is also some evidence that an article on marriage was already anticipated, and cited four times in the new D&C's index, which was prepared under Joseph's direction and probably available prior to his departure. Thus, "if a disagreement existed, it was resolved before the Prophet left for Pontiac." [4]
On July 7, 1878, Joseph F. Smith discussed Oliver's awareness of polygamy at the time of this publication:
To put this matter more correctly before you, I here declare that the principle of plural marriage was not first revealed on the 12th day of July, 1843. It was written for the first time on that date, but it had been revealed to the Prophet many years before that, perhaps as early as 1832. About this time, or subsequently, Joseph, the Prophet, intrusted this fact to Oliver Cowdery; he abused the confidence imposed in him, and brought reproach upon himself, and thereby upon the church by "running before he was sent," and "taking liberties without license," so to speak, hence the publication, by O. Cowdery, about this time, of an article on marriage, which was carefully worded, and afterwards found its way into the Doctrine and Covenants without authority. This article explains itself to those who understand the facts, and is an indisputable evidence of the early existence of the knowledge of the principle of patriarchal marriage by the Prophet Joseph, and also by Oliver Cowdery. [5]
However, there continues to be debate about whether Oliver Cowdery knew about--or prematurely practiced--plural marriage in the 1830s. [6] Oliver would learn about the Fanny Alger marriage, but his reaction at the time seems to have been wholly negative.
The original D&C 101 article outlined the general practice of performing a Latter-day Saint wedding, explained LDS beliefs about the marriage relationship, and denied that the Saints were practicing polygamy.
Some have argued that rumors of "polygamy" may already have been circulating as a result of the Prophet teaching the concept to some of his close associates. However, Brian Hales has argued that there are few if any extant attacks on Joseph or the Saints about polygamy prior to the 1840s:
...if the article was designed to neutralize reports about Joseph Smith and his alleged "crimes," polygamy would not have been included because that allegation was not made then nor at any other time during the Kirtland period according to any documentation currently available. In other words, assuming that the denial of polygamy in the "Marriage" article [of D&C 101] was specifically tied to rumors of Joseph Smith's behavior is problematic, unless other corroborating evidence can be located. [7]
On the other hand, charges of polygamy or "free love" or having wives in common were often made against new or little-known religious or social groups. As Hales reports:
Some [nineteenth-century utopian societies] experimented with novel marital and sexual practices, which focused suspicion on all the groups....Accordingly, early Latter-day Saint efforts to live the law of consecration, even though it sustained traditional monogamy, were instantly misunderstood....
John L. Brooke...wrote: "Among the non-Mormons in Ohio there were suspicions that the community of property dictated in the 'Law of Consecration' included wives."...
It seems plausible, even likely, that beginning in 1831, some uninformed individuals assumed that the law of consecration included a community of wives as one of its tenets, even publishing such claims, although there is no indication that this is how the Mormons themselves interpreted the law of consecration. Understandably, Church leaders would actively seek to deny such untrue allegations in a document on marriage to be included in the 1835 Doctrine and Covenants. [8]
Gilbert Scharffs notes:
The original Section 101 (never claimed as a revelation but approved as a statement of belief) did state that monogamy was the practice of the Church at that time. The section was not written by Joseph Smith and was voted upon by members in his absence. Perhaps the section was intended to prevent members from getting involved with plural marriage until such a time as the practice would be authorized by the Lord Church-wide. When that became the fact, the current Section 132 replaced the old Section 101. [9]
Wiki links |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Notes
The Sunday School lesson manuals, priesthood manuals, seminary books, etc almost never mention Joseph's polygamy. There are some references to the other prophet's plural marriages but not for Joseph. By rarely mentioning Joseph's polygamous marriages in lessons taught in church, talks given at conferences, etc. many church members, especially converts, naturally believe that Brigham Young started polygamy.
D&C 132 (Latter-day Saint scripture):
51 Verily, I say unto you: A commandment I give unto mine handmaid, Emma Smith, your wife, whom I have given unto you, that she stay herself and partake not of that which I commanded you to offer unto her; for I did it, saith the Lord, to prove you all, as I did Abraham, and that I might require an offering at your hand, by covenant and sacrifice.
52 And let mine handmaid, Emma Smith, receive all those that have been given unto my servant Joseph, and who are virtuous and pure before me; and those who are not pure, and have said they were pure, shall be destroyed, saith the Lord God. (D&C 132꞉51-52)
Since it speaks of those "that have been given unto my servant Joseph," this clearly indicates that Joseph was practicing plural marriage.
In this dispensation, the Lord commanded some of the early Saints to practice plural marriage. The Prophet Joseph Smith and those closest to him, including Brigham Young and Heber C. Kimball, were challenged by this command, but they obeyed it. Church leaders regulated the practice. Those entering into it had to be authorized to do so, and the marriages had to be performed through the sealing power of the priesthood. [1]
Institute Manual: Church History in the Fulness of Times:
Later that summer Joseph recorded a revelation on marriage that incorporated principles that had been revealed to him as early as 1831 in Kirtland. In it the Lord declared, “If a man marry a wife by my word, which is my law, and by the new and everlasting covenant, and it is sealed unto them by the Holy Spirit of promise, by him who is anointed, unto whom I have appointed this power and the keys of this priesthood . . . [it] shall be of full force when they are out of the world; and they shall pass by the angels, and the gods, which are set there, to their exaltation and glory in all things, as hath been sealed upon their heads, which glory shall be a fulness and a continuation of the seeds forever and ever” ( D&C 132:19 ).
The law of celestial marriage, as outlined in this revelation, also included the principle of the plurality of wives. In 1831 as Joseph Smith labored on the inspired translation of the holy scriptures, he asked the Lord how he justified the practice of plural marriage among the Old Testament patriarchs. This question resulted in the revelation on celestial marriage, which included an answer to his question about the plural marriages of the patriarchs.
First the Lord explained that for any covenant, including marriage, to be valid in eternity it must meet three requirements (see D&C 132:7 ): (1) It must be “made and entered into and sealed by the Holy Spirit of promise.” (2) It must be performed by the proper priesthood authority. (3) It must be by “revelation and commandment” through the Lord’s anointed prophet (see also vv. 18–19 ). Using Abraham as an example, the Lord said he “received all things, whatsoever he received, by revelation and commandment, by my word” ( v. 29 ). Consequently, the Lord asked, “Was Abraham, therefore, under condemnation? Verily I say unto you, Nay; for I, the Lord, commanded it” ( v. 35 ).
Moreover, Joseph Smith and the Church were to accept the principle of plural marriage as part of the restoration of all things (see v. 45 ). Accustomed to conventional marriage patterns, the Prophet was at first understandably reluctant to engage in this new practice. Due to a lack of historical documentation, we do not know what his early attempts were to comply with the commandment in Ohio. His first recorded plural marriage in Nauvoo was to Louisa Beaman; it was performed by Bishop Joseph B. Noble on 5 April 1841. 12 During the next three years Joseph took additional plural wives in accordance with the Lord’s commands.
As members of the Council of the Twelve Apostles returned from their missions to the British Isles in 1841, Joseph Smith taught them one by one the doctrine of plurality of wives, and each experienced some difficulty in understanding and accepting this doctrine. 13 Brigham Young, for example, recounted his struggle: “I was not desirous of shrinking from any duty, nor of failing in the least to do as I was commanded, but it was the first time in my life that I had desired the grave, and I could hardly get over it for a long time. And when I saw a funeral, I felt to envy the corpse its situation, and to regret that I was not in the coffin.”
After their initial hesitancy and frustration, Brigham Young and others of the Twelve received individual confirmations from the Holy Spirit and accepted the new doctrine of plural marriage. They knew that Joseph Smith was a prophet of God in all things. At first the practice was kept secret and was very limited. Rumors began to circulate about authorities of the Church having additional wives, which greatly distorted the truth and contributed to increased persecution from apostates and outsiders. Part of the difficulty, of course, was the natural aversion Americans held against “polygamy.” This new system appeared to threaten the strongly entrenched tradition of monogamy and the solidarity of the family structure. Later, in Utah, the Saints openly practiced “the principle,” but never without persecution. [2]
The number of dissenters in Nauvoo grew with the addition of Church members who opposed plural marriage and other new doctrines taught by Joseph Smith. William Law, second counselor in the First Presidency, his brother Wilson Law, major general in the Nauvoo Legion, and high council members Austin Cowles and Leonard Soby all believed that Joseph Smith was a fallen prophet. [3]
The Twelve were among the first to receive instruction from Joseph Smith on plural marriage and the temple ordinances. [4]
A large part of the persecution experienced by the Latter-day Saints centered around the practice of plural marriage, which was instituted under the direction of the Prophet Joseph Smith. The law of plural marriage was revealed to the Prophet as early as 1831, but he mentioned it only to a few trusted friends. Under strict commandment from God to obey the law, the Prophet began in 1841 to instruct leading priesthood brethren of the Church concerning plural marriage and their responsibility to live the law. The Prophet Joseph Smith dictated the revelation to William Clayton in 1843, when it was first written. Nine years passed, however, before the revelation was read in general conference and published. [5]
Priesthood/Relief Society Manual Teachings of Presidents of the Church: Joseph Smith:
This book deals with teachings of the Prophet Joseph Smith that have application to our day....This book also does not discuss plural marriage. The doctrines and principles relating to plural marriage were revealed to Joseph Smith as early as 1831. The Prophet taught the doctrine of plural marriage, and a number of such marriages were performed during his lifetime. [6]
Gracia N. Jones, Ensign (1992):
Her [Emma Smith's] great trial came when the prophet revealed to Emma that they would be required to live the ancient law of Abraham—plural marriage. Emma suffered deeply hurt feelings because of it. While she agreed with this doctrine at times, at other times she opposed it. Years later, Emma is purported to have denied that any such doctrine was ever introduced by her husband. [7]
William Hartley, Ensign (1989):
In Nauvoo, the Knight group faced and passed another great test of faith. The Prophet introduced several doctrines relating to the temple, including the temple ceremonies and plural marriage, which some could not accept. But the Knights received the teachings. [8]
Davis Bitton, Ensign (1977):
Then, along with economic privation and an absent father, was for some the institution of plural marriage. Starting during Joseph Smith’s own lifetime but limited to a few dozen families until its official announcement in 1852, plural marriage brought a powerful new challenge to the equanimity of Latter-day Saint family life. Never could it be said that a majority of Latter-day Saint families were polygamous families. If each mother and her children are considered as a single family unit, the percentage reaches something like 10 or 15 percent. These families, by and large, tended to include the most prominent families within Latter-day Saint society.
While there were many examples of success, of harmony, of love, of delightful “aunty” relationships with the plural wives of one’s father, it should also be said that for some the plurality of wives created tensions and unhappiness. “My wives have not spoken to each other for many months,” wrote one husband in 1856. We do not have a thorough study of divorces in Mormon families, polygamous and monogamous, but we do know that permanent separation ended some nineteenth-century marriages. Obviously plural marriage for most meant even more fatherly absence than had existed before. In the words of Professor Eugene Campbell of Brigham Young University, “Many of the normal problems of marriage, such as finance, personality adjustment, sexual relationships, jealousies, child-rearing and discipline were all magnified in plural marriages.”
These factors—those presenting special challenges to Mormon families—are not the whole picture. But they are part of the picture. In the actual recorded experiences of family life we discover, not surprisingly, that behind our surface impression of harmonious, loving families—the families of the family portraits existed most of the challenges which threaten family life today. The point is that in the past century neither the family life of Americans and Europeans generally, nor that of the Latter-day Saints, was as free of problems as we have tended to believe. We now find ourselves in a period of looking on our past. There is a tendency among many of us to overstate the positive, understate the negative. We need not hesitate to see the whole picture as we seek to discover our forefathers. The more we see their fiber and strengths, the more we will appreciate their efforts in building the Church and in raising their children. [9]
Joseph Smith Papers Project (online):
At times revelation became a burden as well as a blessing, at no time more than when plural marriage was revealed. Plural marriage was the final component of the logic of restoration. Smith had prayed for an understanding of Old Testament polygamy and was commanded to do the “works of Abraham.”45 Although he hated adultery and was deeply loyal to his wife Emma, he believed he was to take additional wives as had the ancient patriarchs. He went about it carefully, one woman at a time, usually approaching her relatives first and going through a prescribed wedding ceremony. During his lifetime, he was married to approximately thirty women.46 Although conjugal relations were apparently involved, he spent little time with these women, the need for secrecy and the demands on his time keeping them apart. At first aghast at what her husband was doing, Emma eventually agreed to a few of the plural marriages but then pulled back. She oscillated between hesitant submission and outright opposition to the practice, but according to Maria Jane Johnston Woodward, who worked for a time as a servant in the Smith household, Emma told her, “The principle of plural marriage is right. . . . [I]t is from our Father in Heaven.” After her husband’s death, Emma refused to go west, where plural marriage would be practiced. She never admitted to her children that their father had been involved. [10]
John A. Widtsoe, "Did Joseph Smith Introduce Plural Marriage?", Evidences and Reconciliations:
Moral purity is required of all Latter-day Saints. Men must be as clean as women, and both must be free from any violation of the moral law. That is the basis of all marriages performed under the authority of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
The Church solemnizes two kinds of marriages. First, those that unite husband or wife for the duration of mortal life. These marriages end with death. Second, those that continue the family relationship after death, in the hereafter. This is often known as eternal or celestial marriage.
Faithful members of the Church seek to enjoy both of these kinds of marriages. They wish to be wedded for time and eternity, that is, to continue their associations forever. To be able to do this is one of the happiest privileges of Church membership. Such marriages, usually called sealings, must be performed in the temples, whenever they exist.
Several approaches to eternal marriage may be made: Two living person may be sealed to each other for time and eternity. A living man may be sealed for eternity to a dead woman; or a living woman to a dead man. Two dead persons may be sealed to each other. It is also possible though the Church does not now permit it, to seal two living people for eternity only, with no association on earth.
Further, under a divine command to the Prophet Joseph Smith, it was possible for one man to be sealed to more than one woman for time and for eternity. Thus came plural marriage among the Latter-day Saints. By another divine command, to Wilford Woodruff, a successor to Joseph Smith, this order of marriage was withdrawn in 1890. Since that time the Church has not sanctioned plural marriages. Anyone who enters into them now is married unlawfully, and is excommunicated from the Church.
That Joseph Smith actually was the person who introduced plural marriage into the Church and that he practiced it himself are amply proved by existing facts.
1. The revelation known as section one hundred thirty-two in the Doctrine and Covenants, which contains the doctrine of celestial marriage and also the practice of plural marriage, was dictated to his scribe, William Clayton, by Joseph Smith on July 12, 1843, a year before the martyrdom of the Prophet. It had been received by the Prophet some years before, and taught to many, but was not reduced to writing until 1843. William Clayton lived as an honorable citizen, of the highest character until December 4, 1879, thirty-six years after the revelation was written. He never wavered in his simple declaration that the revelation as now found in the Doctrine and Covenants was dictated to him, sentence by sentence. He adds that "after the whole was written, Joseph asked me to read it through, slowly and carefully, which I did, and he pronounced it correct." (Andrew Jenson, Historical Record, Volume VI, pp. 225, 226)
On the day the revelation was written, or the day after, Joseph C. Kingsbury was asked to make a copy of it. This copy was carefully compared with the original by Bishop Newell K. Whitney, and preserved by him. Elder Kingsbury, of unblemished character and reputation lived fifty-five years after this event (dying October 5, 1898), and always bore solemn testimony to the written origin of the revelation in 1843, through the lips of the Prophet. In further corroboration of the claim that the revelation came from the lips of the Prophet, are the statements of numerous men and women, then living, who either saw the revelation or heard it read. In fact, the document was read to the high council in Nauvoo.
2. A number of men, who in their lives showed themselves honest, have testified that they actually performed the ceremonies that united Joseph Smith to plural wives. Among these were Joseph B. Noble, Hyrum Smith, James Adams, Newell K. Whitney, Willard Richards, and others. Several of these men lived long after the Prophet's death and always declared that they officiated in marrying the Prophet to a plural wife, giving place, date, and the witnesses present.
3. Many of the women who were thus sealed to Joseph Smith lived long after his death. They declared that they lived with the Prophet as husband and wives. These women were of unblemished character, gentle and lovely in their lives who spoke with loving respect of their martyr husband. They substantiated in detail the statements of those who performed the ceremonies.
4. Many of the elders in Nauvoo entered into plural marriage, under the authority of Joseph Smith who was yet living, as certified to by the men and their wives. Among these were William Clayton, Orson Hyde, Hyrum Smith John Smith, Erastus Snow, Lyman Wight, James J. Strang, Gladden Bishop, William Smith, Heber C. Kimball, and Brigham Young. These men and their wives who survived the Prophet, made affidavits of their marriages in Joseph's day in answer to the charge by enemies of the Church that plural marriage was not instituted nor practiced, neither authorized by the Prophet. These men and women were good citizens, so well-known over such long periods of time that their concordant declarations cannot be gainsaid.
5. The Nauvoo Temple records, which are in the possession of the Church likewise furnish evidence that Joseph Smith practiced plural marriage. Before the completion of the temple, marriage sealings were usually performed in rooms in the home of the Prophet. When the temple was dedicated in 1846 for such ceremonies, the plural marriages of Joseph were given temple sanction, and where the marriages were for time only, they were often made to continue through eternity.
This was done within a year and a half of the assassination of the Prophet. Many received plural wives in the Nauvoo Temple. It is utterly improbable, if not impossible, that such a new doctrine could have been conceived and carried out by the men who succeeded the Prophet. There would have been a serious resentment among those who entered the temple, if the teachings of the Prophet had been violated. Such criticism would have overflowed to the outside.
6. After the death of the Prophet, women applied for the privilege of being sealed to him for eternity. They felt no doubt that in the eternal ages they would then share the companionship of the Prophet. They wanted to enjoy eternity with the man whom they revered as one chosen of God to open the last dispensation of the gospel on earth. To these requests, assent was often given. Such action by women who lived in the days of the Prophet implies a belief in plural marriage. These women, who were not in any sense earthly wives of the Prophet, have been counted by uninformed or antagonistic writers as wives of the Prophet.
Women no longer living, whether in Joseph's day or later have also been sealed to the Prophet for eternity. The request for such unions has usually come from relatives or friends who would have their loved one share eternity with the Prophet, rather than with anyone else. Unscrupulous and unreliable writers have even added such marriages to the list of Joseph's wives.
7. Another kind of celestial marriage seems to have been practiced in the early days of plural marriage. It has not been practiced since Nauvoo days, for it is under Church prohibition. Zealous women, married or unmarried, loving the cause of the restored gospel, considered their condition in the hereafter. Some of them asked that they might be sealed to the Prophet for eternity. They were not to be his wives on earth, in mortality, but only after death in the eternities. This came often to be spoken of as celestial marriage. Such marriages led to misunderstandings by those not of the Church, and unfamiliar with its doctrines. To them marriage meant only association on earth. Therefore any ceremony uniting a married woman, for example, to Joseph Smith for eternity seemed adulterous to such people. Yet in any day, in our day, there may be women who prefer to spend eternity with another than their husband on earth.
Such cases, if any, and they must have been few in number, gave enemies of the Church occasion to fan the flaming hatred against the Latter-day Saints. The full truth was not told. Enemies made the most of the truth. They found it difficult to believe that the Church rests on truth and virtue.
The literature and existing documents dealing with plural marriage in Nauvoo in the day of Joseph Smith are very numerous. Hundreds of affidavits on the subject are in the Church Historian's office in Salt Lake City. Most of the books and newspaper and magazine articles on the subject are found there also. (For a fairly condensed but complete discussion consult Andrew Jenson, Historical Record, Vol. VI, pp. 219-236; Joseph Fielding Smith, Blood Atonement and the Origin of Plural Marriage, pp. 67-94; Woman's Exponent, Vol. III and IV; The Deseret News, especially in 1886)
The careful study of all available information leads to but one conclusion. Joseph Smith received the revelation in question, and practiced plural marriage. The issue is not one of doctrine hut of history. No honest student can declare the host of witnesses, hundreds of them, from Nauvoo days, Mormon and non-Mormon of various residence, pursuits and temperaments to have united in lying about the matter. The evidence is confirmed by those who place the introduction of plural marriage on others, for they seek feeble, unworthy shelter in the statement that Joseph Smith did practice plural marriage, but later repented of it. (The Saints Herald, Vol. 1, pp. 9, 26, 27) That is throwing dust in the eyes of seekers after truth. The case is clear. Authentic history says that plural marriage originated with Joseph Smith the Prophet. And so it did. The apparent denials by Church leaders in Nauvoo days that the Church practiced plural marriage were correct. At that time the Church members as a whole had not heard the revelation, nor had they been given an opportunity to accept it. But many of the leaders knew of it and were polygamists.
The chaotic conditions of the years immediately following the Prophet's death, delayed the formal presentation of the revelation. Soon after the Church was established in the Great Salt Lake region, at the conference in 1852, the doctrine of celestial and plural marriage was accepted by the Church as a whole. During the intervening years, however, it was taught and practiced. [11]
Critic's Note:If we take the Book of Mormon witnesses' statements so seriously, shouldn't we also accept other things that they reportedly witnessed just as powerfully? For example, Oliver Cowdery called it "a dirty, nasty, filthy affair..."
Joseph's first polygamous marriage was before the sealing authority was given....The "sealing" power was not restored under LDS belief until April 1836 when Elijah appeared to Joseph and conferred the sealing keys upon him.
One of the wives about whom we know relatively little is Fanny Alger, Joseph's first plural wife, whom he came to know in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant of sorts to Emma (such work was common for young women at the time). There are no first-hand accounts of their relationship (from Joseph or Fanny), nor are there second-hand accounts (from Emma or Fanny's family). All that we do have is third hand (and mostly hostile) accounts, most of them recorded many years after the events.
Unfortunately, this lack of reliable and extensive historical detail leaves much room for critics to claim that Joseph Smith had an affair with Fanny and then later invented plural marriage as way to justify his actions which, again, rests on dubious historical grounds. The problem is we don't know the details of the relationship or exactly of what it consisted, and so are left to assume that Joseph acted honorably (as believers) or dishonorably (as critics).
There is some historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored, so it is perfectly legitimate to argue that Joseph's relationship with Fanny Alger was such a case. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony; and apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Joseph Smith came to know Fanny Alger in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant to Emma. Neither Joseph nor Fanny ever left any first-hand accounts of their relationship. There are no second-hand accounts from Emma or Fanny's family. All that we do have is third hand accounts from people who did not directly observe the events associated with this first plural marriage, and most of them recorded many years after the events.
Benjamin F. Johnson stated that in 1835 he had "learned from my sister’s husband, Lyman R. Sherman, who was close to the Prophet, and received it from him, 'that the ancient order of Plural Marriage was again to be practiced by the Church.' This, at the time did not impress my mind deeply, although there lived then with his family (the Prophet’s) a neighbor’s daughter, Fannie Alger, a very nice and comely young woman about my own age, toward whom not only myself, but every one, seemed partial, for the amiability for her character; and it was whispered even then that Joseph loved her."[12]
Mosiah Hancock discusses the manner in which the proposal was extended to Fanny, and states that a marriage ceremony was performed. Joseph asked Levi Hancock, the brother-in-law of Samuel Alger, Fanny’s father, to request Fanny as his plural wife:
Samuel, the Prophet Joseph loves your daughter Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Uncle Sam says, "Go and talk to the old woman [Fanny’s mother] about it. Twill be as she says." Father goes to his sister and said, "Clarissy, Brother Joseph the Prophet of the most high God loves Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Said she, "Go and talk to Fanny. It will be all right with me." Father goes to Fanny and said, "Fanny, Brother Joseph the Prophet loves you and wishes you for a wife. Will you be his wife?" "I will Levi," said she. Father takes Fanny to Joseph and said, "Brother Joseph I have been successful in my mission." Father gave her to Joseph, repeating the ceremony as Joseph repeated to him.[13]
There is historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony in Kirtland, Ohio in 1833.
Apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Some have wondered how the first plural marriages (such as the Alger marriage) could have occurred before the 1836 restoration of the sealing keys in the Kirtland temple (see D&C 110). This confusion occurs because we tend to conflate several ideas. They were not all initially wrapped together in one doctrine:
Thus, the marriage to Fanny would have occurred under the understanding #1 above. The concept of sealing beyond the grave came later. Therefore, the marriage of Joseph and Fanny would have been a plural marriage, but it would not have been a marriage for eternity.
Perhaps it is worth mentioning that priesthood power already gave the ability to ratify certain ordinances as binding on heaven and earth (D&C 1:8), that the sealing power was given mention in earlier revelations such as Helaman 10:7, and that the coming of Elijah and his turning of the hearts of children and fathers was prophesied in 3 Nephi 25:5-6. This supports the view that it is unlikely that Joseph was just making up the sealing power and priesthood power extemporaneously to justify getting married to Fanny and having sexual relations with her.
Some of Joseph's associates, most notably Oliver Cowdery, perceived Joseph's association with Fanny as an affair rather than a plural marriage. Oliver, in a letter to his brother Warren, asserted that "in every instance I did not fail to affirm that which I had said was strictly true. A dirty, nasty, filthy affair of his and Fanny Alger's was talked over in which I strictly declared that I had never deserted from the truth in the matter, and as I supposed was admitted by himself."[14]
Gary J. Bergera, an advocate of the "affair" theory, wrote:
I do not believe that Fanny Alger, whom [Todd] Compton counts as Smith’s first plural wife, satisfies the criteria to be considered a "wife." Briefly, the sources for such a "marriage" are all retrospective and presented from a point of view favoring plural marriage, rather than, say, an extramarital liaison…Smith’s doctrine of eternal marriage was not formulated until after 1839–40. [15]
There are several problems with this analysis. While it is true that sources on Fanny are all retrospective, the same is true of many early plural marriages. Fanny's marriage has more evidence than some. Bergera says that all the sources about Fanny's marriage come "from a point of view favoring plural marriage," but this claim is clearly false.
For example, Fanny's marriage was mentioned by Ann Eliza Webb Young, a later wife of Brigham Young's who divorced him, published an anti-Mormon book, and spent much of her time giving anti-Mormon, anti-polygamy lectures. Fanny stayed with Ann Eliza's family after leaving Joseph and Emma's house, and both Ann Eliza and her father Chauncey Webb [16] refer to Joseph's relationship to Fanny as a "sealing." [17] Eliza also noted that the Alger family "considered it the highest honor to have their daughter adopted into the prophet's family, and her mother has always claimed that she [Fanny] was sealed to Joseph at that time." [18] This would be a strange attitude to take if their relationship was a mere affair. And, the hostile Webbs had no reason to invent a "sealing" idea if they could have made Fanny into a mere case of adultery.
It seems clear, then, that Joseph, Fanny's family, Levi Hancock, and even hostile witnesses saw their relationship as a marriage, albeit an unorthodox one. The witness of Chauncey Webb and Ann Eliza Webb Young make it untenable to claim that only a later Mormon whitewash turned an affair into a marriage.
It appears that shortly after the April 3 vision, Joseph Smith recorded a first-hand account of the vision in his own personal journal or notes. That original record has not been found and is probably lost. Nonetheless, these important visitations were documented in other contemporaneous records. Within a few days, the Prophet’s secretary Warren Cowdery transcribed Joseph’s first-hand account into a third-hand account to be used in the Church history then being composed. |
|
Despite the importance of Elijah and the Kirtland Temple visitations, Joseph Smith did not publicly teach eternal marriage for perhaps six years after he received the authority to perform those ordinances. |
|
Sometime in late 1835 or early 1836, in a priesthood ceremony performed by Levi Hancock, Joseph secretly married Fanny Alger, a domestic living in the Smith home. When Oliver Cowdery and Emma Smith learned of the relationship, they did not consider it a legitimate marriage. Joseph was unable to convince them the polygamous marriage was approved of God. Fanny left the area and married a non-member a few months later and never returned to the Church. Her family and other who were close to her remained true to Joseph Smith, following him to Nauvoo and later migrating with the Saints to Utah. |
Critical sources |
|
In 1872, William McLellin (then an apostate excommunicated nearly 34 years prior) wrote a letter to Emma and Joseph's son, Joseph Smith III:
Now Joseph I will relate to you some history, and refer you to your own dear Mother for the truth. You will probably remember that I visited your Mother and family in 1847, and held a lengthy conversation with her, retired in the Mansion House in Nauvoo. I did not ask her to tell, but I told her some stories I had heard. And she told me whether I was properly informed. Dr. F. G. Williams practiced with me in Clay Co. Mo. during the latter part of 1838. And he told me that at your birth your father committed an act with a Miss Hill [sic]—a hired girl. Emma saw him, and spoke to him. He desisted, but Mrs. Smith refused to be satisfied. He called in Dr. Williams, O. Cowdery, and S. Rigdon to reconcile Emma. But she told them just as the circumstances took place. He found he was caught. He confessed humbly, and begged forgiveness. Emma and all forgave him. She told me this story was true!! Again I told her I heard that one night she missed Joseph and Fanny Alger. She went to the barn and saw him and Fanny in the barn together alone. She looked through a crack and saw the transaction!!! She told me this story too was verily true. [19]
Some critics interpret "transaction" to mean intercourse in this case and that Emma caught Joseph in the very act. But McLellin reported on the event again three years afterwards in 1875 to J. H. Beadle and makes it clear that he is talking about the wedding or sealing ceremony:
He [McLellin] was in the vicinity during all the Mormon troubles in Northern Missouri, and grieved heavily over the suffering of his former brethren. He also informed me of the spot where the first well authenticated case of polygamy took place in which Joseph Smith was "sealed" to the hired girl. The "sealing" took place in a barn on the hay mow, and was witnessed by Mrs. Smith through a crack in the door! The Doctor was so distressed about this case, (it created some scandal at the time among the Saints,) that long afterwards when he visited Mrs. Emma Smith at Nauvoo, he charged her as she hoped for salvation to tell him the truth about it. And she then and there declared on her honor that it was a fact—"saw it with her own eyes." [20]
Ann Eliza Webb, who was born in 1844, was not even alive at the time of these events, could only only comment based upon what her father told her about Joseph and Fanny. Ann apostatized from the Church and wrote an "expose" called Wife No. 19, or The story of a Life in Bondage. She described Fanny as follows:
Mrs. Smith had an adopted daughter, a very pretty, pleasing young girl, about seventeen years old. She was extremely fond of her; no mother could be more devoted, and their affection for each other was a constant object of remark, so absorbing and genuine did it seem. Consequently is was with a shocked surprise that people heard that sister Emma had turned Fanny out of the house in the night.[21]
The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[22] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
Fawn Brodie, in her critical work No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith, claimed that "there is some evidence that Fannie Alger bore Joseph a child in Kirtland."[23] However, DNA research in 2005 confirmed Fanny Alger’s son Orrison Smith is not the son of Joseph Smith, Jr.[24]
Notes
One of the wives about whom we know relatively little is Fanny Alger, Joseph's first plural wife, whom he came to know in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant of sorts to Emma (such work was common for young women at the time). There are no first-hand accounts of their relationship (from Joseph or Fanny), nor are there second-hand accounts (from Emma or Fanny's family). All that we do have is third hand (and mostly hostile) accounts, most of them recorded many years after the events.
Unfortunately, this lack of reliable and extensive historical detail leaves much room for critics to claim that Joseph Smith had an affair with Fanny and then later invented plural marriage as way to justify his actions which, again, rests on dubious historical grounds. The problem is we don't know the details of the relationship or exactly of what it consisted, and so are left to assume that Joseph acted honorably (as believers) or dishonorably (as critics).
There is some historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored, so it is perfectly legitimate to argue that Joseph's relationship with Fanny Alger was such a case. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony; and apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Joseph Smith came to know Fanny Alger in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant to Emma. Neither Joseph nor Fanny ever left any first-hand accounts of their relationship. There are no second-hand accounts from Emma or Fanny's family. All that we do have is third hand accounts from people who did not directly observe the events associated with this first plural marriage, and most of them recorded many years after the events.
Benjamin F. Johnson stated that in 1835 he had "learned from my sister’s husband, Lyman R. Sherman, who was close to the Prophet, and received it from him, 'that the ancient order of Plural Marriage was again to be practiced by the Church.' This, at the time did not impress my mind deeply, although there lived then with his family (the Prophet’s) a neighbor’s daughter, Fannie Alger, a very nice and comely young woman about my own age, toward whom not only myself, but every one, seemed partial, for the amiability for her character; and it was whispered even then that Joseph loved her."[1]
Mosiah Hancock discusses the manner in which the proposal was extended to Fanny, and states that a marriage ceremony was performed. Joseph asked Levi Hancock, the brother-in-law of Samuel Alger, Fanny’s father, to request Fanny as his plural wife:
Samuel, the Prophet Joseph loves your daughter Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Uncle Sam says, "Go and talk to the old woman [Fanny’s mother] about it. Twill be as she says." Father goes to his sister and said, "Clarissy, Brother Joseph the Prophet of the most high God loves Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Said she, "Go and talk to Fanny. It will be all right with me." Father goes to Fanny and said, "Fanny, Brother Joseph the Prophet loves you and wishes you for a wife. Will you be his wife?" "I will Levi," said she. Father takes Fanny to Joseph and said, "Brother Joseph I have been successful in my mission." Father gave her to Joseph, repeating the ceremony as Joseph repeated to him.[2]
There is historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony in Kirtland, Ohio in 1833.
Apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Some have wondered how the first plural marriages (such as the Alger marriage) could have occurred before the 1836 restoration of the sealing keys in the Kirtland temple (see D&C 110). This confusion occurs because we tend to conflate several ideas. They were not all initially wrapped together in one doctrine:
Thus, the marriage to Fanny would have occurred under the understanding #1 above. The concept of sealing beyond the grave came later. Therefore, the marriage of Joseph and Fanny would have been a plural marriage, but it would not have been a marriage for eternity.
Perhaps it is worth mentioning that priesthood power already gave the ability to ratify certain ordinances as binding on heaven and earth (D&C 1:8), that the sealing power was given mention in earlier revelations such as Helaman 10:7, and that the coming of Elijah and his turning of the hearts of children and fathers was prophesied in 3 Nephi 25:5-6. This supports the view that it is unlikely that Joseph was just making up the sealing power and priesthood power extemporaneously to justify getting married to Fanny and having sexual relations with her.
Some of Joseph's associates, most notably Oliver Cowdery, perceived Joseph's association with Fanny as an affair rather than a plural marriage. Oliver, in a letter to his brother Warren, asserted that "in every instance I did not fail to affirm that which I had said was strictly true. A dirty, nasty, filthy affair of his and Fanny Alger's was talked over in which I strictly declared that I had never deserted from the truth in the matter, and as I supposed was admitted by himself."[3]
Gary J. Bergera, an advocate of the "affair" theory, wrote:
I do not believe that Fanny Alger, whom [Todd] Compton counts as Smith’s first plural wife, satisfies the criteria to be considered a "wife." Briefly, the sources for such a "marriage" are all retrospective and presented from a point of view favoring plural marriage, rather than, say, an extramarital liaison…Smith’s doctrine of eternal marriage was not formulated until after 1839–40. [4]
There are several problems with this analysis. While it is true that sources on Fanny are all retrospective, the same is true of many early plural marriages. Fanny's marriage has more evidence than some. Bergera says that all the sources about Fanny's marriage come "from a point of view favoring plural marriage," but this claim is clearly false.
For example, Fanny's marriage was mentioned by Ann Eliza Webb Young, a later wife of Brigham Young's who divorced him, published an anti-Mormon book, and spent much of her time giving anti-Mormon, anti-polygamy lectures. Fanny stayed with Ann Eliza's family after leaving Joseph and Emma's house, and both Ann Eliza and her father Chauncey Webb [5] refer to Joseph's relationship to Fanny as a "sealing." [6] Eliza also noted that the Alger family "considered it the highest honor to have their daughter adopted into the prophet's family, and her mother has always claimed that she [Fanny] was sealed to Joseph at that time." [7] This would be a strange attitude to take if their relationship was a mere affair. And, the hostile Webbs had no reason to invent a "sealing" idea if they could have made Fanny into a mere case of adultery.
It seems clear, then, that Joseph, Fanny's family, Levi Hancock, and even hostile witnesses saw their relationship as a marriage, albeit an unorthodox one. The witness of Chauncey Webb and Ann Eliza Webb Young make it untenable to claim that only a later Mormon whitewash turned an affair into a marriage.
It appears that shortly after the April 3 vision, Joseph Smith recorded a first-hand account of the vision in his own personal journal or notes. That original record has not been found and is probably lost. Nonetheless, these important visitations were documented in other contemporaneous records. Within a few days, the Prophet’s secretary Warren Cowdery transcribed Joseph’s first-hand account into a third-hand account to be used in the Church history then being composed. |
|
Despite the importance of Elijah and the Kirtland Temple visitations, Joseph Smith did not publicly teach eternal marriage for perhaps six years after he received the authority to perform those ordinances. |
|
Sometime in late 1835 or early 1836, in a priesthood ceremony performed by Levi Hancock, Joseph secretly married Fanny Alger, a domestic living in the Smith home. When Oliver Cowdery and Emma Smith learned of the relationship, they did not consider it a legitimate marriage. Joseph was unable to convince them the polygamous marriage was approved of God. Fanny left the area and married a non-member a few months later and never returned to the Church. Her family and other who were close to her remained true to Joseph Smith, following him to Nauvoo and later migrating with the Saints to Utah. |
Critical sources |
|
In 1872, William McLellin (then an apostate excommunicated nearly 34 years prior) wrote a letter to Emma and Joseph's son, Joseph Smith III:
Now Joseph I will relate to you some history, and refer you to your own dear Mother for the truth. You will probably remember that I visited your Mother and family in 1847, and held a lengthy conversation with her, retired in the Mansion House in Nauvoo. I did not ask her to tell, but I told her some stories I had heard. And she told me whether I was properly informed. Dr. F. G. Williams practiced with me in Clay Co. Mo. during the latter part of 1838. And he told me that at your birth your father committed an act with a Miss Hill [sic]—a hired girl. Emma saw him, and spoke to him. He desisted, but Mrs. Smith refused to be satisfied. He called in Dr. Williams, O. Cowdery, and S. Rigdon to reconcile Emma. But she told them just as the circumstances took place. He found he was caught. He confessed humbly, and begged forgiveness. Emma and all forgave him. She told me this story was true!! Again I told her I heard that one night she missed Joseph and Fanny Alger. She went to the barn and saw him and Fanny in the barn together alone. She looked through a crack and saw the transaction!!! She told me this story too was verily true. [8]
Some critics interpret "transaction" to mean intercourse in this case and that Emma caught Joseph in the very act. But McLellin reported on the event again three years afterwards in 1875 to J. H. Beadle and makes it clear that he is talking about the wedding or sealing ceremony:
He [McLellin] was in the vicinity during all the Mormon troubles in Northern Missouri, and grieved heavily over the suffering of his former brethren. He also informed me of the spot where the first well authenticated case of polygamy took place in which Joseph Smith was "sealed" to the hired girl. The "sealing" took place in a barn on the hay mow, and was witnessed by Mrs. Smith through a crack in the door! The Doctor was so distressed about this case, (it created some scandal at the time among the Saints,) that long afterwards when he visited Mrs. Emma Smith at Nauvoo, he charged her as she hoped for salvation to tell him the truth about it. And she then and there declared on her honor that it was a fact—"saw it with her own eyes." [9]
Ann Eliza Webb, who was born in 1844, was not even alive at the time of these events, could only only comment based upon what her father told her about Joseph and Fanny. Ann apostatized from the Church and wrote an "expose" called Wife No. 19, or The story of a Life in Bondage. She described Fanny as follows:
Mrs. Smith had an adopted daughter, a very pretty, pleasing young girl, about seventeen years old. She was extremely fond of her; no mother could be more devoted, and their affection for each other was a constant object of remark, so absorbing and genuine did it seem. Consequently is was with a shocked surprise that people heard that sister Emma had turned Fanny out of the house in the night.[10]
The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[11] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
Fawn Brodie, in her critical work No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith, claimed that "there is some evidence that Fannie Alger bore Joseph a child in Kirtland."[12] However, DNA research in 2005 confirmed Fanny Alger’s son Orrison Smith is not the son of Joseph Smith, Jr.[13]
Notes
Our Comment: Although Henry eventually remarried, after Brigham Young told him that his wife and children belonged to Brigham and not to Henry, he continued to yearn for Zina and their children. There doesn't seem to be any good, logical reason why Joseph and then Brigham Young would take Henry Jacob's wife Zina from him and force him to abandon his children and find another wife. Henry wrote to Zina while in England “I have had to hear, feel and suffer everything he has—if you only knew my troubles you’d pity me.” Why was it necessary for Joseph and Brigham to unnecessarily torment this faithful man?
LDS apologists acknowledge Joseph married other men's wives
If you believe the concept of eternal marriage, then Joseph Smith literally stole other men's wives and their children, regardless of whether he had sex with them or not. What right did he have to do that - because he was the prophet?
Joseph Smith was sealed to between 11 to 14 women who were married to men who were still living. Some of these men were even active members of the Church.
To conclude that these "unions" were performed without the knowledge or consent of the living husband is a gross oversimplification. Each case is unique. In some cases, the husband was not a member of the Church who didn't believe in marriage after this life and simply didn't care if Joseph was sealing to his wife for eternity. Since the husbands didn't necessarily believe in a "next life," it seems that they had no problem with the idea of their spouse being sealed to Joseph.
For some whose husbands were Church members, there is circumstantial evidence that the husbands approved, since they continued to live with their wives and associate with the Saints.
Summary: Three of Joseph's plural marriages involved women who were married to non-member spouses. Of one, Ruth Vose Sayers, we know very little. She married Edward Sayers in 1841, and they had no children. Her husband remained friendly to Joseph Smith, as far as we know, to the end of Joseph's life. Brian Hales notes that Church Historian Andrew Jensen's documents "regarding Ruth Vose Sayers demonstrate that her marriage was for 'eternity only,' without conjugal relations on earth."
Ruth was sealed to Joseph Smith only for eternity, and not for time, with both her husband’s consent and with Emma’s consent. She "continued to live with Mr. Sayers (remained with her husband) until his death. "[2] Ruth’s husband Edward was not a member of the Church, and was not interested in becoming one. Edward was, however, a good friend of Joseph Smith. Since Edward did not attach "much importance to the theory of a future life," he "insisted that his wife Ruth should be sealed to the Prophet for eternity, as he himself should only claim …her in this life. She was accordingly [then] sealed to the Prophet in Emma Smith’s presence…" [2] Brian Hales notes that in 1869, Ruth signed an affidavit that reads:
Be it remembered that on this first day of May, A.D. 1869, personally appeared before me, Elias Smith, Probate Judge for Said County, Ruth Vose Sayers who was by me Sworn in due form of law and upon her oath Saith that on [blank] day of February A.D. 1843 at the City of Nauvoo County of Hancock, State of Illinois, She was married or Sealed to Joseph Smith President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints, by Hyrum Smith, Presiding Patriarch of Said Church, according to the laws of the Same, regulating Marriage; in the presence [blank] [3]
Hales also notes the following from the research papers of Andrew Jenson:
\Sister Ruth/ Mrs. Sayers was married in her youth to Mr. Edward Sayers, a thoroughly practical horticulturist and florist, and though he was not a member of the Church, yet he willingly joined his fortune with her and they reached Nauvoo together some time in the year 1841; While there the strongest affection sprang up between the Prophet Joseph and Mr. Sayers. The latter not attaching much importance to \the/ theory of a future life insisted that his wife \Ruth/ should be sealed to the Prophet for eternity, as he himself should only claim [page2—the first 3 lines of which are written over illegible erasures] her in this life. She \was/ accordingly the sealed to the Prophet in Emma Smith’s presence and thus were became numbered among the Prophets plural wives. She however \though she/ \continued to live with Mr. Sayers / remained with her husband \until his death.[4]
Notes
Summary: Daniel H. Wells wrote to Joseph F. Smith of a sealing between Joseph and Esther Dutcher. Wells' source of information was Dutcher's husband, Albert Smith (no relation to Joseph): "It seems that she was sealed to Joseph the Prophet in the days of Nauvoo, though she still remained his wife, and afterwards nearly broke his heart by telling him of it, and expressing her intention of adhering to that relationship. He however got to feeling better over it, and acting for Joseph, had her sealed to him [in the temple--all of Joseph's marriages were understood to require resealing in the temple once it was completed], and to himself for time."
There is very little evidence of the sealing of Esther Dutcher to Joseph Smith. Ester was married to Albert Smith (no relation to Joseph Smith or George Albert Smith). The little evidence that exists indicates that she was sealed to Joseph for eternity only, and continued to live with her husband until she died. It also appears that she was sealed to Joseph for eternity before informing her husband of that fact. Thirty-two years after Esther's death, Apostle Daniel H. Wells wrote the following letter to Joseph F. Smith. Wells notes that after Esther's death that,
He [Albert Smith was] also much afflicted with the loss of his first wife. It seems that she was sealed to Joseph the Prophet in the days of Nauvoo, though she still remained his wife, and afterwards nearly broke his heart by telling him of it, and expressing her intention of adhering to that relationship. He however got to feeling better over it, and acting for Joseph, had her sealed to him, and to himself for time.[1]
Summary: Mary Elizabeth Rollins Lightner was among the earliest converts to the Church. She had married Adam Lightner on 11 August 1835.....Later in life, Mary reported that, Joseph Smith "told me about his great vision concerning me. He said I was the first woman God commanded him to take as a plural wife."....Mary described how "[t]he Prophet Joseph tried hard to get Mr. Lightner to go into the water, but he said he did not feel worthy, but would, some other time. Joseph said to me that he never would be baptized, unless it was a few moments before he died." Despite not being a member, Lightner was a loyal friend to the Saints and to Joseph, and died in Utah. Of her sealing to Joseph, Mary wrote: "I could tell you why I stayed with Mr. Lightner. Things the leaders of the Church does not know anything about. I did just as Joseph told me to do, as he knew what troubles I would have to contend with.”
Mary joined the Church at age 12 in Kirtland, in October 1830, and so was among the very first members.[2] She seems to have been mature for her age; she had heard about the Book of Mormon, but had not even seen a copy prior to her baptism. She wrote:
About this time, John Whitmer came and brought a Book of Mormon. There was a meeting that evening, and we learned that Brother Morley had the Book in his possession the only one in that part of the country. I went to his house just before the meeting was to commence, and asked to see the book; Brother Morley put it in my hand, as I looked at it, I felt such a desire to read it, that I could not refrain from asking him to let me take it home and read it, while he attended meeting. He said it would be too late for me to take it back after meeting, and another thing, he had hardly had time to read a chapter in it himself, and but few of the brethren had even seen it, but I pled so earnestly for it, he finally said, "Child, if you will bring this book home before breakfast tomorrow morning, you may take it." He admonished me to be very careful, and see that no harm came to it. If any person in this world was ever perfectly happy in the possession of any coveted treasure I was when I had permission to read that wonderful book. Uncle and Aunt were Methodists, so when I got into the house, I exclaimed, "Oh, Uncle, I have got the 'Golden Bible'." Well, there was consternation in the house for a few moments, and I was severely reprimanded for being so presumptuous as to ask such a favor, when Brother Morley had not read it himself. However, we all took turns reading it until very late in the night as soon as it was light enough to see, I was up and learned the first verse in the book. When I reached Brother Morley's they had been up for only a little while. When I handed him the book, he remarked, "I guess you did not read much in it." I showed him how far we had read. He was surprised and said, "I don't believe you can tell me one word of it." I then repeated the first verse, also the outlines of the history of Nephi. He gazed at me in surprise, and said, "child, take this book home and finish it, I can wait."[3]
In fall of 1831, Mary left with her family for Independence, Missouri. She received the spiritual gift of interpretation of tongues:
Oliver Cowdery, John Whitmer and Thomas B. Marsh often spoke in tongues in addressing the people on the Sabbath day, and I wanted to understand what they said; so I made it a subject of prayer, that the Lord would give me to understand what was the meaning of their words; for they seemed to speak with great power. One evening the brethren came to Uncle's house to converse upon the revelations that had not been printed as yet, but few had looked upon them, for they were in large sheets, not folded. They spoke of them with such reverence, as coming from the Lord; they felt to rejoice that they were counted worthy to be the means of publishing them for the benefit of the whole world. While talking they were filled with the spirit and spoke in tongues. I was called upon to interpret it. I felt the spirit of it in a moment.[4]
Mary and her sister Caroline were the two young women who took copies of the Book of Commandments (the first publication of what we call the Doctrine and Covenants). A mob was destroying the printing office in Missouri, and the girls snatched some unbound printings:
The mob renewed their efforts again by tearing down the printing office, a two story building, and driving Brother Phelps' family out of the lower part of the house and putting their things in the street. They brought out some large sheets of paper, and said, "Here are the Mormon Commandments." My sister Caroline and myself were in a corner of a fence watching them; when they spoke of the commandments I was determined to have some of them. Sister said if I went to get any of them she would go too, but said "They will kill us." While their backs were turned, prying out the gable end of the house, we went, and got our arms full, and were turning away, when some of the mob saw us and called on us to stop, but we ran as fast as we could. Two of them started after us. Seeing a gap in a fence, we entered into a large cornfield, laid the papers on the ground, and hid them with our persons. The corn was from five to six feet high, and very thick; they hunted around considerable, and came very near us but did not find us....They [the members] got them bound in small books and sent me one, which I prized very highly.[5]
The violence worsened, and so Mary and her company resolved to cross the river to safety:
After enduring all manner of grievances we were driven from the county. While we were camped on the banks of the Missouri River waiting to be ferried over, they found there was not money enough to take all over. One or two families must be left behind, and the fear was that if left, they would be killed. So, some of the brethren by the name of Higbee thought they would try and catch some fish, perhaps the ferryman would take them, they put out their lines in the evening; it rained all night and most of the next day, when they took in their lines they found two or three small fish, and a catfish that weighed 14 pounds. On opening it, what was their astonishment to find three bright silver half dollars, just the amount needed to pay for taking their team over the river. This was considered a miracle, and caused great rejoicing among us.[6]
It is clear, then, that Mary had a number of remarkable spiritual experiences early in her life, and a strong testimony of the restored gospel.
Joseph Smith came to Kirtland (prior to their move to Independence) at about the time she finished reading the Book of Mormon (i.e., around age 12):
Brother Whitney brought the Prophet Joseph to our house and introduced him to the older ones of the family (I was not in at the time.) In looking around he saw the Book of Mormon on the shelf, and asked how that book came to be there. He said, "I sent that book to Brother Morley." Uncle told him how his niece had obtained it. He asked, "Where is your niece?" I was sent for; when he saw me he looked at me so earnestly, I felt almost afraid. After a moment or two he came and put his hands on my head and gave me a great blessing, the first I ever received, and made me a present of the book, and said he would give Brother Morley another. He came in time to rebuke the evil spirits, and set the church in order. We all felt that he was a man of God, for he spoke with power, and as one having authority in very deed.[7]
Mary wrote of the first meeting which Joseph held with the Saints in Kirtland:
The Smith family was driven from New York, and a small church had been organized. Oliver Cowdery, Peter Whitmer, and Ziba Peterson were members. Well, I being anxious, though young, to learn about the plates from those who knew all about it, my mother and I went up to the Smith family the next night after they came to Kirtland. As I went in, there were two or three others present. They were all there, from the old gentleman and his wife to all the sons and daughters. As we stood there talking to them, Joseph and Martin Harris came in. Joseph looked around very solemnly. It was the first time some of them had ever seen him.Said he, "There are enough here to hold a little meeting." They got a board and put it across two chairs to make seats. Martin Harris sat on a little box at Joseph's feet. They sang and prayed. Joseph got up and began to speak to us. As he began to speak very solemnly and very earnestly, all at once his countenance changed and he stood mute. Those who looked at him that day said there was a search light within him, over every part of his body. I never saw anything like it on the earth. I could not take my eyes off him; he got so white that anyone who saw him would have thought he was transparent. I remember I thought I could almost see the cheek bones through the flesh. I have been through many changes since but that is photographed on my brain. I shall remember it and see in my mind's eye as long as I remain upon the earth.
He stood some moments. He looked over the congregation as if to pierce every heart. He said, "Do you know who has been in your midst?" One of the Smiths said an angel of the Lord. Martin Harris said, "It was our Lord and Savior, Jesus Christ." Joseph put his hand down on Martin and said: "God revealed that to you. Brethren and sisters, the Spirit of God has been here. The Savior has been in your midst this night and I want you to remember it. There is a veil over your eyes for you could not endure to look upon Him. You must be fed with milk, not with strong meat. I want you to remember this as if it were the last thing that escaped my lips. He has given all of you to me and has sealed you up to everlasting life that where he is, you may be also. And if you are tempted of Satan say, 'Get behind me, Satan.'"
These words are figured upon my brain and I never took my eye off his countenance. Then he knelt down and prayed. I have never heard anything like it before or since. I felt that he was talking to the Lord and that power rested down upon the congregation. Every soul felt it. The spirit rested upon us in every fiber of our bodies, and we received a sermon from the lips of the representative of God.[8]
Some have claimed (in error) that Joseph would teach Mary about plural marriage during this period (see discussion below).
Some have tried to see Joseph as telling Mary in Kirtland at age 12 that she was to be his wife.[9] This does not, however, seem to match her account:
The words of the Prophet that had been revealed to him always have been with me from the beginning to the end of the gospel. Every principle that has been given in the Church by the prophet is true. I know whereon I stand, I know what I believe, I know what I know and I know what I testify to you is the living truth. As I expect to meet it at the bar of the eternal Jehovah, it is true. And when you stand before the bar you will know. He preached polygamy and he not only preached it, but he practiced it. I am a living witness to it. It was given to him before he gave it to the Church. An angel came to him and the last time he came with a drawn sword in his hand and told Joseph if he did not go into that principle, he would slay him. Joseph said he talked to him soberly about it, and told him it was an abomination and quoted scripture to him. He said in the Book of Mormon it was an abomination in the eyes of the Lord, and they were to adhere to these things except the Lord speak. I am the first being that the revelation [D&C 132] was given to him for and I was one thousand miles away in Missouri, for we went up to Jackson County in 1841 [should be 1831].[10]
As she says in the quote above, Joseph got the revelation regarding her, but by then she was a thousand miles away in Missouri. Her family had left Kirtland for Missouri in the fall of 1831; only after her departure did Joseph report the revelation.
Furthermore, in a private letter to Emmeline B. Wells, Mary said that she was not taught anything about plural marriage by Joseph until 1842:
As for Sister Whitney, Bishop Whitney's wife, I shall never forget her. It was at their house that the Prophet Joseph first told me about his great vision concerning me. He said I was the first woman God commanded him to take as a plural wife. That was in 1831. He was very much frightened, the angel appeared to him three times. It was in the early part of Feb. 1842 that he was compelled to reveal it to me personally, by the Angel threatening him. I said I would not accept it until I had seen an immortal being myself. I could tell you about this, but cannot write any more in regard to this subject.[11]
Critics have attempted to portray Joseph as a lech or pedophile, preying on a young child. They claim that he is "grooming" her for later abuse. There are several problems with such a reconstruction. A key one is that, as we have seen, Joseph's revelation regarding her did not come until she was far away in Missouri. (Newel K. Whitney was also not called as a bishop until December 1831.[12])
Mary married Adam Lightner, who was not a member of the Church, on 11 August 1835.[13]
Following the Haun's Mill Massacre in Missouri, the Missouri militia and mob came to capture, kill, or drive out the Saints:
For in the midst of sorrow, news came that the militia (besides the hundreds of the mob), were marching to destroy our city and its inhabitants. A part of the bloodthirsty mob camped near the city and placed a cannon in the middle of the road, intending to blow up the place. Then they sent in a flag of truce, demanding an interview with John Cleminson and wife, and Adam Lightner and wife. We went a short distance to meet them. We saw a number of the brethren standing around the place of meeting, well armed. As we approached, General Clark shook hands with the two men, being old acquaintances, and remarked that Governor Boggs had given him an order for our safe removal before they destroyed the place. I asked my sister-in-law what we should do about it. She replied, "We will do as you say; I was surprised at her answer, as she was the mother of four or five children, and I had but one. So I asked the General if he would let all the Mormon women and children go out? He said, "No." "Will you let my mother's family go out?" He said, "The Governor's orders were that no one but our two families should go but all were to be destroyed." "Then, if that is the case, I refuse to go, for where they die, I will die, for I am a full blooded Mormon, and I am not ashamed to own it." "Oh," said he, "you are infatuated, your Prophet will be killed with the rest." Said I, "If you kill him today, God will raise up another tomorrow." "But think of your husband and child." I then said that he could go, and take the child with him, if he wanted to, but I would suffer with the rest.
Just then a man kneeling down by some brush, jumped up and stepping between the General and myself, said, "Hold on, General," then turned to me and said, "Sister Lightner, God Almighty bless you, I thank my God for one soul that is ready to die for her religion; not a hair of your head shall be harmed, for I will wade to my knees in blood in your behalf." "So will I," said Brother Hyrum Smith, and others. The first speaker was Brother Heber C. Kimball, with whom I was not acquainted at the time. Then the General pleaded with my husband, but it was of no avail.[14]
The Lightners went to Louisville, Kentucky, but once they heard of the Saints regathering at Nauvoo, they sold what little they had and went to join them.[15]
They moved away from Nauvoo to find work, though Joseph told them they would not prosper if they did so. Mary would ultimately believe the prophet was correct. She became very ill, and her life was despaired of:
I prayed for help to get well, but the doctor coming in, said there was no hope for me. But I dreamed that an angel came to me and said if I would go to Nauvoo and call for a Brother Cutler, that worked on the temple, to administer to me, I should be healed. But we could get no team to go. I was in despair; however, my brother was impressed to send for me, he felt that something was wrong, so he sent a boy with an ox team after me. I was so glad, that for a few moments I felt new life. But the people said I would not get a mile from town when he would have to bring back my dead body. But I said I wanted to be buried in Nauvoo, and pleaded with them to take me there, dead or alive. We went a mile and stopped the team; they thought me dying, all the children were crying. I had my senses and motioned for them to go on. We went a few miles further, stopped at a house and asked to stay all night. The woman was willing until she saw me. She said I would die before morning, and she did not want me to die in her house. Mr. Lightner told her that I would certainly die if I was left in the open wagon all night. She finally let us in. She made us as comfortable as she could and fixed me some light food; after drinking some tea, I felt better and had a good night's rest; but she was glad when we left, for she thought I would never see Nauvoo. After traveling a few miles further, we finally reached Nauvoo. They still thought me dying. Mr. Lightner asked Brother Burt if there was an old man by the name of Cutler working on the temple. He said "Yes." Mr. Lightner told him my dream; soon they brought him, he administered to me and I got up and walked to the fire, alone. In two weeks I was able to take care of my children.[16]
At Nauvoo, Joseph and Emma were kind to the Lightners, and Joseph worked to persuade her husband to be baptized: "The Prophet Joseph tried hard to get Mr. Lightner to go into the water, but he said he did not feel worthy, but would, some other time. Joseph said to me that he never would be baptized, unless it was a few moments before he died."[17]
Mary seems to have been prepared spiritually for the doctrine of plural marriage. She reported, "I was not sealed to him until I had a witness. I had been dreaming for a number of years I was his wife. I thought I was a great sinner. I prayed to God to take it from me for I felt it was a sin...."[18] This is yet further evidence that she knew nothing of plural marriage until Nauvoo; she would not have been mystified or felt guilty about dreaming about being Joseph's wife if she had been taught the doctrine and accepted it in 1831.
In 1842, Joseph told Mary about plural marriage. Her reaction is not that of a child who has been groomed, of a woman over-awed by the prophet's status, or someone who meekly submits. She was offended:
I have never told a mortal and shall never tell a mortal I had such a talk from a married man."[19]
I was not sealed to him until I had a witness....but when Joseph sent for me he told me all of these things. "Well," said I, "don't you think it was an angel of the devil that told you these things?" Said he, "No, it was an angel of God. God Almighty showed me the difference between an angel of light and Satan's angels.[20]
Mary clearly did not believe Joseph at first; even the prophet's appeal to a revelation from an angel is not enough for her. She was quite prepared to think that this was an evil deception:
Well, I talked with him for a long time and finally I told him I would never be sealed to him until I had a witness. Said he, "You shall have a witness." Said I, "If God told you that, why does he not tell me?"..."Well," said he, "pray earnestly for the angel said to me you should have a witness." Well, Brigham Young was with me. He said if I had a witness he wanted to know it. "Why should I tell you?" said I. "Well," said he, "I want to know for myself." Said he, "Do you know what Joseph said? Since we left the office the angel appeared to him and told him he was well pleased with him and that you should have a witness."[21]
Joseph does not hesitate to tell a suspicious and reluctant Mary that she will have a divine witness—a strange and risky act for a predator to undertake.
Mary described her search for a witness:
I made it a subject of prayer and I worried about it because I did not dare to speak to a living being except Brigham Young. I went out and got between three haystacks where no one could see me. As I knelt down I thought, why not pray as Moses did? He prayed with his hands raised. When his hands were raised, Israel was victorious, but when they were not raised, the Philistines were victorious. I lifted my hands and I have heard Joseph say the angels covered their faces. I knelt down and if ever a poor mortal prayed, I did. A few nights after that an angel of the Lord came to me and if ever a thrill went through a mortal, it went through me. I gazed upon the clothes and figure but the eyes were like lightning. They pierced me from the crown of my head to the soles of my feet. I was frightened almost to death for a moment. I tried to waken my aunt, but I could not. The angel leaned over me and the light was very great, although it was night. When my aunt woke up she said she had seen a figure in white robes pass from our bed to my mother's bed and pass out of the window.[22]
Mary received a witness, and her aunt (who knew nothing of her conversation with Joseph) served as a second witness of the experience. We might argue that Joseph so bedazzled Mary that she hallucinated—a dubious claim—but he cannot have fabricated her aunt's unwitting verification.
Mary reported her experience to Joseph:
Joseph came up the next Sabbath. He said, "Have you had a witness yet?" "No." "Well," said he, "the angel expressly told me you should have." Said I, "I have not had a witness, but I have seen something I have never seen before. I saw an angel and I was frightened almost to death. I did not speak." He studied a while and put his elbows on his knees and his face in his hands. He looked up and said, "How could you have been such a coward?" Said I, "I was weak." "Did you think to say, `Father, help me?'" "No." "Well, if you had just said that, your mouth would have been opened for that was an angel of the living God. He came to you with more knowledge, intelligence, and light than I have ever dared to reveal." I said, "If that was an angel of light, why did he not speak to me?" "You covered your face and for this reason the angel was insulted." Said I, "Will it ever come again?" He thought a moment and then said, "No, not the same one, but if you are faithful you shall see greater things than that." And then he gave me three signs of what would take place in my own family, although my husband was far away from me at the time. Every work came true. I went forward and was sealed to him.[23]
Even the angelic vision does not suffice for Mary. She received three more (unspecified) signs which Joseph predicted. She told the same story in a letter:
As it is, I can never forget that [angel's] face, it seems to be ever before me. A few days after this Joseph asked [p. 48] me if I had received a witness Yet? I said no, he said you soon will have; for the Angel expresly told me you should Have--then I told him what I had seen, for I fully realized what I had lost by my cowardice...After receiving other Testimonies, I felt I could no longer disbelieve, and in the month of March 1841 Brigham Young Sealed us for time, and all Eternity....[24]
The weight of these witnesses convinced her, and she entered plural marriage. None of this is consistent with a woman who has been "groomed" or otherwise manipulated. She has put Joseph's claims to a severe test, and has found him justified in every particular.
Mary was a woman of considerable spiritual gifts and strength of mind. She said, near the end of her life:
But I want you to remember what I have said, that it is my testimony, as long as you live. I want to say to you as I said before that Joseph said if I was faithful, I should see greater things than the angel. Since then I have seen other persons, three came together and stood before me just as the sun went down—Joseph, Hyrum and Heber C. Kimball. It was prophesied that I should see Joseph before I died. Still, I was not thinking about that. I was thinking about a sermon I had heard. All at once I looked up and they stood before me. Joseph stood in the middle in a circle like the new moon and he stood with his arms over their shoulders. They bowed to me about a dozen times or more. I pinched myself to be sure I was awake, and I looked around the room to see where I had placed things. I thought I would shake hands with them. They saw my confusion and understood it and they laughed, and I thought Brother Kimball would almost kill himself laughing. I had no fear. As I went to shake hands with them, they bowed, smiled and began to fade. They went like the sun sinks behind a mountain or a cloud. It gave me more courage and hope than I ever had before....[25]
Thus, her visionary and revelatory experiences were not confined to times when somehow under the influence of Joseph's charisma.
Mary Elizabeth Rollins was married to a non-Mormon, Adam Lightner. Mary did not proceed with the sealing to Joseph until she had given up attempting to persuade her husband Adam to join:
My husband did not belong to the Church. I begged him and pled with him to join but he would not. He said he did not believe in it, though he thought a great deal of Joseph. He sacrificed his property rather than testify against Joseph, Hyrum and George A. Smith. After he said this, I went forward and was sealed to Joseph for eternity.[26]
After being sealed to Joseph, Mary continued to live with her husband Adam until his death in 1885. Although this particular statement, and the evidence that she continued to live with her husband until his death, indicates a sealing for eternity only, on other occasions Mary actually referred to being sealed to Joseph for "time and eternity." Joseph also told her that she was to be sealed to him for eternity, and she initially resisted the idea until she received an angelic visitation and confirmation.
Notes
Presendia Huntington was married to Norman Buell when she was sixteen years old. Both Presendia and Norman originally joined the Church, but Norman later left it while Presendia remained a believing member. Since she was unable to be sealed for eternity to her earthly husband, she was sealed to Joseph Smith instead. Presendia's 1881 biography notes her husband's rejection of the Church as the reason she decided to be sealed to Joseph Smith for eternity,
I was maried to Norman Buell Jan 6th 1827. both joined the Church in in [sic] Kirtland Geauga Co Ohio he left the church in Mo in 1839 the Lord gave me strength to stand alone & keep the faith amid heavy persecution in 1841 I entered into the new & everlasting Covenant was sealed to Joseph Smith the Prophet & Seer & to the best of my ability I have honored Plural Marriage never speking one word against the principal. [1]
An affidavit signed by Presendia on May 1, 1869 states:
Be it remembered that on this first day of May A.D. 1869 personally appeared before me Elias Smith Probate Judge for Said County Presenda Lathrop Huntington \Kimball/ who was by me Sworn in due form of law and upon her oath saith, that on the eleventh day of December A.D. 1841, at the City of Nauvoo, County of Hancock State of Illinois, She was married or Sealed to Joseph Smith, President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints by Dimick B. Huntington, a High-Priest in Said Church, according to the laws of the Same regulating Marriage; in the presence of Fanny Maria Huntington. [2]
Summary: There is considerable debate as to whether Sarah Kingsley was sealed to Joseph Smith. [19] Danel Bachman's pioneering study on plural marriage argued that there was "little supporting evidence for [her]…inclusion" on a list of Joseph's wives. [20] Todd Compton argues for Sarah's inclusion, since she is included on Andrew Jenson's list of plural wives, had a proxy marriage to Joseph Smith in the temple following the martyrdom, and because Eliza R. Snow is known to have been sealed to Joseph at Sarah's home. Compton holds—and I find his reasoning persuasive—that Joseph's decision to marry Eliza in front of Sarah makes little sense if Sarah had not already been introduced to plural marriage. (Though it must be admitted that Sarah could have been aware of plural marriage, but not practicing it.) Compton's argument is strengthened by the fact that Andrew Jenson also had access to Eliza R. Snow as a witness, so she could have confirmed Sarah's sealing.
Sarah was married to non-Mormon John Cleveland. John was not interested in joining the Church, but was friendly to the Saints.
In the days of Joseph. Mother [Sarah M. Kingsley (Howe)] Cleveland by advice, was sealed to the prophet in Nauvoo but lived with her [non-LDS] husband John Cleveland.[3]
When the Saints moved west, Sarah wished to go with them, even to the point of leaving her non-LDS husband. Brigham Young advised her to remain with him:
Brigham Young and council...counseled her to stay with her husband as he was a good man, having shown himself kind ever helping those in need, although for some reason his mind was darkened as to the gospel. She obeyed council and stayed with her husband, and was faithful and true to her relation and died a faithful member of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints.[4]
Summary: Sylvia Session's mother Patty joined the Church in 1833, and was sealed to Joseph Smith on 9 March 1842. The reaction of her husband David is unknown, but he remained a faithful member and diligent missionary. He later married a plural wife, which caused difficulties in their marriage.
Patty and her husband David Sessions were active members of the Church. They received their endowment in Nauvoo in 1845. Patty had been sealed for eternity to Joseph Smith three years earlier in 1842. After her husband David's death, she was sealed "for time" (re-married to an earthly husband) to John Parry in 1852. Patty's diary states,
Patty Bartlett daughter of Enoch and Anne Bartlett was born February 4, 1795 \Bethel Mane/ and was married to David Session June 28th 1812 who was the son of David and Rachel Sessions, he was born April the 4th 1790 Veshire Vermont I was Batpised into the church of Jesus Christ \of later day saints/ July 2, 1834 Mr Sessions was Baptised Aug <st> 1735 we received our we received our endowment Dec 16 1845 in Nauvoo. . . .
I was sealed to Joseph Smith by Willard Richards March 9, 1842 in Newel K Whitneys chamber Nauvoo for Eternity and I and if I do not live to attend to it myself when there is a place prepared I want some one to attend to it for me according to order Sylvia \my daughter/ was present when I was sealed to Joseph Smith.I was after Mr. Sessions death sealed to John Parry senior for time on the 27 of March 1852 G[reat] S[alt] L. City.[1]
Nothing is stated regarding what her husband David thought of her sealing to Joseph, or whether or not he agreed to it. Brian Hales notes that, "David and Patty Sessions attended the Nauvoo Temple together, receiving their endowments on December 15, 1845, but they were not sealed in marriage." It would seem apparent that David was fully aware of her sealing to Joseph.
Summary: The inclusion of "Mrs. Durfee," as she was known, on the list of Joseph's wives is strongly contested among historians. Durfee is not found on Andrew Jenson's list of Joseph's plural wives. Todd Compton argues that Durfee's post-martyrdom proxy sealing to Joseph is evidence of a living marriage, as is the fact that she taught plural marriage to other prospective wives. Compton also holds that two hostile sources (John C. Bennett and Sarah Pratt) confirm Durfee as a plural wife.
Elizabeth's husband Jabez Dufee was active in the Church. Elizabeth chose to be sealed for eternity to Joseph Smith. Brian Hales notes that, "It appears that the couple experienced some marital turmoil before the sealing or perhaps as a consequence of it. Jabez was endowed on a different day than Elizabeth when the Nauvoo Temple opened in the winter of 1845 and Elizabeth was resealed by proxy to Joseph Smith on January 22, 1846, but Jabez did not participate either as a proxy husband or witness." [1]
Summary: Elizabeth Davis was born to Gilbert Davis and Abigail Reeves on March 11, 1791. She joined the Church on April 10, 1831. Two years later the twice widowed Elizabeth married Jabez Durfee on March 3, 1834. Casting their lot with the Saints, she and Jabez moved to Missouri and later Nauvoo.
Summary: Elvira was married to Joseph at age twenty-nine. Her husband, Jonathan Holmes, was a pall-bearer at Joseph Smith's funeral. As Todd Compton remarks, "Though it is impossible to know for certain, the fact that Holmes was so close to Joseph Smith suggests that he knew of Smith’s marriage to his wife and permitted it…He later stood as proxy for Smith as Elvira married the prophet for eternity in the Nauvoo temple…This ‘first husband’ never wavered in his loyalty to the Mormon leader…."
A letter by William Wright talks of Joseph asking Jonathan Holmes to marry Elvira. Joseph was later sealed to her for eternity.
I was well acquainted with two of Joseph’s wives, LaVina [Elvira] and Eliza [Snow or Partridge]. I came to Utah in ’69, and rented LaVina Holmes farm. Before Joseph was shot, he asked Jonathan Holmes if he would marry and take care of LaVina, but if LaVina wanted him to take care of her he would take her. He would fill that mission to please his Father in Heaven.[2]
Brian Hales notes that, "It seems to corroborate that Jonathan may have been given a “mission” to marry Elvira and “take care of her” in a legal pretend marriage. After the martyrdom, Jonathan would have been free to take Elivira as his own wife. She did not conceive her first child until seven months after Joseph’s death. The couple went on to have a total of five children together." [3]
Notes
In 1839, at age 18, Zina arrived with her parents in Nauvoo after being driven out of Missouri. Faithful LDS missionary Henry Jacobs courted her during 1840–41. At the same time, Joseph Smith had taught Zina the doctrine of plural marriage, and thrice asked her to marry him. She declined each time, and she and Henry were wed 7 March 1841.[1] Zina and Henry were married by John C. Bennett, then mayor of Nauvoo. They had invited Joseph to perform the ceremony, but Bennett stepped in when Joseph did not arrive:
…Zina asked the Prophet to perform the marriage. They went to the Clerk’s office and the Prophet did not arrive, so they were married by John C. Bennett. When they saw Joseph they asked him why he didn’t come, and he told them the Lord had made it known to him that she was to be his Celestial wife.[2]
Family tradition holds, then, that Zina and Henry were aware of Joseph's plural marriage teachings and his proposal to Zina. While this perspective is late and after-the-fact, it is consistent with the Jacobs' behaviour thereafter. Zina's family also wrote that Henry believed that "whatever the Prophet did was right, without making the wisdom of God's authorities bend to the reasoning of any man." [3]
On 27 October 1841, Zina was sealed to Joseph Smith by her brother, Dimick Huntington. She was six months pregnant by Henry, and continued to live with him.
Joseph Smith and Brigham Young's "mistreatment" of Henry and their "theft" of his family have received a great deal of publicity, thanks to late 19th century anti-Mormon sources, and Fawn Brodie increased their cachet for a 20th century audience.[4] For present purposes, we will focus on Zina. She had refused Joseph's suit three times, and chosen to marry Henry. Why did she decide to be sealed to Joseph?
When interrogated by a member of the RLDS Church, Zina refused to be drawn into specifics. She made her motivations clear, and explained that God had prepared her mind for Joseph's teachings even before she had heard them:
- Q. "Can you give us the date of that marriage with Joseph Smith?"
- A. "No, sir, I could not."
- Q. "Not even the year?"
- A. "No, I do not remember. It was something too sacred to be talked about; it was more to me than life or death. I never breathed it for years. I will tell you the facts. I had dreams—I am no dreamer but I had dreams that I could not account for. I know this is the work of the Lord; it was revealed to me, even when young. Things were presented to my mind that I could not account for. When Joseph Smith revealed this order [Celestial marriage] I knew what it meant; the Lord was preparing my mind to receive it." [5]
Henry was to stand as proxy for Zina's post-martyrdom sealing to Joseph, and her marriage for time to Brigham Young. He and Zina separated soon thereafter, and Henry was soon gone on one of his many missions for the Church.[6]
Zina herself clearly explains the basis for her choice:
…when I heard that God had revealed the law of Celestial marriage that we would have the privilege of associating in family relationships in the worlds to come, I searched the scriptures and by humble prayer to my Heavenly Father I obtained a testimony for myself that God had required that order to be established in his Church.[7] Faced with questions from her RLDS interviewer that she felt exceeded propriety, Zina became evasive. She finally terminated the interview by saying, "Mr. Wight, you are speaking on the most sacred experiences of my life…."[8]
Zina married Henry Jacobs in 1840, and was sealed to Joseph Smith for eternity in 1841,
Be it remembered that on this first day of May A.D. eighteen sixty nine before me Elias Smith Probate Judge for Said County personally appeared, Zina Diantha Huntington ^Young^ who was by me Sworn in due form of law, and upon her oath Saith, that on the twenty-Seventh day of October A.D. 1841, at the City of Nauvoo, County of Hancock, State of Illinois, She was married or Sealed to Joseph Smith, President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints, by Dimick B. Huntington, a High Priest in Said Church, according to the laws of the same; regulating marriage; In the presence of Fanny Maria Huntington.[9]
There are many stories and accusations related to the marriage of Zina and Henry, and her sealing to Joseph. For details regarding each of these allegations, see Brian and Laura Hales, "Zina Diantha Huntington," josephsmithspolygamy.org off-site.
See also: Allen Wyatt, "Zina and Her Men: An Examination of the Changing Marital State of Zina Diantha Huntington Jacobs Smith Young," FAIR Conference, 2006.
Allen Wyatt explains how this story originated,
The Charge by William Hall
Critics of the early Saints have, often with glee, latched onto William Hall’s story and used it as a prime example of ecclesiastical abuse, pitting a powerful Brigham Young against a penniless and ill Henry Jacobs, with Zina as some kind of prize for the winner of their imagined contest. It is easy to understand how one might see things that way; it is certainly the way that William Hall portrayed the episode:
At a place called, by the Mormons, Pisgah, in Iowa, as they were passing through to Council Bluffs, Brigham Young spoke in this wise, in the hearing of hundreds: He said it was time for men who were walking in other men’s shoes to step out of them. "Brother Jacobs," he says, "the woman you claim for a wife does not belong to you. She is the spiritual wife of brother Joseph, sealed up to him. I am his proxy, and she, in this behalf, with her children, are my property. You can go where you please, and get another, but be sure to get one of your own kindred spirit."37
The immediate problem with such a statement is that there is no contemporary corroboration for it. Hall states that Brigham’s statement was made in the hearing of hundreds of people, yet there are no other diaries that indicate such a statement or, indeed, any statement from Brigham to Henry. The statement itself would need to have been made sometime between Henry’s arrival at Mt. Pisgah (May 18) and his departure on his mission (approximately June 1).
For instance, Patty Bartlett Sessions, who was a detailed journal writer, arrived at Mt. Pisgah in the same company as the Jacobs’ and left Mt. Pisgah on June 2, 1846. None of her diary entries for the period refer to any such statement by Brigham Young, and it is safe to assume that she would have been among the "hundreds" referenced by William Hall. In fact, Sessions continues to refer to Zina as either "Zina Jacobs" or "sister Jacobs" as late as June 3, 1847,38 which reference would seem unlikely if she had heard Brigham claim Zina (and her children) as his property and exile Henry.
The diary of William Huntington records only one semi-public and one fully public meeting between May 18 and the first of June. There was a prayer meeting for selected individuals held on May 31,39 and a meeting in the grove near Huntington’s house on June 1 that turned into a "special conference" at which "considerable business" was done.40 There is, however, no record in his diary of any denouncing of his son-in-law by Brigham.[10]
For more information, see Allen Wyatt, "Zina and Her Men: An Examination of the Changing Marital State of Zina Diantha Huntington Jacobs Smith Young," FAIR presentation transcript, 2006. FAIR link
Notes
The record is frustratingly incomplete regarding the question of which marriages were consummated, it is likewise spotty with regards to whether Joseph fathered children by his plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to consider this question in any detail, though her standard of evidence was depressingly low. Subsequent authors have returned to the problem, though unanimity has been elusive (see Table 1). Ironically, Brodie did not even mention the case of Josephine Lyon, now considered the most likely potential child of Joseph.
Notation:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36]
It is claimed that Joseph Smith fathered children with some of his plural wives, and that he covered up the evidence of pregnancies. It is also claimed that Joseph Smith had intimate relations with other men’s wives to whom he had been sealed, and that children resulted from these unions.
Critics of Joseph Smith have long had difficulty reconciling their concept of Joseph as a promiscuous womanizer with the fact that the only recorded children of the prophet are those that he had with Emma. Science is now shedding new light on this issue as DNA research has eliminated most of the possibilities that had long been rumored to be descendants of Joseph Smith. In the case of at least two, however, DNA cannot tell us either way. The historical reasoning for justifying that Joseph had children by these wives is dubious.
DNA analysis has determined that Josephine Fisher is not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr., [37] but for many years she appeared to be the strongest possibility. The resolution of this question was difficult to resolve until the appropriate DNA analysis techniques became available. These findings have been replicated in non-Latter-day Saint, peer-reviewed, reputable journals.[38]
The case of Josephine Fisher relied on a deathbed conversation:
Just prior to my mothers death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret from me and from all others but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith….[39]
Perhaps significantly, Josephine's name shares a clear link with Joseph's. Whether this account proved that she was his biological daughter had long been debated:
Rex Cooper…has questioned the interpretation that Smith was Fisher's biological father. He posits that because Fisher's mother was sealed to Smith, Fisher was his daughter only in a spiritual sense…More problematic is whether there is a discrepancy between what Fisher understood and what her mother meant. That is, did Fisher interpret her mother's remarks to mean she was the biological daughter of Joseph Smith and thus state that with more certitude than was warranted, when in fact her mother meant only that in the hereafter Fisher would belong to Joseph Smith's family through Session's sealing to him? Because Sessions was on her deathbed, when one's thoughts naturally turn to the hereafter, the latter is a reasonable explanation.[40]
As Danel Bachman notes, however, there seems to be relatively little doubt that
[t]he desire for secrecy as well as the delicacy of the situation assure us that Mrs. Sessions was not merely explaining to her daughter that she was Smith's child by virtue of a temple sealing. The plain inference arising from Jenson's curiosity in the matter and Mrs. Fisher's remarks is that she was, in fact, the offspring of Joseph Smith.[41]
However, DNA evidence now disproves this theory. It is possible, then, that Fisher misunderstood her mother, but this seems unlikely. Any unreliability is more likely to arise because of a dying woman's confusion than from miscommunication. No evidence exists for such confusion, though we cannot rule it out.
Josephine's account is also noteworthy because her mother emphasizes that "…she [had] been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon was out of fellowship with the Church."[42] This may explain her reasoning for being sealed to Joseph at all—her husband was out of fellowship. Todd Compton opines that "[i]t seems unlikely that Sylvia would deny [her husband] cohabitation rights after he was excommunicated," but this conclusion seems based on little but a gut reaction.[43] These women took their religion seriously; given Sylvia's deathbed remarks, this was a point she considered important enough to emphasize. She apparently believed it would provide an explanation for something that her daughter might have otherwise misunderstood.
There is also clear evidence that at least some early members of the Church would have taken a similar attitude toward sexual relations with an unbelieving spouse. My own third-great grandfather, Isaiah Moses Coombs, provides a striking illustration of this from the general membership of the Church.
Coombs had immigrated to Utah, but his non-member spouse refused to accompany him. Heartsick, he consulted Brigham Young for advice. Young "sat with one hand on my knee, looking at my face and listen[ing] attentively." Then, Young took the new arrival "by the hand in his fatherly way," and said "[Y]ou had better take a mission to the States…to preach the gospel and visit your wife…visit your wife as often as you please; preach the gospel to her, and if she is worth having she will come with you when you return to the valley. God bless and prosper you."[44]
Coombs did as instructed, but was not successful in persuading his wife. His description of his thoughts is intriguing, and worth quoting at length:
I may as well state here, however, that during all my stay in the States, [my wife and I] were nothing more to each other than friends. I never proposed or hinted for a closer intimacy only on condition of her baptism into the Church. I felt that I could not take her as a wife on any other terms and stand guiltless in the sight of God or my own conscience…I could not yield to her wishes and she would not bend to mine. And so I merely visited her as a friend. This was a source of wonder to our mutual acquaintances; and well it might be for had not my faith been founded on the eternal rock of Truth, I never could have stood such a test, I never could have withstood the temptations that assailed me, but I should have yielded and have abandoned myself to the life of carnal pleasure that awaited me in the arms of my beautiful and adored wife. She was now indeed beautiful. I had thought her lovely as a child—as a maiden she had seemed to me surpassing fair, but as a woman with a form well developed and all the charms of her persona matured, she far surpassed in womanly beauty anything I had ever dreamed of.[45]
Coombs' account is startlingly blunt and explicit for the age. Yet, if this young twenty-two-year-old male refused marital intimacy with his wife (whom he married knowing their religious differences), Compton's confidence that Sylvia Sessions would not deny marital relations to her excommunicated husband seems misplaced. Sessions may, like Coombs, have seen her faithfulness to the sealing ordinances sufficient to "eventually either in this life or that which is to come enable me to bind my [spouse] to me in bands that could not be broken." Like him, she may have believed that "[My spouse] was blind then but the day would come when [he] would see."[46]
More importantly, however, is Brian Hales’ more recent work, which demonstrates that Sylvia Sessions Lyon may well have not been married to her husband when sealed to Joseph Smith, contrary to Compton’s conclusion. Thus, rather than being a case of polyandry with sexual relations with two men (Joseph and her first husband) Lyons is instead a case of straight-forward plural marriage.[47] Given that Joseph has been ruled out as Josephine's father, it may be that Sylvia's emphasis to Josephine about being Joseph's "daughter" referred to a spiritual or sealing sense, and she wished to explain to her daughter why Josephine was, then, sealed to Joseph Smith rather than her biological father.
Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[48]
Angus M. Cannon seems to have been aware of Fisher's claim to be a child of Joseph Smith, though only second hand. He told a sceptical Joseph Smith III of
one case where it was said by the girl's grandmother that your father has a daughter born of a plural wife. The girl's grandmother was Mother Sessions, who lived in Nauvoo and died here in the valley. Aunt Patty Sessions asserts that the girl was born within the time after your father was said to have taken the mother.[49]
Clearly, Cannon has no independent knowledge of the case, but reports a story similar to Josephine's affidavit. Cannon's statement is more important because it illustrates how the LDS Church's insistence that Joseph Smith had practiced plural marriage led some of the RLDS Church :to ask why no children by these wives existed. Lucy Walker reported [the RLDS] seem surprised that there was no issue from asserted plural marriages with their father. Could they but realize the hazardous life he lived, after that revelation was given, they would comprehend the reason. He was harassed and hounded and lived in constant fear of being betrayed by those who ought to have been true to him.[50] Thus the absence of children was something of an embarrassment to the Utah Church, which members felt a need to explain. It would have been greatly to their advantage to produce Joseph's offspring, but could not.[51]
Anxious to demonstrate that Joseph's plural marriages were marriages in the fullest sense, Lucy M. Walker (wife of Joseph's cousin, George A. Smith) reported seeing Joseph washing blood from his hands in Nauvoo. When asked about the blood, Joseph reportedly told her he had been helping Emma deliver one of his plural wives' children.[52] Yet, even this late account tells us little about the paternity of the children—Joseph was close to these women (and their husbands, in the case of polyandry), and given the Saints' belief in priesthood blessings, they may have well welcomed his involvement.
Even by the turn of the century, the LDS Church had no solid evidence of children by Joseph. "I knew he had three children," said Mary Elizabeth Lightner, "They told me. I think two of them are living today but they are not known as his children as they go by other names."[53] Again, evidence for children is frustratingly vague—Lightner had only heard rumours, and could not provide any details. It would seem to me, however, that this remark of Lightner's rules out her children as possible offspring of Joseph. Her audience was clearly interested in Joseph having children, and she was happy to assert that such children existed. If her own children qualified, why did she not mention them?
Two of Marinda Nancy Johnson Hyde's children have been suggested as possible children. The first, Orson, died in infancy, making DNA testing impossible. Compton notes, however, that "Marinda had no children while Orson was on his mission to Jerusalem, then became pregnant soon after Orson returned home. (He arrived in Nauvoo on December 7, 1842, and Marinda bore Orson Washington Hyde on November 9, 1843),"[54] putting the conception date around 16 February 1843.
Frank Hyde's birth date is unclear; he was born on 23 January in either 1845 or 1846.[55] This would place his conception around 2 May, of either 1844 or 1845. In the former case, Frank was conceived less than two months prior to Joseph's martyrdom. Orson Hyde left for Washington, D.C., around 4 April 1844,[56] and did not return until 6 August 1844, making Joseph's paternity more likely than Orson's if the earlier birth date is correct.[57] The key source for this claim is Fawn Brodie, who includes no footnote or reference. Given Brodie's tendency to misread evidence on potential children, this claim should be approached with caution.
Frank's death certificate lists Orson Hyde as the father, however, and places his birth in 1846, which would require conception nearly a year after Joseph's death.[58] A child by Joseph would have brought prestige to the family and Church, and Orson and Nancy had divorced long before Frank Henry's death.[59] It seems unlikely, therefore, that Orson would be credited with paternity over Joseph if any doubt existed. Without further data, Brodie's dating should probably be regarded as an error, ruling out Joseph as a possible father.
Scientific ingenuity has also been applied to the question of Joseph's paternity. Y-chromosome studies have conclusively eliminated Orrison Smith (son of Fanny Alger), Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, John Reed Hancock, Moroni Llewellyn Pratt, and Oliver Buell as Joseph's offspring.[60]
Two additional children—George Algernon Lightner and Orson W. Hyde—died in infancy, leaving no descendants to test, though as noted above Lightner can probably be excluded on the basis of his mother's testimony.
The testing of female descendants' DNA is much move involved, but work continues and may provide the only definitive means of ruling in or out potential children.
The case of Oliver Buell is an interesting one, since Fawn Brodie was insistent that he was Joseph's son. She based part of this argument on a photograph of Buell, which revealed a face which she claimed was "overwhelmingly on the side of Joseph's paternity."[61] A conception on this date would make Oliver two to three weeks overdue at birth, which makes Brodie's theory less plausible.[62]
Furthermore, prior the DNA results, Bachman and Compton pointed out that Brodie's timeline poses serious problems for her theory—Oliver's conception would have had to occurred between 16 April 1839 (when Joseph was allowed to escape during a transfer from Liberty Jail)[63] and 18 April, when the Huntingtons left Far West.[64] Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois to the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack, while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order in force.[65] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun's Mill, along Shoal Creek.[66] Yet, by 22 April Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by travel "off from the main road as much as possible"[67] "both by night and by day."[68] This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be meeting a woman, much less conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other Church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the prophet’s direction, who did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois.[69]
Brodie's inclusion of Oliver Buell is also inconsistent, since he was born prior to Joseph's sealing to Prescinda. By including Oliver as a child, Brodie wishes to paint Joseph as an indiscriminate womanizer. Yet, her theory of plural marriage argues that Joseph "had too much of the Puritan in him, and he could not rest until he had redefined the nature of sin and erected a stupendous theological edifice to support his new theories on marriage."[70] Thus, Brodie argues that Joseph created plural marriage to justify his immorality—yet, she then has him conceiving a child with Prescinda before being sealed to her. By her own argument, the paternity must therefore be seen as doubtful.[71]
Despite Brodie's enthusiasm, no other author has included Oliver on their list of possible children (see Table 1). And, DNA evidence has conclusively ruled him out. Oliver is an excellent example of Brodie's tendency to ignore and misread evidence which did not fit her preconceptions, and suggests that caution is warranted before one condemns Joseph for a pre-plural marriage "affair" or other improprieties. Since Brodie was not interested in giving Joseph the benefit of the doubt, or avoiding a rush to judgment, her decision is not surprising.
John Reed Hancock is another of Brodie's suggestions, though no other author has followed her. The evidence for Joseph having married Clarissa Reed Hancock is scant,[72] and as with Oliver Buell it is unlikely (even under Brodie's jaded theory of plural marriage as justification for adultery) that Joseph would have conceived a child with a woman to whom he was not polygamously married. DNA testing has since confirmed our justified scepticism of Brodie's claim.[73]
Bachman mentions a "seventh child" of Prescinda's, likely John Hyrum Buell, for whom the timeline would better accommodate conception by Joseph Smith. There is no other evidence for Joseph's paternity, however, save Ettie V. Smith's account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years Among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Prescinda said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hyrum's father.[74] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[75]
Besides being implausible, Ettie gets virtually every other detail wrong—she insists that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions, only to return and find their wives being courted by Joseph. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[76] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions, and their wives did not charge that Joseph had propositioned them. Jacobs had served missions, but was present during Joseph's sealing to his wife, and did not object (see Chapter 9). Jacobs was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[77] and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[78] as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[79]
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hyrum as a potential child (and carelessly misreads Ettie Smith's remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hyrum). No other historian has even mentioned this child, much less argued that Buell was not the father (see Table 1).
A few other possibilities should be mentioned, though the evidence surrounding them is tenuous. Sarah Elizabeth Holmes was born to Marietta Carter, though "No evidence links her with Joseph Smith."[80] The Dibble children suffer from chronology problems, and a lack of good evidence that Joseph and their mother was associated. Loren Dibble was, however, claimed by some Mormons as a child of Joseph’s when confronted with Joseph Smith III’s skepticism.[81]
Joseph Albert Smith was born to Esther Dutcher, but the available evidence supports her polyandrous sealing to Joseph as for eternity only. Carolyn Delight has no evidence at all of a connection to Joseph—the only source is a claim to Ugo Perego, a modern DNA researcher.[82] No textual or documentary evidence is known for her at all.
We have elsewhere seen the tenuous basis for many conclusions about the Fanny Alger marriage (see here and here). The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[83] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
A family tradition—repeated by anti-Mormon Wyl—holds that Eliza R. Snow was pregnant and shoved down the stairs by a jealous Emma before being required to leave the Smith home.[84] The tradition holds that Eliza, "heavy with child" subsequently miscarried. While Eliza was required to leave the home and Emma was likely upset with her, no contemporary evidence points to a pregnancy.[85] Eliza's diary says nothing about the loss of a child, which would be a strange omission given her love of children.[86] It seems unlikely that Eliza would have still been teaching school in an advanced state of pregnancy, especially given that her appearance as a pregnant "unwed mother" would have been scandalous in Nauvoo. Emma's biographers note that "Eliza continued to teach school for a month after her abrupt departure from the Smith household. Her own class attendance record shows that she did not miss a day during the months she taught the Smith children, which would be unlikely had she suffered a miscarriage."[87] Given Emma's treatment of the Partridge sisters, who were also required to leave the Smith household, Emma certainly needed no pregnancy to raise her ire against Joseph's plural wives.
Eliza repeatedly testified to the physical nature of her relationship with Joseph Smith (see Chapter 9), and was not shy about criticizing Emma on the subject of plural marriage.[88] Yet, she never reported having been pregnant, or used her failed pregnancy as evidence for the reality of plural marriage.
In the absence of further information, both of these reported pregnancies must be regarded as extremely speculative.
Sylvia was married to Windsor Lyon by Joseph Smith in Nauvoo. She was sealed to Joseph Smith at some point after she was married. Brian Hales notes that , "This marriage triangle is unique among all of the Prophet’s plural marriages because there is strong evidence that Sylvia bore children to both men. She became pregnant by Windsor Lyon in October of 1838, September of 1840, and April of 1842. Then a year later became pregnant with a daughter (named Josephine—born February 8, 1844) that was purportedly fathered by the Prophet." Sylvia's daughter, who had the intriguing name "Josephine," made the following statement:
Just prior to my mothers [Sylvia Sessions Lyon] death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days on earth were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret fro me and from others until no but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith, she having been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon had was out of fellowship with the Church.
For many years, Josephine appeared to be the only viable candidate as a child of Joseph Smiths "polyandrous" sealings. However, DNA analysis ultimately disproved the paternity claim: Josephine was not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr.[89]
It appears, however, that Sylvia may have considered herself divorced from Windsor after he was excommunicated from the Church and left Nauvoo. Hales points out that "Currently, no documentation of a legal divorce between Windsor and Sylvia after his excommunication has been found. However, in the mid-nineteenth century, religious laws often trumped legal proceedings. Stanley B. Kimball observed: 'Some church leaders at that time considered civil marriage by non-Mormon clergymen to be as unbinding as their baptisms. Some previous marriages . . . were annulled simply by ignoring them.'" [90] The sealing to Joseph occurred after Windor's excommunication. Andrew Jenson, in his historical record, referred to Sylvia as a "formerly the wife of Windsor Lyons." [91] There is no known evidence that Windsor lived with Sylvia after he returned to Nauvoo, but Sylvia did "rejoin" Windsor after he was rebaptised in 1846. Hales states, "No details are available to clarify what authority was used to reconfirm the marriage relationship between Sylvia and Windsor after their previous marital separation. Most likely the couple consulted with Brigham Young or Heber C. Kimball, who authorized their rejoining. Whether a private religious marriage ceremony for time was performed or the couple resumed observing their legal marriage is unknown. Importantly, even with the renewed conjugality between Windsor and Sylvia after Joseph Smith’s death, no evidence has been found to support her involvement in sexual polyandry at any time." [92]
It is claimed that Prescindia Lathrop Huntington Buell admitted that she did not know who was the father of her child—Joseph Smith or her first husband. Sometimes Sarah Pratt (wife of apostle Orson Pratt) is mistakenly identified as the woman in this story. [93] Others sometimes mention Orson Hyde's wife as the source of this rumor. [94]
The source for this claim is a notoriously unreliable anti-Mormon work. It makes several errors of fact in the very paragraph in which the claim is made.
It is implausible that the supposed admission upon which the claim is based would be made. There are major historical problems of geography and timeline for Joseph to have even been a potential father of Buell's child.
The claim cannot be substantiated.
This book was written by Nelson Winch Green, who reported what estranged member Marry Ettie V. Coray Smith reportedly told him.
Even other anti-Mormon authors who had lived in Utah regarded it as nearly worthless. Fanny Stenhouse wrote:
Much has already been written on this subject much that is in accordance with facts, and much that is exaggerated and false. Hitherto, with but one exception [Mrs. Ettie V. Smith is noted in the footnote as the work referred to] that of a lady who wrote very many years ago, and who in her writings, so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where the one ended and the other began no woman who really was a Mormon and lived in Polygamy ever wrote the history of her own personal experience. Books have been published, and narratives have appeared in the magazines and journals, purporting to be written by Mormon wives; it is, however, perhaps, unnecessary for me to state that, notwithstanding such narratives may be imposed upon the Gentile world as genuine, that they were written by persons outside the Mormon faith would in a moment be detected by any intelligent Saint who took the trouble to peruse them. [95]
So, we must remember that this work is not regarded as generally reliable today, and it was not regarded as reliable even by the Church's enemies in the 19th century.
The source for this claim is an anti-Mormon book. The relevant passage reads:
The Prophet had sent some time before this, three men, Law, Foster and Jacobs, on missions, and they had just returned, and found their wives blushing under the prospective honors of spiritual wifeism; and another woman, Mrs. Buel [sic], had left her husband, a Gentile, to grace the Prophet's retinue, on horseback, when he reviewed the Nauvoo Legion. I heard the latter woman say afterwards in Utah, that she did not know whether Mr. Buel [sic] or the Prophet was the father of her son. These men [Law, Foster and Jacobs] established a press in Nauvoo, to expose his alleged vicious teachings and practices, which a revelation from Joseph destroyed. [96]
As might be expected, then, there are many claims in this passage that are in error. We know that the following are false:
Thus, in the single paragraph we have several basic errors of fact. Why should we believe the gossip of what Mrs. Buell is claimed to have said?
Furthermore, such an admission would be out of character for a believing Utah woman of the 19th century. As Todd Compton notes:
Talk of sexuality was avoided by the Victorian, puritanical Mormons; in diaries, the word 'pregnant' or 'expecting' is never or rarely used. Women are merely 'sick' until they have a child. Polyandry was rarely discussed openly by Mormon women. [97]
Fawn Brodie painted a fanciful scenario in which Joseph would have been able to potentially father a Buell child. However, she misread the historical information, and it is difficult, as Todd Compton has demonstrated, for Joseph to have even had contact with her at the proper time to conceive a child. [98] This would suggest that there were no grounds for Mrs. Buell—or a modern reader—to conclude that Joseph might have been the father.
Nauvoo Polygamy author George D. Smith tells his readers that "until decisive DNA testing of possible [Joseph] Smith descendants—daughters as well as sons—from plural wives can be accomplished, ascertaining whether Smith fathered children with any of his plural wives remains hypothetical" (pp. 228–29, cf. p. 473). This is true, but G. D. Smith fails to tell us that all those who have been definitively tested so far—Oliver Buell, Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, Moroni Pratt, and Orrison Smith—have been excluded. Would he have neglected, I wonder, to mention a positive DNA test?
The consequences of George D. Smith's less-than-rigorous approach to sources becomes clear in the case of Oliver Buell, son of Presendia.[99] Huntington Buell, one of Joseph’s polyandrous plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to suggest that Oliver Buell was Joseph’s son, and she was so convinced (based on photographic evidence)[100]Fawn Brodie to Dale Morgan, Letter, 24 March 1945, Dale Morgan papers, Marriott Library, University of Utah; cited by Todd Compton, "Fawn Brodie on Joseph Smith's Plural Wives and Polygamy: A Critical View," in Reconsidering No Man Knows My History: Fawn M. Brodie and Joseph Smith in Retrospect, ed. Newell G. Bringhurst (Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press, 1996), 166.</ref> In a footnote, G. D. Smith notes that Todd Compton "considers it improbable that Joseph and Presendia would have found time together during the brief window of opportunity after his release from prison in Missouri" (p. 80 n. 63).[101]
This slight nod toward an opposite point of view is inadequate, however. G. D. Smith does not mention and hence does not confront the strongest evidence. Compton’s argument against Joseph’s paternity does not rest just on a "narrow window" of opportunity but on the fact that Brodie seriously misread the geography required by that window. It is not merely a question of dates. Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois toward the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order.[102] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun’s Mill, along Shoal Creek.[103] Yet by April 22 Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by traveling "off from the main road as much as possible"[104]:320-321 "both by night and by day."[104]:327 This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the Prophet’s direction. Joseph did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois, contrary to Brodie’s misreading.[104]:315, 319, 322-23, 327 Timing is the least of the problems with G. D. Smith’s theory.
Despite Brodie’s enthusiasm, few other authors have included Oliver on their list of possible children.[105] With so many authors ranged against him, G. D. Smith ought not to act as if Compton’s analysis is merely about dates.
G. D. Smith also soft-pedals the most vital evidence—the DNA.[106] He makes no mention in the main text that Oliver’s paternity has been definitively ruled out by DNA testing. This admission is confined to a footnote, and its impact is minimized by its placement. After noting Compton’s disagreement with the main text’s suggestion that Oliver might be Joseph’s son, G. D. Smith writes, "There is no DNA connection," and cites a Deseret News article. He immediately follows this obtuse phrasing with a return to Compton, who finds it "‘unlikely, though not impossible, that Joseph Smith was the actual father of another Buell child,’ John Hiram, Presendia’s seventh child during her marriage to Buell and born in November 1843" (p. 80 n. 63). Thus the most salient fact—that Joseph is certainly not Oliver's father—is sandwiched between a vicarious discussion with Compton about whether Oliver or John could be Joseph’s sons. Since G. D. Smith knows there is definitive evidence against Joseph’s paternity in Oliver’s case, why mention the debate at all only to hide the answer in the midst of a long endnote? That Brodie is so resoundingly rebutted on textual, historical, and genetic grounds provides a cautionary lesson in presuming that her certainty counts for much.[107]
Two pages later, G. D. Smith again tells us of a Buell child being sealed to a proxy for Joseph with "wording [that] hints that it might have been Smith’s child." "It is not clear," he tells us, "which of her children it might have been" (p. 82). In fact, what is clear is that he has not assimilated the implications of the DNA data. John Hiram, the seventh child about whom Compton is skeptical, is the only other option. Yet the only evidence for this child belonging to Joseph is Ettie V. Smith’s account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Presendia said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hiram’s father.[108] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[109]
Besides being implausible, Ettie’s account gets virtually every other detail wrong—insisting that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions only to return to find Joseph preaching plural marriage. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[110] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions. Jacobs had served missions but was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor. He was also, contrary to Ettie’s claims, present when Joseph was sealed polyandrously to his (Jacobs’s) wife.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[111]:618 and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[111]:x as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[111]:xi-xii
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hiram as a potential child, going so far as to carelessly misread Ettie Smith’s remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hiram. No other historian has argued that Buell was not the father.[112] There is no good evidence whatever that any of Presendia’s children were Joseph’s. It is not clear why G. D. Smith clings to the idea.
Few authors agree on which children should even be considered as Joseph's potential children. Candidates which some find overwhelmingly likely are dismissed—or even left unmentioned—by others. Recent scholars have included between one to four potential children as options. Of these, Josephine Lyon was the most persuasive, until her relationship to Joseph Smith was ultimately disproven through DNA testing. Orson W. Hyde died in infancy, and so can never be definitively excluded as a possible child, though the dates of conception argue against Joseph's paternity. Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[113]
This table is in the same order as Table 1.
Notation:
Brodie;[114] Bachman;[115]; and Compton.[116]
As always, we are left where we began—with more suspicions and possibilities than certitudes. One's attitude toward Joseph and the Saints will influence, more than anything else, how these conflicting data are interpreted.
The uncertainty surrounding Joseph's offspring is even more astonishing when we appreciate how much such a child would have been valued. The Utah Church of the 19th century was anxious to prove that Joseph had practiced full plural marriage, and that their plural families merely continued what he started. Any child of Joseph's would have been treasured, and the family honoured. There was a firm expectation that even Joseph's sons by Emma would have an exalted place in the LDS hierarchy if they were to repent and return to the Church.[117] As Alma Allred noted, "Susa Young Gates indicated that [Brigham Young] wasn’t aware of such a child when she wrote that her father and the other apostles were especially grieved that Joseph did not have any issue in the Church."[118]
In 1884, George Q. Cannon bemoaned this lack of Joseph's posterity:
There may be faithful men who will have unfaithful sons, who may not be as faithful as they might be; but faithful posterity will come, just as I believe it will be the case with the Prophet Joseph's seed. To-day he has not a soul descended from him personally, in this Church. There is not a man bearing the Holy Priesthood, to stand before our God in the Church that Joseph was the means in the hands of God, of founding—not a man to-day of his own blood,—that is, by descent,—to stand before the Lord, and represent him among these Latter-day Saints.[119]
Brigham and Cannon, a member of the First Presidency, would have known of Joseph's offspring if any of the LDS leadership did. Yet, despite the religious and public relations value which such a child would have provided, they knew of none. It is possible that Joseph had children by his plural wives, but by no means certain. The data are surprisingly ephemeral.
Doctrine and Covenants 132꞉63 states,
But if one or either of the ten virgins, after she is espoused, shall be with another man, she has committed adultery, and shall be destroyed; for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men; for herein is the work of my Father continued, that he may be glorified.
Polygamy was not permitted only for the purpose of procreation. Joseph established the practice of plural marriage as part of the "restoration of all things," (D&C 132: 40, 45) and introduced it to a number of others within the Church. This alone may have been the purpose of Joseph's initiation of the practice. The establishment of the practice ultimately did have the effect of "raising up seed"...just not through Joseph Smith.
As Brian Hales writes:
Joseph Smith dictated what is now Doctrine and Covenant section 132 on July 12, 1843. This revelation, along with his other statements, provide several reasons why he believed plural marriage could be introduced among the Latter-day Saints.The earliest justification mentioned by the Prophet was as a part of the "restitution of all things" prophesied in Acts 3:19–21. Old Testament prophets practiced polygamy, so it could be a part of the restoration of "all things" (see D&C 132:40, 45).
Several members who knew Joseph Smith left accounts of him referring to a connection between the two during the Kirtland period.
Benjamin F. Johnson recalled in 1903: "In 1835 at Kirtland I learned from my Sisters Husband, Lyman R. Shirman,[120] who was close to the Prophet, and Received it from him. That the ancient order of plural marriage was again to be practiced by the Church."[121]
A few years later in 1841, Joseph Smith attempted to broach the topic publicly. Helen Mar Kimball remembered: "He [Joseph] astonished his hearers by preaching on the restoration of all things, and said that as it was anciently with Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, so it would be again, etc."[122] Joseph Smith was a prophet-restorer, which helps to explain why the command to practice plural marriage has been labeled a "restoration," even though it is not a salvific ordinance.[123]
Brian Hales addresses one aspect of D&C 132 that may be overlooked in casual readings:
The fourth reason Joseph Smith gave for the practice of plural marriage dwarfs the other three explanations in significance because it deals with eternity. The message of D&C 132:16–17 states that men and women who are not sealed in eternal marriages during this life (or vicariously later) "remain separately and singly, without exaltation, in their saved condition, to all eternity."In other words, "exaltation," the highest salvation, requires eternal marriage. No unmarried person can be exalted according to Joseph Smith’s teachings. Doctrine and Covenants section 132 seems to anticipate more worthy women than men as it approves a plurality of wives[124] and disallows a plurality of husbands.[125] Verse 63 states that a plurality of wives is "for their [the wives] exaltation in the eternal worlds." Section 132 supports that eternity was the primary focus of the Joseph’s marriage theology rather than plurality or sexuality. Eternal, rather than plural, marriage was his zenith doctrine. It appears that the crucial objective of polygamy on earth was to allow all worthy women to be eternally sealed to a husband and thus obtain all the ordinances needed for exaltation. According to these teachings, a plurality of wives in some form may be practiced in eternity, but not by all worthy men and women. We know that polygamy on earth is unequal and difficult, but we know nothing about how eternal marriage or eternal plural marriage might feel in eternity. Brigham Young acknowledged that eternal marriage (not plural marriage) is "the thread which runs from the beginning to the end" in God’s plan for His children:
The whole subject of the marriage [not plural marriage] relation is not in my reach, nor in any other man’s reach on this earth. It is without beginning of days or end of years; it is a hard matter to reach. We can tell some things with regard to it; it lays the foundation for worlds, for angels, and for the Gods; for intelligent beings to be crowned with glory, immortality, and eternal lives. In fact, it is the thread which runs from the beginning to the end of the holy Gospel of salvation—of the Gospel of the Son of God; it is from eternity to eternity.[126][127]
Another author commenting on this verse made a compelling case for this theology being put into D&C 132: 63:
Here is the text in its entirety, from verse 62: "for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men." [Emphasis added.] You want to get legalistic? Let’s get legalistic. Just for fun, let’s parse the living snot out of this.This clause begins with multiplying and replenishing as a primary justification. Then we get the word "and" thrown in there. You’re reading this as if it says "they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, in order to fulfil the promise…" But that’s not what it says.
"And" suggests we’re about to get a second reason, not a clarification of the first. In fact, a tight, strict-constructionist reading of this verse reveals three different and distinct reasons for plural marriage, not "only" the replenishment of the earth, [. . .]So let’s review the three reasons:
1. Multiply and replenish the earth.
[. . .] D&C 132 is unequivocal on this point, just as it is unequivocal on the two points that follow.
2. Fulfil [sic] "the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world."
What promise? This seems to have reference to the "restitution of all things, which God hath spoken by the mouth of all his holy prophets since the world began." (Acts 3:21) Joseph cited the need to restore ancient practices to prepare for the Second Coming as a justification for polygamy, and this verse provides a credible scriptural context for him to do so. So just relying on this phrase – plural marriage is acceptable because it fulfills God’s promises – would be justification enough for the practice, at least according to D&C 132.
3. For "their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men."
Oh, this one’s my favorite. Notice the emphasis I added on the "that." The word appears there to create a conditional clause. You claim the bearing of souls is the same thing as multiplying and replenishing the earth, but the actual text insists that the bearing of the souls of men will only be made possible by "exaltation in the eternal worlds." This is a promise of eternal increase, of bearing souls after the earth is no longer around to be replenished. Big, big difference.
And right here, with Reason #3, we have a clear rationale and justification for Joseph being sealed to women with whom he made no attempts to multiply and replenish the earth – i.e. no sex.[128]
Both modern and 19th century members of the Church have proposed a variety of explanations for the practice of plural marriage. Not all of these suggestions can be supported by the available data. |
|
Joseph identified four reasons for the restoration of plural marriage. |
|
Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. |
|
Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. |
Some wonder if sexual relations were included in Joseph Smith’s plural marriages. The answer is yes or no, depending upon the type of plural marriage. Those marriages, often called “sealings,” were of two types. Some were for this life and the next (called “time-and-eternity”) and could include sexuality on earth. Others were limited to the next life (called “eternity-only”) and did not allow intimacy in mortality. Overall, evidence indicates that less than half of Joseph Smith’s polygamous unions were consummated and sexual relations in the others occurred infrequently. |
|
It appears the Prophet experienced sexual relations with less than half of the women sealed to him. There is no credible evidence that Joseph had sex with three subgroups of his plural wives: (1) fourteen-year-old wives, (2) non-wives (or women to whom he was not married), and (3) legally married women who were experiencing conjugal relations with their civil husbands. |
|
No children are known to have been born to Joseph and his plural wives. |
Notes
Sarah Ann Whitney's marriage to Joseph Smith was unusual in that, at some point after the marriage, Joseph actually requested that Joseph C. Kingsbury marry her civilly in order to allay any suspicions regarding their plural marriage. This marriage, however, was a "pretend" marriage according to Kingsbury,
[I] was imployed in Joseph Smith’s Store under the direction of Bishop Newel K Whitney untill the fall of 1842 and on the 16th day Oct Caroline my Wife Died. . . . how thankfull I feal thinking I shall see & meat her again to enjoy each other society for ever to part no more & also my little sons . . . and on the 29th of April 1843 I according to President Joseph Smith council & others agreed to stand by Sarah \Ann/ Whitney as supposed to be her husband & had a pretended marriage for the purpose of bringing about the purposes of bringing about the purposes of God in the last days as spoken by the mouth of the prophet Isiah Jeremiah Ezekiel and also Joseph Smith, & Sarah Ann should rec-d a great glory Honner & Eternal Lives and I Also Should Rec-d a Great Glory Honner & Eternal Lives to the full desire of my heart in having my companion Caroline in the first resurrection to hail her & no one to have power to take her from me & we Both shall be crowned & enthroned togeather in the Celestial Kingdom of God Enjoying Each others Society in all of the fullness of the Gospel of Jesus Christ & our little ones with us as is Recorded in this blessing that President Joseph Smith Sealed upon my head on the Twenty third day of March 1843 as follows. [1]
Sarah Ann and Joseph Kingsbury acted the part of husband and wife publicly, but apparently never consummated the marriage. Sarah married Heber C. Kimabll for time, not eternally, after Joseph's death and had seven children. According to Brian Hales, Joseph Kingsbury later billed the church for his services of acting as "front husband" for one of Joseph's plural wives. [2]
Mary Heron was married to John Snider, who was an active member of the Church. Very little information is available regarding her sealing to Joseph. Brian Hales notes that, "John was never sealed to Mary during their lifetimes, even though a proxy sealing after her death would have been possible. Curiously, John waited until two weeks after Mary’s passing away to obtain his own temple endowments. Perhaps the timing of John Snider’s first temple visit was coincidental, or possibly a sealing between Mary and Joseph Smith had created an awkward situation while they were both living." [3]
The following is from a love letter Joseph Smith wrote when he wanted to arrange a liaison with Newel K. Whitney's daughter Sarah Ann, whom Smith had secretly married without Emma's knowledge three weeks prior to this time.
Critics of the Church would have us believe that this is a private, secret "love letter" from Joseph to Sarah Ann, however, Joseph wrote this letter to the Whitney's, addressing it to Sarah's parents. The "matter" to which he refers is likely the administration of ordinances rather than the arrangement of some sort of private tryst with one of his plural wives. Why would one invite your bride's parents to such an encounter? Joseph doesn't want Emma gone because he wants to be alone with Sarah Ann—a feat that would be difficult to accomplish with her parents there—he wants Emma gone either because she is opposed to plural marriage (the contention that would result from an encounter between Emma and the Whitney's just a few weeks after Joseph's sealing to Sarah Ann would hardly be conducive to having the spirit present in order to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads"), or because she may have been followed or spied upon by Joseph's enemies, putting either Joseph or the Whitneys in danger.
On the 16th of August, 1842, while Joseph was in hiding at the Sayer's, Emma expressed concern for Joseph's safety. She sent a letter to Joseph in which she noted,
There are more ways than one to take care of you, and I believe that you can still direct in your business concerns if we are all of us prudent in the matter. If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph wrote the next day in his journal,
Several rumors were afloat in the city, intimating that my retreat had been discovered, and that it was no longer safe for me to remain at Brother Sayers'; consequently Emma came to see me at night, and informed me of the report. It was considered wisdom that I should remove immediately, and accordingly I departed in company with Emma and Brother Derby, and went to Carlos Granger's, who lived in the north-east part of the city. Here we were kindly received and well treated." (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, pp. 117-118)
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney, and &c." Scholars agree that the third person referred to was the Whitney's daughter Sarah Ann, to whom Joseph had been sealed in a plural marriage, without Emma's knowledge, three weeks prior. The full letter, with photographs of the original document, was published by Michael Marquardt in 1973,[4] and again in 1984 by Dean C. Jessee in The Personal Writings of Joseph Smith.[5] The complete text of the letter reads as follows (original spelling has been retained):
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
Some critics point to this letter as evidence the Joseph wrote a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann, requesting that she visit him while he was in seclusion. Others believe that the letter was a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring their daughter to him so that he could obtain "comfort," with the implication that "comfort" involved intimate relations.
Did Joseph Smith write a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann Whitney? Was this letter a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring her to Joseph? Was Joseph trying to keep Sarah Ann and Emma from encountering one another? Certain sentences extracted from the letter might lead one to believe one or all of these things. Critics use this to their advantage by extracting only the portions of the letter which support the conclusions above. We present here four examples of how the text of the letter has been employed by critics in order to support their position that Joseph was asking the Whitney's to bring Sarah Ann over for an intimate encounter. The text of the full letter is then examined again in light of these treatments.
Consider the following excerpt from a website that is critical of the Church. Portions of the Whitney letter are extracted and presented in the following manner:
... the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty. ... Only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater friendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I will tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. ... I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont, dont fail to come to night, I subscribe myself your most obedient, and affectionate, companion, and friend. Joseph Smith.
—’’Rethinking Mormonism’’, "Did Joseph Smith have sex with his wives?" (Web page)
This certainly has all of the elements of a secret "love letter:" The statement that it would not be safe if Emma were there, the request to "burn this letter as soon as you read it," and the stealthy instructions for approaching the house. The question is, who was this letter addressed to? The critics on their web site clearly want you to believe that this was a private letter to Sarah Ann.
Here is the way that Van Wagoner presents selected excerpts of the same letter. In this case, at least, he acknowledges that the letter was addressed to "the Whitney’s," rather than Sarah, but adds his own opinion that it "detailed [Joseph’s] problems in getting to see Sarah Ann without Emma's knowledge:"
My feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us ... if you three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me, now is the time to Afford me succor ... the only thing to be careful is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safety.
—Richard S. Van Wagoner, Mormon Polygamy: A History, 48.
This version, presented by George D. Smith, presents excerpts from the letter which makes it sound like Joseph was absolutely lusting for the company of Sarah Ann. Smith even makes Napoleon Bonaparte a Joseph Smith doppelgänger by quoting a letter from the future Emperor to Josephine of their first night together:
"I have awakened full of you. The memory of last night has given my senses no rest. . . . What an effect you have on my heart! I send you thousands of kisses—but don’t kiss me. Your kisses sear my blood" (p. xi). George Smith then claims that a "young man of ambition and vision penned his own letter of affection to a young woman. It was the summer of 1842 when thirty-six-year-old Joseph Smith, hiding from the law down by the Mississippi River in Illinois, confessed:"
Smith then compares the excerpts from Napoleon's letter above to portions of the Whitney letter:
My feelings are so strong for you . . . come and see me in this my lonely retreat . . . now is the time to afford me succour . . . I have a room intirely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect saf[e]ty, I know it is the will of God that you should comfort me.
—George D. Smith, "Nauvoo Polygamy: We Called It Celestial Marriage," Free Inquiry [Council for Secular Humanism] 28/3 (April–May 2008): 44–46.
Finally, we have a version which acknowledges the full contents of the letter...but only after presenting it in the manner described above numerous times. The author eventually provides the full text of this letter (150 pages after its comparison with Napoleon). Since there are no extant "love letters" from Joseph Smith to any of his plural wives, the mileage that the author of Nauvoo Polygamy..."but we called it celestial marriage" extracts from the single letter to the Whitney's is simply astounding:
- "[i]t was eleven years after the Smiths roomed with the Whitneys that Joseph expressed a romantic interest in their daughter, as well." (p. 31)
- "recommended his friend, whose seventeen-year-old daughter he had just married, should 'come a little a head, and nock…at the window.'" (p. 53)
- "Emma Hale, Joseph's wife of fifteen years, had left his side just twenty-four hours earlier. Now Joseph declared that he was "lonesome," and he pleaded with Sarah Ann to visit him under cover of darkness. After all, they had been married just three weeks earlier. (p. 53)
- "As will be seen, conjugal visits appear furtive and constantly shadowed by the threat of disclosure." (p. 63)
- "when Joseph requested that Sarah Ann Whitney visit him and ‘nock at the window,’ he reassured his new young wife that Emma would not be there, telegraphing his fear of discovery if Emma happened upon his trysts." (p. 65)
- "Three weeks after the wedding, Joseph took steps to spend some time with his newest bride." (p. 138)
- "It was the ninth night of Joseph's concealment, and Emma had visited him three times, written him several letters, and penned at least one letter on his behalf…For his part, Joseph's private note about his love for Emma was so endearing it found its way into the official church history. In it, he vowed to be hers 'forevermore.' Yet within this context of reassurance and intimacy, a few hours later the same day, even while Joseph was still in grave danger and when secrecy was of the utmost urgency, he made complicated arrangements for a visit from his fifteenth plural wife, Sarah Ann Whitney." (p. 142)
- "Smith urged his seventeen-year-old bride to 'come to night' and 'comfort' him—but only if Emma had not returned….Joseph judiciously addressed the letter to 'Brother, and Sister, Whitney, and &c." (p. 142-143)
- "Invites Whitneys to visit, Sarah Ann to 'comfort me' if Emma not there. Invitation accepted." (p.. 147)
- "As if Sarah Ann Whitney's liaison were not enough…another marriage took place…." (p. 155)
- "summer 1842 call for an intimate visit from Sarah Ann Whitney…substantiate[s] the intimate relationships he was involved in during those two years." (p. 185)
- "his warning to Sarah Ann to proceed carefully in order to make sure Emma would not find them in their hiding place." (p. 236)
- "Just as Joseph sought comfort from Sarah Ann the day Emma departed from his hideout…." (p. 236)
- "Elizabeth [Whitney] was arranging conjugal visits between her daughter, Sarah Ann, and [Joseph]…." (p. 366)
One must assume that this is the closest thing that the author could find to a love letter, because the "real" love letters from Joseph to his plural wives do not exist. The author had to make do with this one, despite the fact that it did not precisely fit the bill. With judicious pruning, however, it can be made to sound sufficiently salacious to suit the purpose at hand: to "prove" that Joseph lusted after women.
In contrast to the sources above, Compton actually provides the complete text of the letter up front, and concludes that "[t]he Mormon leader is putting the Whitney's in the difficult position of having to learn about Emma's movements, avoid her, then meet secretly with him" and that the "cloak-and-dagger atmosphere in this letter is typical of Nauvoo polygamy." [6]
As always, it is helpful to view the entire set of statements in content. Let's revisit the entire letter, this time with the selections extracted by the critics highlighted:
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
So, let’s take a look at the portions of the letter that are not highlighted.
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney." Sarah Ann is not mentioned by name, but is included as "&c.," which is the equivalent of saying "and so on," or "etc." This hardly implies that what follows is a private "love letter" to Sarah Ann herself.
Could this have been an appeal to Sarah's parents to bring her to Joseph? In Todd Compton's opinion, Joseph "cautiously avoids writing Sarah's name." [7] However, Joseph stated in the letter who he wanted to talk to:
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams;
Joseph wants to talk to "you three," meaning Newel, Elizabeth and Sarah Ann.
Interestingly enough, the one portion of the letter in which Joseph actually gives a reason for this meeting is often excluded by critics:
..one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me...
According to Richard L. Bushman, this may have been "a reference perhaps to the sealing of Newel and Elizabeth in eternal marriage three days later." [8] Compton adds, "This was not just a meeting of husband and plural wife, it was a meeting with Sarah's family, with a religious aspect.[9]
In addition to the stated purpose of the meeting, Joseph "may have been a lonely man who needed people around him every moment." [10] Consider this phrase (included in Van Wagoner's treatment, but excluded by the others):
...it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am al[l]ied, do love me, now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile. (emphasis added)
These are not the words of a man asking his secret lover to meet him for a private tryst—they are the words of a man who wants the company of friends.
So, what about Emma? The letter certainly contains dire warnings about having the Whitney's avoid an encounter with Emma. We examine several possible reasons for the warning about Emma. Keep in mind Emma's stated concern just two days prior,
If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph had been sealed to Sarah Ann three weeks before without Emma's knowledge.[11] Joseph may have wished to offer a sealing blessing to Newel and Elizabeth Whitney at this time. Given Joseph's indication to the Whitneys that he wished to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads," and the fact that Emma herself was not sealed until she consented to the doctrine of plural marriage nine months later, Joseph may have felt that Emma’s presence would create an uncomfortable situation for all involved—particularly if she became aware of his sealing to Sarah Ann.
If Joseph was in hiding, he had good reason to avoid being found (hence the request to burn the letter that disclosed his location). He would also not want his friends present in case he were to be found. Anyone that was searching for Joseph knew that Emma could lead them to him if they simply observed and followed her. If this were the case, the most dangerous time for the Whitney's to visit Joseph may have been when Emma was there—not necessarily because Emma would have been angered by finding Sarah Ann (after all, Emma did not know about the sealing, and she would have found all three Whitney's there—not just Sarah Ann), but because hostile men might have found the Whitney's with Joseph. Note that Joseph's letter states that "when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible." Joseph wanted the Whitneys to avoid observation by anyone, and not just by Emma.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Critics of the Church would have us believe that this is a private, secret "love letter" from Joseph to Sarah Ann, however, Joseph wrote this letter to the Whitney's, addressing it to Sarah's parents. The "matter" to which he refers is likely the administration of ordinances rather than the arrangement of some sort of private tryst with one of his plural wives. Why would one invite your bride's parents to such an encounter? Joseph doesn't want Emma gone because he wants to be alone with Sarah Ann—a feat that would be difficult to accomplish with her parents there—he wants Emma gone either because she is opposed to plural marriage (the contention that would result from an encounter between Emma and the Whitney's just a few weeks after Joseph's sealing to Sarah Ann would hardly be conducive to having the spirit present in order to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads"), or because she may have been followed or spied upon by Joseph's enemies, putting either Joseph or the Whitneys in danger.
On the 16th of August, 1842, while Joseph was in hiding at the Sayer's, Emma expressed concern for Joseph's safety. She sent a letter to Joseph in which she noted,
There are more ways than one to take care of you, and I believe that you can still direct in your business concerns if we are all of us prudent in the matter. If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph wrote the next day in his journal,
Several rumors were afloat in the city, intimating that my retreat had been discovered, and that it was no longer safe for me to remain at Brother Sayers'; consequently Emma came to see me at night, and informed me of the report. It was considered wisdom that I should remove immediately, and accordingly I departed in company with Emma and Brother Derby, and went to Carlos Granger's, who lived in the north-east part of the city. Here we were kindly received and well treated." (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, pp. 117-118)
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney, and &c." Scholars agree that the third person referred to was the Whitney's daughter Sarah Ann, to whom Joseph had been sealed in a plural marriage, without Emma's knowledge, three weeks prior. The full letter, with photographs of the original document, was published by Michael Marquardt in 1973,[1] and again in 1984 by Dean C. Jessee in The Personal Writings of Joseph Smith.[2] The complete text of the letter reads as follows (original spelling has been retained):
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
Some critics point to this letter as evidence the Joseph wrote a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann, requesting that she visit him while he was in seclusion. Others believe that the letter was a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring their daughter to him so that he could obtain "comfort," with the implication that "comfort" involved intimate relations.
Did Joseph Smith write a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann Whitney? Was this letter a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring her to Joseph? Was Joseph trying to keep Sarah Ann and Emma from encountering one another? Certain sentences extracted from the letter might lead one to believe one or all of these things. Critics use this to their advantage by extracting only the portions of the letter which support the conclusions above. We present here four examples of how the text of the letter has been employed by critics in order to support their position that Joseph was asking the Whitney's to bring Sarah Ann over for an intimate encounter. The text of the full letter is then examined again in light of these treatments.
Consider the following excerpt from a website that is critical of the Church. Portions of the Whitney letter are extracted and presented in the following manner:
... the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty. ... Only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater friendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I will tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. ... I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont, dont fail to come to night, I subscribe myself your most obedient, and affectionate, companion, and friend. Joseph Smith.
—’’Rethinking Mormonism’’, "Did Joseph Smith have sex with his wives?" (Web page)
This certainly has all of the elements of a secret "love letter:" The statement that it would not be safe if Emma were there, the request to "burn this letter as soon as you read it," and the stealthy instructions for approaching the house. The question is, who was this letter addressed to? The critics on their web site clearly want you to believe that this was a private letter to Sarah Ann.
Here is the way that Van Wagoner presents selected excerpts of the same letter. In this case, at least, he acknowledges that the letter was addressed to "the Whitney’s," rather than Sarah, but adds his own opinion that it "detailed [Joseph’s] problems in getting to see Sarah Ann without Emma's knowledge:"
My feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us ... if you three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me, now is the time to Afford me succor ... the only thing to be careful is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safety.
—Richard S. Van Wagoner, Mormon Polygamy: A History, 48.
This version, presented by George D. Smith, presents excerpts from the letter which makes it sound like Joseph was absolutely lusting for the company of Sarah Ann. Smith even makes Napoleon Bonaparte a Joseph Smith doppelgänger by quoting a letter from the future Emperor to Josephine of their first night together:
"I have awakened full of you. The memory of last night has given my senses no rest. . . . What an effect you have on my heart! I send you thousands of kisses—but don’t kiss me. Your kisses sear my blood" (p. xi). George Smith then claims that a "young man of ambition and vision penned his own letter of affection to a young woman. It was the summer of 1842 when thirty-six-year-old Joseph Smith, hiding from the law down by the Mississippi River in Illinois, confessed:"
Smith then compares the excerpts from Napoleon's letter above to portions of the Whitney letter:
My feelings are so strong for you . . . come and see me in this my lonely retreat . . . now is the time to afford me succour . . . I have a room intirely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect saf[e]ty, I know it is the will of God that you should comfort me.
—George D. Smith, "Nauvoo Polygamy: We Called It Celestial Marriage," Free Inquiry [Council for Secular Humanism] 28/3 (April–May 2008): 44–46.
Finally, we have a version which acknowledges the full contents of the letter...but only after presenting it in the manner described above numerous times. The author eventually provides the full text of this letter (150 pages after its comparison with Napoleon). Since there are no extant "love letters" from Joseph Smith to any of his plural wives, the mileage that the author of Nauvoo Polygamy..."but we called it celestial marriage" extracts from the single letter to the Whitney's is simply astounding:
- "[i]t was eleven years after the Smiths roomed with the Whitneys that Joseph expressed a romantic interest in their daughter, as well." (p. 31)
- "recommended his friend, whose seventeen-year-old daughter he had just married, should 'come a little a head, and nock…at the window.'" (p. 53)
- "Emma Hale, Joseph's wife of fifteen years, had left his side just twenty-four hours earlier. Now Joseph declared that he was "lonesome," and he pleaded with Sarah Ann to visit him under cover of darkness. After all, they had been married just three weeks earlier. (p. 53)
- "As will be seen, conjugal visits appear furtive and constantly shadowed by the threat of disclosure." (p. 63)
- "when Joseph requested that Sarah Ann Whitney visit him and ‘nock at the window,’ he reassured his new young wife that Emma would not be there, telegraphing his fear of discovery if Emma happened upon his trysts." (p. 65)
- "Three weeks after the wedding, Joseph took steps to spend some time with his newest bride." (p. 138)
- "It was the ninth night of Joseph's concealment, and Emma had visited him three times, written him several letters, and penned at least one letter on his behalf…For his part, Joseph's private note about his love for Emma was so endearing it found its way into the official church history. In it, he vowed to be hers 'forevermore.' Yet within this context of reassurance and intimacy, a few hours later the same day, even while Joseph was still in grave danger and when secrecy was of the utmost urgency, he made complicated arrangements for a visit from his fifteenth plural wife, Sarah Ann Whitney." (p. 142)
- "Smith urged his seventeen-year-old bride to 'come to night' and 'comfort' him—but only if Emma had not returned….Joseph judiciously addressed the letter to 'Brother, and Sister, Whitney, and &c." (p. 142-143)
- "Invites Whitneys to visit, Sarah Ann to 'comfort me' if Emma not there. Invitation accepted." (p.. 147)
- "As if Sarah Ann Whitney's liaison were not enough…another marriage took place…." (p. 155)
- "summer 1842 call for an intimate visit from Sarah Ann Whitney…substantiate[s] the intimate relationships he was involved in during those two years." (p. 185)
- "his warning to Sarah Ann to proceed carefully in order to make sure Emma would not find them in their hiding place." (p. 236)
- "Just as Joseph sought comfort from Sarah Ann the day Emma departed from his hideout…." (p. 236)
- "Elizabeth [Whitney] was arranging conjugal visits between her daughter, Sarah Ann, and [Joseph]…." (p. 366)
One must assume that this is the closest thing that the author could find to a love letter, because the "real" love letters from Joseph to his plural wives do not exist. The author had to make do with this one, despite the fact that it did not precisely fit the bill. With judicious pruning, however, it can be made to sound sufficiently salacious to suit the purpose at hand: to "prove" that Joseph lusted after women.
In contrast to the sources above, Compton actually provides the complete text of the letter up front, and concludes that "[t]he Mormon leader is putting the Whitney's in the difficult position of having to learn about Emma's movements, avoid her, then meet secretly with him" and that the "cloak-and-dagger atmosphere in this letter is typical of Nauvoo polygamy." [3]
As always, it is helpful to view the entire set of statements in content. Let's revisit the entire letter, this time with the selections extracted by the critics highlighted:
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
So, let’s take a look at the portions of the letter that are not highlighted.
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney." Sarah Ann is not mentioned by name, but is included as "&c.," which is the equivalent of saying "and so on," or "etc." This hardly implies that what follows is a private "love letter" to Sarah Ann herself.
Could this have been an appeal to Sarah's parents to bring her to Joseph? In Todd Compton's opinion, Joseph "cautiously avoids writing Sarah's name." [4] However, Joseph stated in the letter who he wanted to talk to:
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams;
Joseph wants to talk to "you three," meaning Newel, Elizabeth and Sarah Ann.
Interestingly enough, the one portion of the letter in which Joseph actually gives a reason for this meeting is often excluded by critics:
..one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me...
According to Richard L. Bushman, this may have been "a reference perhaps to the sealing of Newel and Elizabeth in eternal marriage three days later." [5] Compton adds, "This was not just a meeting of husband and plural wife, it was a meeting with Sarah's family, with a religious aspect.[6]
In addition to the stated purpose of the meeting, Joseph "may have been a lonely man who needed people around him every moment." [7] Consider this phrase (included in Van Wagoner's treatment, but excluded by the others):
...it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am al[l]ied, do love me, now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile. (emphasis added)
These are not the words of a man asking his secret lover to meet him for a private tryst—they are the words of a man who wants the company of friends.
So, what about Emma? The letter certainly contains dire warnings about having the Whitney's avoid an encounter with Emma. We examine several possible reasons for the warning about Emma. Keep in mind Emma's stated concern just two days prior,
If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph had been sealed to Sarah Ann three weeks before without Emma's knowledge.[8] Joseph may have wished to offer a sealing blessing to Newel and Elizabeth Whitney at this time. Given Joseph's indication to the Whitneys that he wished to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads," and the fact that Emma herself was not sealed until she consented to the doctrine of plural marriage nine months later, Joseph may have felt that Emma’s presence would create an uncomfortable situation for all involved—particularly if she became aware of his sealing to Sarah Ann.
If Joseph was in hiding, he had good reason to avoid being found (hence the request to burn the letter that disclosed his location). He would also not want his friends present in case he were to be found. Anyone that was searching for Joseph knew that Emma could lead them to him if they simply observed and followed her. If this were the case, the most dangerous time for the Whitney's to visit Joseph may have been when Emma was there—not necessarily because Emma would have been angered by finding Sarah Ann (after all, Emma did not know about the sealing, and she would have found all three Whitney's there—not just Sarah Ann), but because hostile men might have found the Whitney's with Joseph. Note that Joseph's letter states that "when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible." Joseph wanted the Whitneys to avoid observation by anyone, and not just by Emma.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Critics of the Church would have us believe that this is a private, secret "love letter" from Joseph to Sarah Ann, however, Joseph wrote this letter to the Whitney's, addressing it to Sarah's parents. The "matter" to which he refers is likely the administration of ordinances rather than the arrangement of some sort of private tryst with one of his plural wives. Why would one invite your bride's parents to such an encounter? Joseph doesn't want Emma gone because he wants to be alone with Sarah Ann—a feat that would be difficult to accomplish with her parents there—he wants Emma gone either because she is opposed to plural marriage (the contention that would result from an encounter between Emma and the Whitney's just a few weeks after Joseph's sealing to Sarah Ann would hardly be conducive to having the spirit present in order to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads"), or because she may have been followed or spied upon by Joseph's enemies, putting either Joseph or the Whitneys in danger.
On the 16th of August, 1842, while Joseph was in hiding at the Sayer's, Emma expressed concern for Joseph's safety. She sent a letter to Joseph in which she noted,
There are more ways than one to take care of you, and I believe that you can still direct in your business concerns if we are all of us prudent in the matter. If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph wrote the next day in his journal,
Several rumors were afloat in the city, intimating that my retreat had been discovered, and that it was no longer safe for me to remain at Brother Sayers'; consequently Emma came to see me at night, and informed me of the report. It was considered wisdom that I should remove immediately, and accordingly I departed in company with Emma and Brother Derby, and went to Carlos Granger's, who lived in the north-east part of the city. Here we were kindly received and well treated." (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, pp. 117-118)
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney, and &c." Scholars agree that the third person referred to was the Whitney's daughter Sarah Ann, to whom Joseph had been sealed in a plural marriage, without Emma's knowledge, three weeks prior. The full letter, with photographs of the original document, was published by Michael Marquardt in 1973,[1] and again in 1984 by Dean C. Jessee in The Personal Writings of Joseph Smith.[2] The complete text of the letter reads as follows (original spelling has been retained):
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
Some critics point to this letter as evidence the Joseph wrote a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann, requesting that she visit him while he was in seclusion. Others believe that the letter was a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring their daughter to him so that he could obtain "comfort," with the implication that "comfort" involved intimate relations.
Did Joseph Smith write a private and secret "love letter" to Sarah Ann Whitney? Was this letter a request to Sarah Ann's parents to bring her to Joseph? Was Joseph trying to keep Sarah Ann and Emma from encountering one another? Certain sentences extracted from the letter might lead one to believe one or all of these things. Critics use this to their advantage by extracting only the portions of the letter which support the conclusions above. We present here four examples of how the text of the letter has been employed by critics in order to support their position that Joseph was asking the Whitney's to bring Sarah Ann over for an intimate encounter. The text of the full letter is then examined again in light of these treatments.
Consider the following excerpt from a website that is critical of the Church. Portions of the Whitney letter are extracted and presented in the following manner:
... the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty. ... Only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater friendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I will tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. ... I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont, dont fail to come to night, I subscribe myself your most obedient, and affectionate, companion, and friend. Joseph Smith.
—’’Rethinking Mormonism’’, "Did Joseph Smith have sex with his wives?" (Web page)
This certainly has all of the elements of a secret "love letter:" The statement that it would not be safe if Emma were there, the request to "burn this letter as soon as you read it," and the stealthy instructions for approaching the house. The question is, who was this letter addressed to? The critics on their web site clearly want you to believe that this was a private letter to Sarah Ann.
Here is the way that Van Wagoner presents selected excerpts of the same letter. In this case, at least, he acknowledges that the letter was addressed to "the Whitney’s," rather than Sarah, but adds his own opinion that it "detailed [Joseph’s] problems in getting to see Sarah Ann without Emma's knowledge:"
My feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us ... if you three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me, now is the time to Afford me succor ... the only thing to be careful is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safety.
—Richard S. Van Wagoner, Mormon Polygamy: A History, 48.
This version, presented by George D. Smith, presents excerpts from the letter which makes it sound like Joseph was absolutely lusting for the company of Sarah Ann. Smith even makes Napoleon Bonaparte a Joseph Smith doppelgänger by quoting a letter from the future Emperor to Josephine of their first night together:
"I have awakened full of you. The memory of last night has given my senses no rest. . . . What an effect you have on my heart! I send you thousands of kisses—but don’t kiss me. Your kisses sear my blood" (p. xi). George Smith then claims that a "young man of ambition and vision penned his own letter of affection to a young woman. It was the summer of 1842 when thirty-six-year-old Joseph Smith, hiding from the law down by the Mississippi River in Illinois, confessed:"
Smith then compares the excerpts from Napoleon's letter above to portions of the Whitney letter:
My feelings are so strong for you . . . come and see me in this my lonely retreat . . . now is the time to afford me succour . . . I have a room intirely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect saf[e]ty, I know it is the will of God that you should comfort me.
—George D. Smith, "Nauvoo Polygamy: We Called It Celestial Marriage," Free Inquiry [Council for Secular Humanism] 28/3 (April–May 2008): 44–46.
Finally, we have a version which acknowledges the full contents of the letter...but only after presenting it in the manner described above numerous times. The author eventually provides the full text of this letter (150 pages after its comparison with Napoleon). Since there are no extant "love letters" from Joseph Smith to any of his plural wives, the mileage that the author of Nauvoo Polygamy..."but we called it celestial marriage" extracts from the single letter to the Whitney's is simply astounding:
- "[i]t was eleven years after the Smiths roomed with the Whitneys that Joseph expressed a romantic interest in their daughter, as well." (p. 31)
- "recommended his friend, whose seventeen-year-old daughter he had just married, should 'come a little a head, and nock…at the window.'" (p. 53)
- "Emma Hale, Joseph's wife of fifteen years, had left his side just twenty-four hours earlier. Now Joseph declared that he was "lonesome," and he pleaded with Sarah Ann to visit him under cover of darkness. After all, they had been married just three weeks earlier. (p. 53)
- "As will be seen, conjugal visits appear furtive and constantly shadowed by the threat of disclosure." (p. 63)
- "when Joseph requested that Sarah Ann Whitney visit him and ‘nock at the window,’ he reassured his new young wife that Emma would not be there, telegraphing his fear of discovery if Emma happened upon his trysts." (p. 65)
- "Three weeks after the wedding, Joseph took steps to spend some time with his newest bride." (p. 138)
- "It was the ninth night of Joseph's concealment, and Emma had visited him three times, written him several letters, and penned at least one letter on his behalf…For his part, Joseph's private note about his love for Emma was so endearing it found its way into the official church history. In it, he vowed to be hers 'forevermore.' Yet within this context of reassurance and intimacy, a few hours later the same day, even while Joseph was still in grave danger and when secrecy was of the utmost urgency, he made complicated arrangements for a visit from his fifteenth plural wife, Sarah Ann Whitney." (p. 142)
- "Smith urged his seventeen-year-old bride to 'come to night' and 'comfort' him—but only if Emma had not returned….Joseph judiciously addressed the letter to 'Brother, and Sister, Whitney, and &c." (p. 142-143)
- "Invites Whitneys to visit, Sarah Ann to 'comfort me' if Emma not there. Invitation accepted." (p.. 147)
- "As if Sarah Ann Whitney's liaison were not enough…another marriage took place…." (p. 155)
- "summer 1842 call for an intimate visit from Sarah Ann Whitney…substantiate[s] the intimate relationships he was involved in during those two years." (p. 185)
- "his warning to Sarah Ann to proceed carefully in order to make sure Emma would not find them in their hiding place." (p. 236)
- "Just as Joseph sought comfort from Sarah Ann the day Emma departed from his hideout…." (p. 236)
- "Elizabeth [Whitney] was arranging conjugal visits between her daughter, Sarah Ann, and [Joseph]…." (p. 366)
One must assume that this is the closest thing that the author could find to a love letter, because the "real" love letters from Joseph to his plural wives do not exist. The author had to make do with this one, despite the fact that it did not precisely fit the bill. With judicious pruning, however, it can be made to sound sufficiently salacious to suit the purpose at hand: to "prove" that Joseph lusted after women.
In contrast to the sources above, Compton actually provides the complete text of the letter up front, and concludes that "[t]he Mormon leader is putting the Whitney's in the difficult position of having to learn about Emma's movements, avoid her, then meet secretly with him" and that the "cloak-and-dagger atmosphere in this letter is typical of Nauvoo polygamy." [3]
As always, it is helpful to view the entire set of statements in content. Let's revisit the entire letter, this time with the selections extracted by the critics highlighted:
Nauvoo August 18th 1842
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams; for my feelings are so strong for you since what has pased lately between us, that the time of my abscence from you seems so long, and dreary, that it seems, as if I could not live long in this way: and <if you> three would come and see me in this my lonely retreat, it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am alied, do love me; now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile, for you know I foretold you of these things. I am now at Carlos Graingers, Just back of Brother Hyrams farm, it is only one mile from town, the nights are very pleasant indeed, all three of you come <can> come and See me in the fore part of the night, let Brother Whitney come a little a head, and nock at the south East corner of the house at <the> window; it is next to the cornfield, I have a room inti=rely by myself, the whole matter can be attended to with most perfect safty, I <know> it is the will of God that you should comfort <me> now in this time of affliction, or not at[ta]l now is the time or never, but I hav[e] no kneed of saying any such thing, to you, for I know the goodness of your hearts, and that you will do the will of the Lord, when it is made known to you; the only thing to be careful of; is to find out when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible, I know it is a heroick undertakeing; but so much the greater frendship, and the more Joy, when I see you I <will> tell you all my plans, I cannot write them on paper, burn this letter as soon as you read it; keep all locked up in your breasts, my life depends upon it. one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me, I close my letter, I think Emma wont come tonight if she dont dont fail to come to night. I subscribe myself your most obedient, <and> affectionate, companion, and friend.
Joseph Smith
So, let’s take a look at the portions of the letter that are not highlighted.
Dear, and Beloved, Brother and Sister, Whitney, and &c.—
The letter is addressed to "Brother and Sister Whitney." Sarah Ann is not mentioned by name, but is included as "&c.," which is the equivalent of saying "and so on," or "etc." This hardly implies that what follows is a private "love letter" to Sarah Ann herself.
Could this have been an appeal to Sarah's parents to bring her to Joseph? In Todd Compton's opinion, Joseph "cautiously avoids writing Sarah's name." [4] However, Joseph stated in the letter who he wanted to talk to:
I take this oppertunity to communi[c]ate, some of my feelings, privetely at this time, which I want you three Eternaly to keep in your own bosams;
Joseph wants to talk to "you three," meaning Newel, Elizabeth and Sarah Ann.
Interestingly enough, the one portion of the letter in which Joseph actually gives a reason for this meeting is often excluded by critics:
..one thing I want to see you for is <to> git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads, &c. you wi will pardon me for my earnest=ness on <this subject> when you consider how lonesome I must be, your good feelings know how to <make> every allowance for me...
According to Richard L. Bushman, this may have been "a reference perhaps to the sealing of Newel and Elizabeth in eternal marriage three days later." [5] Compton adds, "This was not just a meeting of husband and plural wife, it was a meeting with Sarah's family, with a religious aspect.[6]
In addition to the stated purpose of the meeting, Joseph "may have been a lonely man who needed people around him every moment." [7] Consider this phrase (included in Van Wagoner's treatment, but excluded by the others):
...it would afford me great relief, of mind, if those with whom I am al[l]ied, do love me, now is the time to afford me succour, in the days of exile. (emphasis added)
These are not the words of a man asking his secret lover to meet him for a private tryst—they are the words of a man who wants the company of friends.
So, what about Emma? The letter certainly contains dire warnings about having the Whitney's avoid an encounter with Emma. We examine several possible reasons for the warning about Emma. Keep in mind Emma's stated concern just two days prior,
If it was pleasant weather I should contrive to see you this evening, but I dare not run too much of a risk, on account of so many going to see you. (History of the Church, Vol.5, Ch.6, p.109)
Joseph had been sealed to Sarah Ann three weeks before without Emma's knowledge.[8] Joseph may have wished to offer a sealing blessing to Newel and Elizabeth Whitney at this time. Given Joseph's indication to the Whitneys that he wished to "git the fulness of my blessings sealed upon our heads," and the fact that Emma herself was not sealed until she consented to the doctrine of plural marriage nine months later, Joseph may have felt that Emma’s presence would create an uncomfortable situation for all involved—particularly if she became aware of his sealing to Sarah Ann.
If Joseph was in hiding, he had good reason to avoid being found (hence the request to burn the letter that disclosed his location). He would also not want his friends present in case he were to be found. Anyone that was searching for Joseph knew that Emma could lead them to him if they simply observed and followed her. If this were the case, the most dangerous time for the Whitney's to visit Joseph may have been when Emma was there—not necessarily because Emma would have been angered by finding Sarah Ann (after all, Emma did not know about the sealing, and she would have found all three Whitney's there—not just Sarah Ann), but because hostile men might have found the Whitney's with Joseph. Note that Joseph's letter states that "when Emma comes then you cannot be safe, but when she is not here, there is the most perfect safty: only be careful to escape observation, as much as possible." Joseph wanted the Whitneys to avoid observation by anyone, and not just by Emma.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
No one denies that Brigham Young had sex with his many wives. He had over 50 children. So why question whether or not Joseph had sex with his wives, even the ones who were already married to other men?
If Joseph was commanded to marry these women for the express purpose of multiplying and replenishing the earth, he would have been breaking the "commandment" from God if he did not try to procreate with his wives.
The record is frustratingly incomplete regarding the question of which marriages were consummated, it is likewise spotty with regards to whether Joseph fathered children by his plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to consider this question in any detail, though her standard of evidence was depressingly low. Subsequent authors have returned to the problem, though unanimity has been elusive (see Table 1). Ironically, Brodie did not even mention the case of Josephine Lyon, now considered the most likely potential child of Joseph.
Notation:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36]
It is claimed that Joseph Smith fathered children with some of his plural wives, and that he covered up the evidence of pregnancies. It is also claimed that Joseph Smith had intimate relations with other men’s wives to whom he had been sealed, and that children resulted from these unions.
Critics of Joseph Smith have long had difficulty reconciling their concept of Joseph as a promiscuous womanizer with the fact that the only recorded children of the prophet are those that he had with Emma. Science is now shedding new light on this issue as DNA research has eliminated most of the possibilities that had long been rumored to be descendants of Joseph Smith. In the case of at least two, however, DNA cannot tell us either way. The historical reasoning for justifying that Joseph had children by these wives is dubious.
DNA analysis has determined that Josephine Fisher is not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr., [37] but for many years she appeared to be the strongest possibility. The resolution of this question was difficult to resolve until the appropriate DNA analysis techniques became available. These findings have been replicated in non-Latter-day Saint, peer-reviewed, reputable journals.[38]
The case of Josephine Fisher relied on a deathbed conversation:
Just prior to my mothers death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret from me and from all others but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith….[39]
Perhaps significantly, Josephine's name shares a clear link with Joseph's. Whether this account proved that she was his biological daughter had long been debated:
Rex Cooper…has questioned the interpretation that Smith was Fisher's biological father. He posits that because Fisher's mother was sealed to Smith, Fisher was his daughter only in a spiritual sense…More problematic is whether there is a discrepancy between what Fisher understood and what her mother meant. That is, did Fisher interpret her mother's remarks to mean she was the biological daughter of Joseph Smith and thus state that with more certitude than was warranted, when in fact her mother meant only that in the hereafter Fisher would belong to Joseph Smith's family through Session's sealing to him? Because Sessions was on her deathbed, when one's thoughts naturally turn to the hereafter, the latter is a reasonable explanation.[40]
As Danel Bachman notes, however, there seems to be relatively little doubt that
[t]he desire for secrecy as well as the delicacy of the situation assure us that Mrs. Sessions was not merely explaining to her daughter that she was Smith's child by virtue of a temple sealing. The plain inference arising from Jenson's curiosity in the matter and Mrs. Fisher's remarks is that she was, in fact, the offspring of Joseph Smith.[41]
However, DNA evidence now disproves this theory. It is possible, then, that Fisher misunderstood her mother, but this seems unlikely. Any unreliability is more likely to arise because of a dying woman's confusion than from miscommunication. No evidence exists for such confusion, though we cannot rule it out.
Josephine's account is also noteworthy because her mother emphasizes that "…she [had] been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon was out of fellowship with the Church."[42] This may explain her reasoning for being sealed to Joseph at all—her husband was out of fellowship. Todd Compton opines that "[i]t seems unlikely that Sylvia would deny [her husband] cohabitation rights after he was excommunicated," but this conclusion seems based on little but a gut reaction.[43] These women took their religion seriously; given Sylvia's deathbed remarks, this was a point she considered important enough to emphasize. She apparently believed it would provide an explanation for something that her daughter might have otherwise misunderstood.
There is also clear evidence that at least some early members of the Church would have taken a similar attitude toward sexual relations with an unbelieving spouse. My own third-great grandfather, Isaiah Moses Coombs, provides a striking illustration of this from the general membership of the Church.
Coombs had immigrated to Utah, but his non-member spouse refused to accompany him. Heartsick, he consulted Brigham Young for advice. Young "sat with one hand on my knee, looking at my face and listen[ing] attentively." Then, Young took the new arrival "by the hand in his fatherly way," and said "[Y]ou had better take a mission to the States…to preach the gospel and visit your wife…visit your wife as often as you please; preach the gospel to her, and if she is worth having she will come with you when you return to the valley. God bless and prosper you."[44]
Coombs did as instructed, but was not successful in persuading his wife. His description of his thoughts is intriguing, and worth quoting at length:
I may as well state here, however, that during all my stay in the States, [my wife and I] were nothing more to each other than friends. I never proposed or hinted for a closer intimacy only on condition of her baptism into the Church. I felt that I could not take her as a wife on any other terms and stand guiltless in the sight of God or my own conscience…I could not yield to her wishes and she would not bend to mine. And so I merely visited her as a friend. This was a source of wonder to our mutual acquaintances; and well it might be for had not my faith been founded on the eternal rock of Truth, I never could have stood such a test, I never could have withstood the temptations that assailed me, but I should have yielded and have abandoned myself to the life of carnal pleasure that awaited me in the arms of my beautiful and adored wife. She was now indeed beautiful. I had thought her lovely as a child—as a maiden she had seemed to me surpassing fair, but as a woman with a form well developed and all the charms of her persona matured, she far surpassed in womanly beauty anything I had ever dreamed of.[45]
Coombs' account is startlingly blunt and explicit for the age. Yet, if this young twenty-two-year-old male refused marital intimacy with his wife (whom he married knowing their religious differences), Compton's confidence that Sylvia Sessions would not deny marital relations to her excommunicated husband seems misplaced. Sessions may, like Coombs, have seen her faithfulness to the sealing ordinances sufficient to "eventually either in this life or that which is to come enable me to bind my [spouse] to me in bands that could not be broken." Like him, she may have believed that "[My spouse] was blind then but the day would come when [he] would see."[46]
More importantly, however, is Brian Hales’ more recent work, which demonstrates that Sylvia Sessions Lyon may well have not been married to her husband when sealed to Joseph Smith, contrary to Compton’s conclusion. Thus, rather than being a case of polyandry with sexual relations with two men (Joseph and her first husband) Lyons is instead a case of straight-forward plural marriage.[47] Given that Joseph has been ruled out as Josephine's father, it may be that Sylvia's emphasis to Josephine about being Joseph's "daughter" referred to a spiritual or sealing sense, and she wished to explain to her daughter why Josephine was, then, sealed to Joseph Smith rather than her biological father.
Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[48]
Angus M. Cannon seems to have been aware of Fisher's claim to be a child of Joseph Smith, though only second hand. He told a sceptical Joseph Smith III of
one case where it was said by the girl's grandmother that your father has a daughter born of a plural wife. The girl's grandmother was Mother Sessions, who lived in Nauvoo and died here in the valley. Aunt Patty Sessions asserts that the girl was born within the time after your father was said to have taken the mother.[49]
Clearly, Cannon has no independent knowledge of the case, but reports a story similar to Josephine's affidavit. Cannon's statement is more important because it illustrates how the LDS Church's insistence that Joseph Smith had practiced plural marriage led some of the RLDS Church :to ask why no children by these wives existed. Lucy Walker reported [the RLDS] seem surprised that there was no issue from asserted plural marriages with their father. Could they but realize the hazardous life he lived, after that revelation was given, they would comprehend the reason. He was harassed and hounded and lived in constant fear of being betrayed by those who ought to have been true to him.[50] Thus the absence of children was something of an embarrassment to the Utah Church, which members felt a need to explain. It would have been greatly to their advantage to produce Joseph's offspring, but could not.[51]
Anxious to demonstrate that Joseph's plural marriages were marriages in the fullest sense, Lucy M. Walker (wife of Joseph's cousin, George A. Smith) reported seeing Joseph washing blood from his hands in Nauvoo. When asked about the blood, Joseph reportedly told her he had been helping Emma deliver one of his plural wives' children.[52] Yet, even this late account tells us little about the paternity of the children—Joseph was close to these women (and their husbands, in the case of polyandry), and given the Saints' belief in priesthood blessings, they may have well welcomed his involvement.
Even by the turn of the century, the LDS Church had no solid evidence of children by Joseph. "I knew he had three children," said Mary Elizabeth Lightner, "They told me. I think two of them are living today but they are not known as his children as they go by other names."[53] Again, evidence for children is frustratingly vague—Lightner had only heard rumours, and could not provide any details. It would seem to me, however, that this remark of Lightner's rules out her children as possible offspring of Joseph. Her audience was clearly interested in Joseph having children, and she was happy to assert that such children existed. If her own children qualified, why did she not mention them?
Two of Marinda Nancy Johnson Hyde's children have been suggested as possible children. The first, Orson, died in infancy, making DNA testing impossible. Compton notes, however, that "Marinda had no children while Orson was on his mission to Jerusalem, then became pregnant soon after Orson returned home. (He arrived in Nauvoo on December 7, 1842, and Marinda bore Orson Washington Hyde on November 9, 1843),"[54] putting the conception date around 16 February 1843.
Frank Hyde's birth date is unclear; he was born on 23 January in either 1845 or 1846.[55] This would place his conception around 2 May, of either 1844 or 1845. In the former case, Frank was conceived less than two months prior to Joseph's martyrdom. Orson Hyde left for Washington, D.C., around 4 April 1844,[56] and did not return until 6 August 1844, making Joseph's paternity more likely than Orson's if the earlier birth date is correct.[57] The key source for this claim is Fawn Brodie, who includes no footnote or reference. Given Brodie's tendency to misread evidence on potential children, this claim should be approached with caution.
Frank's death certificate lists Orson Hyde as the father, however, and places his birth in 1846, which would require conception nearly a year after Joseph's death.[58] A child by Joseph would have brought prestige to the family and Church, and Orson and Nancy had divorced long before Frank Henry's death.[59] It seems unlikely, therefore, that Orson would be credited with paternity over Joseph if any doubt existed. Without further data, Brodie's dating should probably be regarded as an error, ruling out Joseph as a possible father.
Scientific ingenuity has also been applied to the question of Joseph's paternity. Y-chromosome studies have conclusively eliminated Orrison Smith (son of Fanny Alger), Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, John Reed Hancock, Moroni Llewellyn Pratt, and Oliver Buell as Joseph's offspring.[60]
Two additional children—George Algernon Lightner and Orson W. Hyde—died in infancy, leaving no descendants to test, though as noted above Lightner can probably be excluded on the basis of his mother's testimony.
The testing of female descendants' DNA is much move involved, but work continues and may provide the only definitive means of ruling in or out potential children.
The case of Oliver Buell is an interesting one, since Fawn Brodie was insistent that he was Joseph's son. She based part of this argument on a photograph of Buell, which revealed a face which she claimed was "overwhelmingly on the side of Joseph's paternity."[61] A conception on this date would make Oliver two to three weeks overdue at birth, which makes Brodie's theory less plausible.[62]
Furthermore, prior the DNA results, Bachman and Compton pointed out that Brodie's timeline poses serious problems for her theory—Oliver's conception would have had to occurred between 16 April 1839 (when Joseph was allowed to escape during a transfer from Liberty Jail)[63] and 18 April, when the Huntingtons left Far West.[64] Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois to the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack, while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order in force.[65] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun's Mill, along Shoal Creek.[66] Yet, by 22 April Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by travel "off from the main road as much as possible"[67] "both by night and by day."[68] This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be meeting a woman, much less conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other Church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the prophet’s direction, who did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois.[69]
Brodie's inclusion of Oliver Buell is also inconsistent, since he was born prior to Joseph's sealing to Prescinda. By including Oliver as a child, Brodie wishes to paint Joseph as an indiscriminate womanizer. Yet, her theory of plural marriage argues that Joseph "had too much of the Puritan in him, and he could not rest until he had redefined the nature of sin and erected a stupendous theological edifice to support his new theories on marriage."[70] Thus, Brodie argues that Joseph created plural marriage to justify his immorality—yet, she then has him conceiving a child with Prescinda before being sealed to her. By her own argument, the paternity must therefore be seen as doubtful.[71]
Despite Brodie's enthusiasm, no other author has included Oliver on their list of possible children (see Table 1). And, DNA evidence has conclusively ruled him out. Oliver is an excellent example of Brodie's tendency to ignore and misread evidence which did not fit her preconceptions, and suggests that caution is warranted before one condemns Joseph for a pre-plural marriage "affair" or other improprieties. Since Brodie was not interested in giving Joseph the benefit of the doubt, or avoiding a rush to judgment, her decision is not surprising.
John Reed Hancock is another of Brodie's suggestions, though no other author has followed her. The evidence for Joseph having married Clarissa Reed Hancock is scant,[72] and as with Oliver Buell it is unlikely (even under Brodie's jaded theory of plural marriage as justification for adultery) that Joseph would have conceived a child with a woman to whom he was not polygamously married. DNA testing has since confirmed our justified scepticism of Brodie's claim.[73]
Bachman mentions a "seventh child" of Prescinda's, likely John Hyrum Buell, for whom the timeline would better accommodate conception by Joseph Smith. There is no other evidence for Joseph's paternity, however, save Ettie V. Smith's account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years Among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Prescinda said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hyrum's father.[74] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[75]
Besides being implausible, Ettie gets virtually every other detail wrong—she insists that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions, only to return and find their wives being courted by Joseph. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[76] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions, and their wives did not charge that Joseph had propositioned them. Jacobs had served missions, but was present during Joseph's sealing to his wife, and did not object (see Chapter 9). Jacobs was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[77] and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[78] as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[79]
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hyrum as a potential child (and carelessly misreads Ettie Smith's remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hyrum). No other historian has even mentioned this child, much less argued that Buell was not the father (see Table 1).
A few other possibilities should be mentioned, though the evidence surrounding them is tenuous. Sarah Elizabeth Holmes was born to Marietta Carter, though "No evidence links her with Joseph Smith."[80] The Dibble children suffer from chronology problems, and a lack of good evidence that Joseph and their mother was associated. Loren Dibble was, however, claimed by some Mormons as a child of Joseph’s when confronted with Joseph Smith III’s skepticism.[81]
Joseph Albert Smith was born to Esther Dutcher, but the available evidence supports her polyandrous sealing to Joseph as for eternity only. Carolyn Delight has no evidence at all of a connection to Joseph—the only source is a claim to Ugo Perego, a modern DNA researcher.[82] No textual or documentary evidence is known for her at all.
We have elsewhere seen the tenuous basis for many conclusions about the Fanny Alger marriage (see here and here). The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[83] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
A family tradition—repeated by anti-Mormon Wyl—holds that Eliza R. Snow was pregnant and shoved down the stairs by a jealous Emma before being required to leave the Smith home.[84] The tradition holds that Eliza, "heavy with child" subsequently miscarried. While Eliza was required to leave the home and Emma was likely upset with her, no contemporary evidence points to a pregnancy.[85] Eliza's diary says nothing about the loss of a child, which would be a strange omission given her love of children.[86] It seems unlikely that Eliza would have still been teaching school in an advanced state of pregnancy, especially given that her appearance as a pregnant "unwed mother" would have been scandalous in Nauvoo. Emma's biographers note that "Eliza continued to teach school for a month after her abrupt departure from the Smith household. Her own class attendance record shows that she did not miss a day during the months she taught the Smith children, which would be unlikely had she suffered a miscarriage."[87] Given Emma's treatment of the Partridge sisters, who were also required to leave the Smith household, Emma certainly needed no pregnancy to raise her ire against Joseph's plural wives.
Eliza repeatedly testified to the physical nature of her relationship with Joseph Smith (see Chapter 9), and was not shy about criticizing Emma on the subject of plural marriage.[88] Yet, she never reported having been pregnant, or used her failed pregnancy as evidence for the reality of plural marriage.
In the absence of further information, both of these reported pregnancies must be regarded as extremely speculative.
Sylvia was married to Windsor Lyon by Joseph Smith in Nauvoo. She was sealed to Joseph Smith at some point after she was married. Brian Hales notes that , "This marriage triangle is unique among all of the Prophet’s plural marriages because there is strong evidence that Sylvia bore children to both men. She became pregnant by Windsor Lyon in October of 1838, September of 1840, and April of 1842. Then a year later became pregnant with a daughter (named Josephine—born February 8, 1844) that was purportedly fathered by the Prophet." Sylvia's daughter, who had the intriguing name "Josephine," made the following statement:
Just prior to my mothers [Sylvia Sessions Lyon] death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days on earth were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret fro me and from others until no but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith, she having been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon had was out of fellowship with the Church.
For many years, Josephine appeared to be the only viable candidate as a child of Joseph Smiths "polyandrous" sealings. However, DNA analysis ultimately disproved the paternity claim: Josephine was not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr.[89]
It appears, however, that Sylvia may have considered herself divorced from Windsor after he was excommunicated from the Church and left Nauvoo. Hales points out that "Currently, no documentation of a legal divorce between Windsor and Sylvia after his excommunication has been found. However, in the mid-nineteenth century, religious laws often trumped legal proceedings. Stanley B. Kimball observed: 'Some church leaders at that time considered civil marriage by non-Mormon clergymen to be as unbinding as their baptisms. Some previous marriages . . . were annulled simply by ignoring them.'" [90] The sealing to Joseph occurred after Windor's excommunication. Andrew Jenson, in his historical record, referred to Sylvia as a "formerly the wife of Windsor Lyons." [91] There is no known evidence that Windsor lived with Sylvia after he returned to Nauvoo, but Sylvia did "rejoin" Windsor after he was rebaptised in 1846. Hales states, "No details are available to clarify what authority was used to reconfirm the marriage relationship between Sylvia and Windsor after their previous marital separation. Most likely the couple consulted with Brigham Young or Heber C. Kimball, who authorized their rejoining. Whether a private religious marriage ceremony for time was performed or the couple resumed observing their legal marriage is unknown. Importantly, even with the renewed conjugality between Windsor and Sylvia after Joseph Smith’s death, no evidence has been found to support her involvement in sexual polyandry at any time." [92]
It is claimed that Prescindia Lathrop Huntington Buell admitted that she did not know who was the father of her child—Joseph Smith or her first husband. Sometimes Sarah Pratt (wife of apostle Orson Pratt) is mistakenly identified as the woman in this story. [93] Others sometimes mention Orson Hyde's wife as the source of this rumor. [94]
The source for this claim is a notoriously unreliable anti-Mormon work. It makes several errors of fact in the very paragraph in which the claim is made.
It is implausible that the supposed admission upon which the claim is based would be made. There are major historical problems of geography and timeline for Joseph to have even been a potential father of Buell's child.
The claim cannot be substantiated.
This book was written by Nelson Winch Green, who reported what estranged member Marry Ettie V. Coray Smith reportedly told him.
Even other anti-Mormon authors who had lived in Utah regarded it as nearly worthless. Fanny Stenhouse wrote:
Much has already been written on this subject much that is in accordance with facts, and much that is exaggerated and false. Hitherto, with but one exception [Mrs. Ettie V. Smith is noted in the footnote as the work referred to] that of a lady who wrote very many years ago, and who in her writings, so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where the one ended and the other began no woman who really was a Mormon and lived in Polygamy ever wrote the history of her own personal experience. Books have been published, and narratives have appeared in the magazines and journals, purporting to be written by Mormon wives; it is, however, perhaps, unnecessary for me to state that, notwithstanding such narratives may be imposed upon the Gentile world as genuine, that they were written by persons outside the Mormon faith would in a moment be detected by any intelligent Saint who took the trouble to peruse them. [95]
So, we must remember that this work is not regarded as generally reliable today, and it was not regarded as reliable even by the Church's enemies in the 19th century.
The source for this claim is an anti-Mormon book. The relevant passage reads:
The Prophet had sent some time before this, three men, Law, Foster and Jacobs, on missions, and they had just returned, and found their wives blushing under the prospective honors of spiritual wifeism; and another woman, Mrs. Buel [sic], had left her husband, a Gentile, to grace the Prophet's retinue, on horseback, when he reviewed the Nauvoo Legion. I heard the latter woman say afterwards in Utah, that she did not know whether Mr. Buel [sic] or the Prophet was the father of her son. These men [Law, Foster and Jacobs] established a press in Nauvoo, to expose his alleged vicious teachings and practices, which a revelation from Joseph destroyed. [96]
As might be expected, then, there are many claims in this passage that are in error. We know that the following are false:
Thus, in the single paragraph we have several basic errors of fact. Why should we believe the gossip of what Mrs. Buell is claimed to have said?
Furthermore, such an admission would be out of character for a believing Utah woman of the 19th century. As Todd Compton notes:
Talk of sexuality was avoided by the Victorian, puritanical Mormons; in diaries, the word 'pregnant' or 'expecting' is never or rarely used. Women are merely 'sick' until they have a child. Polyandry was rarely discussed openly by Mormon women. [97]
Fawn Brodie painted a fanciful scenario in which Joseph would have been able to potentially father a Buell child. However, she misread the historical information, and it is difficult, as Todd Compton has demonstrated, for Joseph to have even had contact with her at the proper time to conceive a child. [98] This would suggest that there were no grounds for Mrs. Buell—or a modern reader—to conclude that Joseph might have been the father.
Nauvoo Polygamy author George D. Smith tells his readers that "until decisive DNA testing of possible [Joseph] Smith descendants—daughters as well as sons—from plural wives can be accomplished, ascertaining whether Smith fathered children with any of his plural wives remains hypothetical" (pp. 228–29, cf. p. 473). This is true, but G. D. Smith fails to tell us that all those who have been definitively tested so far—Oliver Buell, Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, Moroni Pratt, and Orrison Smith—have been excluded. Would he have neglected, I wonder, to mention a positive DNA test?
The consequences of George D. Smith's less-than-rigorous approach to sources becomes clear in the case of Oliver Buell, son of Presendia.[99] Huntington Buell, one of Joseph’s polyandrous plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to suggest that Oliver Buell was Joseph’s son, and she was so convinced (based on photographic evidence)[100]Fawn Brodie to Dale Morgan, Letter, 24 March 1945, Dale Morgan papers, Marriott Library, University of Utah; cited by Todd Compton, "Fawn Brodie on Joseph Smith's Plural Wives and Polygamy: A Critical View," in Reconsidering No Man Knows My History: Fawn M. Brodie and Joseph Smith in Retrospect, ed. Newell G. Bringhurst (Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press, 1996), 166.</ref> In a footnote, G. D. Smith notes that Todd Compton "considers it improbable that Joseph and Presendia would have found time together during the brief window of opportunity after his release from prison in Missouri" (p. 80 n. 63).[101]
This slight nod toward an opposite point of view is inadequate, however. G. D. Smith does not mention and hence does not confront the strongest evidence. Compton’s argument against Joseph’s paternity does not rest just on a "narrow window" of opportunity but on the fact that Brodie seriously misread the geography required by that window. It is not merely a question of dates. Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois toward the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order.[102] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun’s Mill, along Shoal Creek.[103] Yet by April 22 Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by traveling "off from the main road as much as possible"[104]:320-321 "both by night and by day."[104]:327 This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the Prophet’s direction. Joseph did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois, contrary to Brodie’s misreading.[104]:315, 319, 322-23, 327 Timing is the least of the problems with G. D. Smith’s theory.
Despite Brodie’s enthusiasm, few other authors have included Oliver on their list of possible children.[105] With so many authors ranged against him, G. D. Smith ought not to act as if Compton’s analysis is merely about dates.
G. D. Smith also soft-pedals the most vital evidence—the DNA.[106] He makes no mention in the main text that Oliver’s paternity has been definitively ruled out by DNA testing. This admission is confined to a footnote, and its impact is minimized by its placement. After noting Compton’s disagreement with the main text’s suggestion that Oliver might be Joseph’s son, G. D. Smith writes, "There is no DNA connection," and cites a Deseret News article. He immediately follows this obtuse phrasing with a return to Compton, who finds it "‘unlikely, though not impossible, that Joseph Smith was the actual father of another Buell child,’ John Hiram, Presendia’s seventh child during her marriage to Buell and born in November 1843" (p. 80 n. 63). Thus the most salient fact—that Joseph is certainly not Oliver's father—is sandwiched between a vicarious discussion with Compton about whether Oliver or John could be Joseph’s sons. Since G. D. Smith knows there is definitive evidence against Joseph’s paternity in Oliver’s case, why mention the debate at all only to hide the answer in the midst of a long endnote? That Brodie is so resoundingly rebutted on textual, historical, and genetic grounds provides a cautionary lesson in presuming that her certainty counts for much.[107]
Two pages later, G. D. Smith again tells us of a Buell child being sealed to a proxy for Joseph with "wording [that] hints that it might have been Smith’s child." "It is not clear," he tells us, "which of her children it might have been" (p. 82). In fact, what is clear is that he has not assimilated the implications of the DNA data. John Hiram, the seventh child about whom Compton is skeptical, is the only other option. Yet the only evidence for this child belonging to Joseph is Ettie V. Smith’s account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Presendia said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hiram’s father.[108] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[109]
Besides being implausible, Ettie’s account gets virtually every other detail wrong—insisting that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions only to return to find Joseph preaching plural marriage. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[110] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions. Jacobs had served missions but was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor. He was also, contrary to Ettie’s claims, present when Joseph was sealed polyandrously to his (Jacobs’s) wife.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[111]:618 and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[111]:x as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[111]:xi-xii
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hiram as a potential child, going so far as to carelessly misread Ettie Smith’s remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hiram. No other historian has argued that Buell was not the father.[112] There is no good evidence whatever that any of Presendia’s children were Joseph’s. It is not clear why G. D. Smith clings to the idea.
Few authors agree on which children should even be considered as Joseph's potential children. Candidates which some find overwhelmingly likely are dismissed—or even left unmentioned—by others. Recent scholars have included between one to four potential children as options. Of these, Josephine Lyon was the most persuasive, until her relationship to Joseph Smith was ultimately disproven through DNA testing. Orson W. Hyde died in infancy, and so can never be definitively excluded as a possible child, though the dates of conception argue against Joseph's paternity. Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[113]
This table is in the same order as Table 1.
Notation:
Brodie;[114] Bachman;[115]; and Compton.[116]
As always, we are left where we began—with more suspicions and possibilities than certitudes. One's attitude toward Joseph and the Saints will influence, more than anything else, how these conflicting data are interpreted.
The uncertainty surrounding Joseph's offspring is even more astonishing when we appreciate how much such a child would have been valued. The Utah Church of the 19th century was anxious to prove that Joseph had practiced full plural marriage, and that their plural families merely continued what he started. Any child of Joseph's would have been treasured, and the family honoured. There was a firm expectation that even Joseph's sons by Emma would have an exalted place in the LDS hierarchy if they were to repent and return to the Church.[117] As Alma Allred noted, "Susa Young Gates indicated that [Brigham Young] wasn’t aware of such a child when she wrote that her father and the other apostles were especially grieved that Joseph did not have any issue in the Church."[118]
In 1884, George Q. Cannon bemoaned this lack of Joseph's posterity:
There may be faithful men who will have unfaithful sons, who may not be as faithful as they might be; but faithful posterity will come, just as I believe it will be the case with the Prophet Joseph's seed. To-day he has not a soul descended from him personally, in this Church. There is not a man bearing the Holy Priesthood, to stand before our God in the Church that Joseph was the means in the hands of God, of founding—not a man to-day of his own blood,—that is, by descent,—to stand before the Lord, and represent him among these Latter-day Saints.[119]
Brigham and Cannon, a member of the First Presidency, would have known of Joseph's offspring if any of the LDS leadership did. Yet, despite the religious and public relations value which such a child would have provided, they knew of none. It is possible that Joseph had children by his plural wives, but by no means certain. The data are surprisingly ephemeral.
Doctrine and Covenants 132꞉63 states,
But if one or either of the ten virgins, after she is espoused, shall be with another man, she has committed adultery, and shall be destroyed; for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men; for herein is the work of my Father continued, that he may be glorified.
Polygamy was not permitted only for the purpose of procreation. Joseph established the practice of plural marriage as part of the "restoration of all things," (D&C 132: 40, 45) and introduced it to a number of others within the Church. This alone may have been the purpose of Joseph's initiation of the practice. The establishment of the practice ultimately did have the effect of "raising up seed"...just not through Joseph Smith.
As Brian Hales writes:
Joseph Smith dictated what is now Doctrine and Covenant section 132 on July 12, 1843. This revelation, along with his other statements, provide several reasons why he believed plural marriage could be introduced among the Latter-day Saints.The earliest justification mentioned by the Prophet was as a part of the "restitution of all things" prophesied in Acts 3:19–21. Old Testament prophets practiced polygamy, so it could be a part of the restoration of "all things" (see D&C 132:40, 45).
Several members who knew Joseph Smith left accounts of him referring to a connection between the two during the Kirtland period.
Benjamin F. Johnson recalled in 1903: "In 1835 at Kirtland I learned from my Sisters Husband, Lyman R. Shirman,[120] who was close to the Prophet, and Received it from him. That the ancient order of plural marriage was again to be practiced by the Church."[121]
A few years later in 1841, Joseph Smith attempted to broach the topic publicly. Helen Mar Kimball remembered: "He [Joseph] astonished his hearers by preaching on the restoration of all things, and said that as it was anciently with Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, so it would be again, etc."[122] Joseph Smith was a prophet-restorer, which helps to explain why the command to practice plural marriage has been labeled a "restoration," even though it is not a salvific ordinance.[123]
Brian Hales addresses one aspect of D&C 132 that may be overlooked in casual readings:
The fourth reason Joseph Smith gave for the practice of plural marriage dwarfs the other three explanations in significance because it deals with eternity. The message of D&C 132:16–17 states that men and women who are not sealed in eternal marriages during this life (or vicariously later) "remain separately and singly, without exaltation, in their saved condition, to all eternity."In other words, "exaltation," the highest salvation, requires eternal marriage. No unmarried person can be exalted according to Joseph Smith’s teachings. Doctrine and Covenants section 132 seems to anticipate more worthy women than men as it approves a plurality of wives[124] and disallows a plurality of husbands.[125] Verse 63 states that a plurality of wives is "for their [the wives] exaltation in the eternal worlds." Section 132 supports that eternity was the primary focus of the Joseph’s marriage theology rather than plurality or sexuality. Eternal, rather than plural, marriage was his zenith doctrine. It appears that the crucial objective of polygamy on earth was to allow all worthy women to be eternally sealed to a husband and thus obtain all the ordinances needed for exaltation. According to these teachings, a plurality of wives in some form may be practiced in eternity, but not by all worthy men and women. We know that polygamy on earth is unequal and difficult, but we know nothing about how eternal marriage or eternal plural marriage might feel in eternity. Brigham Young acknowledged that eternal marriage (not plural marriage) is "the thread which runs from the beginning to the end" in God’s plan for His children:
The whole subject of the marriage [not plural marriage] relation is not in my reach, nor in any other man’s reach on this earth. It is without beginning of days or end of years; it is a hard matter to reach. We can tell some things with regard to it; it lays the foundation for worlds, for angels, and for the Gods; for intelligent beings to be crowned with glory, immortality, and eternal lives. In fact, it is the thread which runs from the beginning to the end of the holy Gospel of salvation—of the Gospel of the Son of God; it is from eternity to eternity.[126][127]
Another author commenting on this verse made a compelling case for this theology being put into D&C 132: 63:
Here is the text in its entirety, from verse 62: "for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men." [Emphasis added.] You want to get legalistic? Let’s get legalistic. Just for fun, let’s parse the living snot out of this.This clause begins with multiplying and replenishing as a primary justification. Then we get the word "and" thrown in there. You’re reading this as if it says "they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, in order to fulfil the promise…" But that’s not what it says.
"And" suggests we’re about to get a second reason, not a clarification of the first. In fact, a tight, strict-constructionist reading of this verse reveals three different and distinct reasons for plural marriage, not "only" the replenishment of the earth, [. . .]So let’s review the three reasons:
1. Multiply and replenish the earth.
[. . .] D&C 132 is unequivocal on this point, just as it is unequivocal on the two points that follow.
2. Fulfil [sic] "the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world."
What promise? This seems to have reference to the "restitution of all things, which God hath spoken by the mouth of all his holy prophets since the world began." (Acts 3:21) Joseph cited the need to restore ancient practices to prepare for the Second Coming as a justification for polygamy, and this verse provides a credible scriptural context for him to do so. So just relying on this phrase – plural marriage is acceptable because it fulfills God’s promises – would be justification enough for the practice, at least according to D&C 132.
3. For "their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men."
Oh, this one’s my favorite. Notice the emphasis I added on the "that." The word appears there to create a conditional clause. You claim the bearing of souls is the same thing as multiplying and replenishing the earth, but the actual text insists that the bearing of the souls of men will only be made possible by "exaltation in the eternal worlds." This is a promise of eternal increase, of bearing souls after the earth is no longer around to be replenished. Big, big difference.
And right here, with Reason #3, we have a clear rationale and justification for Joseph being sealed to women with whom he made no attempts to multiply and replenish the earth – i.e. no sex.[128]
Both modern and 19th century members of the Church have proposed a variety of explanations for the practice of plural marriage. Not all of these suggestions can be supported by the available data. |
|
Joseph identified four reasons for the restoration of plural marriage. |
|
Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. |
|
Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. |
Some wonder if sexual relations were included in Joseph Smith’s plural marriages. The answer is yes or no, depending upon the type of plural marriage. Those marriages, often called “sealings,” were of two types. Some were for this life and the next (called “time-and-eternity”) and could include sexuality on earth. Others were limited to the next life (called “eternity-only”) and did not allow intimacy in mortality. Overall, evidence indicates that less than half of Joseph Smith’s polygamous unions were consummated and sexual relations in the others occurred infrequently. |
|
It appears the Prophet experienced sexual relations with less than half of the women sealed to him. There is no credible evidence that Joseph had sex with three subgroups of his plural wives: (1) fourteen-year-old wives, (2) non-wives (or women to whom he was not married), and (3) legally married women who were experiencing conjugal relations with their civil husbands. |
|
No children are known to have been born to Joseph and his plural wives. |
Notes
"Plural Marriage and Families in Early Utah," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
Latter-day Saints do not understand all of God’s purposes for instituting, through His prophets, the practice of plural marriage during the 19th century. The Book of Mormon identifies one reason for God to command it: to increase the number of children born in the gospel covenant in order to "raise up seed unto [the Lord]" (Jacob 2:30). Plural marriage did result in the birth of large numbers of children within faithful Latter-day Saint homes. It also shaped 19th-century Mormon society in other ways: marriage became available to virtually all who desired it; per-capita inequality of wealth was diminished as economically disadvantaged women married into more financially stable households; and ethnic intermarriages were increased, which helped to unite a diverse immigrant population. Plural marriage also helped create and strengthen a sense of cohesion and group identification among Latter-day Saints. Church members came to see themselves as a "peculiar people," covenant-bound to carry out the commands of God despite outside opposition, willing to endure ostracism for their principles.[1]
Many have asked what the scriptures say about the reasons the Lord gave for plural marriage. All such reasons are outlined in this article.
"For if I will, saith the Lord of Hosts, raise up seed unto me, I will command my people; otherwise they shall hearken unto these things."
Here, the Lord gives one reason for plural marriage, "to raise up seed unto me."
As Latter-day Saint scholar Brian Hales has written:
Again from Brian Hales:
In the only recorded revelation on plural marriage received by Joseph Smith, the Lord further stated (D&C 132:63):
"they [the plural wives] are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men; for herein is the work of my Father continued, that he may be glorified."
This passage suggests that plural marriage served the purpose of multiplying and replenishing the earth.
D&C 132:34-36 reads:
This scripture suggests that one of the purposes of polygamy was to provide an Abrahamic-like test for the early Saints. Many people recalled how difficult it was to practice polygamy.
Hellen Mar Kimball recalled:
I did not try to conceal the fact of its having been a trial, but confessed that it had been one of the severest of my life; but that it had also proven one of the greatest of blessings. I could truly say it had done the most towards making me a Saint and a free woman, in every sense of the word; and I knew many others who could say the same, and to whom it had proven one of the greatest boons—a ‘blessing in disguise.'[2]
It is often not the Lord's pattern to give a multitude of reasons for His commandments, and we are often left to draw our own conclusions—which may be completely wrong (Moses 5꞉6-8). We often obey when we do not understand why a command has been given—we only know that it has been given. We should remember the caution of Elder Dallin H. Oaks:
...It's not the pattern of the Lord to give reasons. We can put reasons to commandments. When we do we're on our own. Some people [have] put reasons to [commandments] and they turned out to be spectacularly wrong.[3]
Trying to fully understand the purposes behind such a commandment in today's mindset can also make this subject difficult. It is important to note that we do not have all the historical information surrounding the inception and implementation of the practice. Rather than trying to understand the Lord's purposes in retrospect on a limited scope, one should remember the above scriptures in Jacob and D&C 132. Other benefits, although potentially advantageous, are not given as reasons by the Lord.
If the only purpose of polygamy, at least in Joseph Smith's case, was to "raise up seed," then why did Joseph not have children by his plural wives? He was certainly capable of having children, as demonstrated by those that he had by Emma, many of whom died. Yet, there is no conclusive evidence to date of Joseph having had children by any of his plural wives, and DNA testing has ruled out most of those who were suspected of being such.
Joseph was commanded to restore the practice of polygamy as part of the "restoration of all things." It was obviously not intended that Joseph use the practice to produce progeny.
Among Joseph's plural marriages and/or sealings, between eight to eleven of them were to women who were already married. Of the eight well-documented cases, five of the husbands were Latter-day Saints, and the other three were either not active in or not associated with the Church. In all cases, these women continued to live with their husbands, most of them doing so until their husbands died. These eternal marriages appear to have had little effect upon the lives of the women involved, with the exception that they would be sealed to Joseph in the afterlife rather than to their earthly husbands. No children from these marriages have ever been identified. These were sealings which would only affect Joseph's association with these women in the afterlife.
Both modern and 19th century members of the Church have proposed a variety of explanations for the practice of plural marriage. Not all of these suggestions can be supported by the available data. |
|
Joseph identified four reasons for the restoration of plural marriage. |
|
Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. |
|
Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. |
Any such list as this is therefore tentative. Any or all of these things could have been intended by the Lord for the benefit of the Church and the Saints. A few of these benefits which have been suggested include:
Other benefits which we do not yet see or understand could also have been intended. But, it reminds us plural marriage may have accomplished more than we sometimes appreciate.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Faithful Mormon and wife of Joseph Smith, Sylvia Sessions (Lyon), on her deathbed told her daughter, Josephine, that she (Josephine) was the daughter of Joseph Smith. Josephine testified: "She (Sylvia) then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith, she having been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon was out of fellowship with the Church."Author's sources: Affidavit to Church Historian Andrew Jenson, 24 Feb. 1915
The record is frustratingly incomplete regarding the question of which marriages were consummated, it is likewise spotty with regards to whether Joseph fathered children by his plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to consider this question in any detail, though her standard of evidence was depressingly low. Subsequent authors have returned to the problem, though unanimity has been elusive (see Table 1). Ironically, Brodie did not even mention the case of Josephine Lyon, now considered the most likely potential child of Joseph.
Notation:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36]
It is claimed that Joseph Smith fathered children with some of his plural wives, and that he covered up the evidence of pregnancies. It is also claimed that Joseph Smith had intimate relations with other men’s wives to whom he had been sealed, and that children resulted from these unions.
Critics of Joseph Smith have long had difficulty reconciling their concept of Joseph as a promiscuous womanizer with the fact that the only recorded children of the prophet are those that he had with Emma. Science is now shedding new light on this issue as DNA research has eliminated most of the possibilities that had long been rumored to be descendants of Joseph Smith. In the case of at least two, however, DNA cannot tell us either way. The historical reasoning for justifying that Joseph had children by these wives is dubious.
DNA analysis has determined that Josephine Fisher is not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr., [37] but for many years she appeared to be the strongest possibility. The resolution of this question was difficult to resolve until the appropriate DNA analysis techniques became available. These findings have been replicated in non-Latter-day Saint, peer-reviewed, reputable journals.[38]
The case of Josephine Fisher relied on a deathbed conversation:
Just prior to my mothers death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret from me and from all others but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith….[39]
Perhaps significantly, Josephine's name shares a clear link with Joseph's. Whether this account proved that she was his biological daughter had long been debated:
Rex Cooper…has questioned the interpretation that Smith was Fisher's biological father. He posits that because Fisher's mother was sealed to Smith, Fisher was his daughter only in a spiritual sense…More problematic is whether there is a discrepancy between what Fisher understood and what her mother meant. That is, did Fisher interpret her mother's remarks to mean she was the biological daughter of Joseph Smith and thus state that with more certitude than was warranted, when in fact her mother meant only that in the hereafter Fisher would belong to Joseph Smith's family through Session's sealing to him? Because Sessions was on her deathbed, when one's thoughts naturally turn to the hereafter, the latter is a reasonable explanation.[40]
As Danel Bachman notes, however, there seems to be relatively little doubt that
[t]he desire for secrecy as well as the delicacy of the situation assure us that Mrs. Sessions was not merely explaining to her daughter that she was Smith's child by virtue of a temple sealing. The plain inference arising from Jenson's curiosity in the matter and Mrs. Fisher's remarks is that she was, in fact, the offspring of Joseph Smith.[41]
However, DNA evidence now disproves this theory. It is possible, then, that Fisher misunderstood her mother, but this seems unlikely. Any unreliability is more likely to arise because of a dying woman's confusion than from miscommunication. No evidence exists for such confusion, though we cannot rule it out.
Josephine's account is also noteworthy because her mother emphasizes that "…she [had] been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon was out of fellowship with the Church."[42] This may explain her reasoning for being sealed to Joseph at all—her husband was out of fellowship. Todd Compton opines that "[i]t seems unlikely that Sylvia would deny [her husband] cohabitation rights after he was excommunicated," but this conclusion seems based on little but a gut reaction.[43] These women took their religion seriously; given Sylvia's deathbed remarks, this was a point she considered important enough to emphasize. She apparently believed it would provide an explanation for something that her daughter might have otherwise misunderstood.
There is also clear evidence that at least some early members of the Church would have taken a similar attitude toward sexual relations with an unbelieving spouse. My own third-great grandfather, Isaiah Moses Coombs, provides a striking illustration of this from the general membership of the Church.
Coombs had immigrated to Utah, but his non-member spouse refused to accompany him. Heartsick, he consulted Brigham Young for advice. Young "sat with one hand on my knee, looking at my face and listen[ing] attentively." Then, Young took the new arrival "by the hand in his fatherly way," and said "[Y]ou had better take a mission to the States…to preach the gospel and visit your wife…visit your wife as often as you please; preach the gospel to her, and if she is worth having she will come with you when you return to the valley. God bless and prosper you."[44]
Coombs did as instructed, but was not successful in persuading his wife. His description of his thoughts is intriguing, and worth quoting at length:
I may as well state here, however, that during all my stay in the States, [my wife and I] were nothing more to each other than friends. I never proposed or hinted for a closer intimacy only on condition of her baptism into the Church. I felt that I could not take her as a wife on any other terms and stand guiltless in the sight of God or my own conscience…I could not yield to her wishes and she would not bend to mine. And so I merely visited her as a friend. This was a source of wonder to our mutual acquaintances; and well it might be for had not my faith been founded on the eternal rock of Truth, I never could have stood such a test, I never could have withstood the temptations that assailed me, but I should have yielded and have abandoned myself to the life of carnal pleasure that awaited me in the arms of my beautiful and adored wife. She was now indeed beautiful. I had thought her lovely as a child—as a maiden she had seemed to me surpassing fair, but as a woman with a form well developed and all the charms of her persona matured, she far surpassed in womanly beauty anything I had ever dreamed of.[45]
Coombs' account is startlingly blunt and explicit for the age. Yet, if this young twenty-two-year-old male refused marital intimacy with his wife (whom he married knowing their religious differences), Compton's confidence that Sylvia Sessions would not deny marital relations to her excommunicated husband seems misplaced. Sessions may, like Coombs, have seen her faithfulness to the sealing ordinances sufficient to "eventually either in this life or that which is to come enable me to bind my [spouse] to me in bands that could not be broken." Like him, she may have believed that "[My spouse] was blind then but the day would come when [he] would see."[46]
More importantly, however, is Brian Hales’ more recent work, which demonstrates that Sylvia Sessions Lyon may well have not been married to her husband when sealed to Joseph Smith, contrary to Compton’s conclusion. Thus, rather than being a case of polyandry with sexual relations with two men (Joseph and her first husband) Lyons is instead a case of straight-forward plural marriage.[47] Given that Joseph has been ruled out as Josephine's father, it may be that Sylvia's emphasis to Josephine about being Joseph's "daughter" referred to a spiritual or sealing sense, and she wished to explain to her daughter why Josephine was, then, sealed to Joseph Smith rather than her biological father.
Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[48]
Angus M. Cannon seems to have been aware of Fisher's claim to be a child of Joseph Smith, though only second hand. He told a sceptical Joseph Smith III of
one case where it was said by the girl's grandmother that your father has a daughter born of a plural wife. The girl's grandmother was Mother Sessions, who lived in Nauvoo and died here in the valley. Aunt Patty Sessions asserts that the girl was born within the time after your father was said to have taken the mother.[49]
Clearly, Cannon has no independent knowledge of the case, but reports a story similar to Josephine's affidavit. Cannon's statement is more important because it illustrates how the LDS Church's insistence that Joseph Smith had practiced plural marriage led some of the RLDS Church :to ask why no children by these wives existed. Lucy Walker reported [the RLDS] seem surprised that there was no issue from asserted plural marriages with their father. Could they but realize the hazardous life he lived, after that revelation was given, they would comprehend the reason. He was harassed and hounded and lived in constant fear of being betrayed by those who ought to have been true to him.[50] Thus the absence of children was something of an embarrassment to the Utah Church, which members felt a need to explain. It would have been greatly to their advantage to produce Joseph's offspring, but could not.[51]
Anxious to demonstrate that Joseph's plural marriages were marriages in the fullest sense, Lucy M. Walker (wife of Joseph's cousin, George A. Smith) reported seeing Joseph washing blood from his hands in Nauvoo. When asked about the blood, Joseph reportedly told her he had been helping Emma deliver one of his plural wives' children.[52] Yet, even this late account tells us little about the paternity of the children—Joseph was close to these women (and their husbands, in the case of polyandry), and given the Saints' belief in priesthood blessings, they may have well welcomed his involvement.
Even by the turn of the century, the LDS Church had no solid evidence of children by Joseph. "I knew he had three children," said Mary Elizabeth Lightner, "They told me. I think two of them are living today but they are not known as his children as they go by other names."[53] Again, evidence for children is frustratingly vague—Lightner had only heard rumours, and could not provide any details. It would seem to me, however, that this remark of Lightner's rules out her children as possible offspring of Joseph. Her audience was clearly interested in Joseph having children, and she was happy to assert that such children existed. If her own children qualified, why did she not mention them?
Two of Marinda Nancy Johnson Hyde's children have been suggested as possible children. The first, Orson, died in infancy, making DNA testing impossible. Compton notes, however, that "Marinda had no children while Orson was on his mission to Jerusalem, then became pregnant soon after Orson returned home. (He arrived in Nauvoo on December 7, 1842, and Marinda bore Orson Washington Hyde on November 9, 1843),"[54] putting the conception date around 16 February 1843.
Frank Hyde's birth date is unclear; he was born on 23 January in either 1845 or 1846.[55] This would place his conception around 2 May, of either 1844 or 1845. In the former case, Frank was conceived less than two months prior to Joseph's martyrdom. Orson Hyde left for Washington, D.C., around 4 April 1844,[56] and did not return until 6 August 1844, making Joseph's paternity more likely than Orson's if the earlier birth date is correct.[57] The key source for this claim is Fawn Brodie, who includes no footnote or reference. Given Brodie's tendency to misread evidence on potential children, this claim should be approached with caution.
Frank's death certificate lists Orson Hyde as the father, however, and places his birth in 1846, which would require conception nearly a year after Joseph's death.[58] A child by Joseph would have brought prestige to the family and Church, and Orson and Nancy had divorced long before Frank Henry's death.[59] It seems unlikely, therefore, that Orson would be credited with paternity over Joseph if any doubt existed. Without further data, Brodie's dating should probably be regarded as an error, ruling out Joseph as a possible father.
Scientific ingenuity has also been applied to the question of Joseph's paternity. Y-chromosome studies have conclusively eliminated Orrison Smith (son of Fanny Alger), Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, John Reed Hancock, Moroni Llewellyn Pratt, and Oliver Buell as Joseph's offspring.[60]
Two additional children—George Algernon Lightner and Orson W. Hyde—died in infancy, leaving no descendants to test, though as noted above Lightner can probably be excluded on the basis of his mother's testimony.
The testing of female descendants' DNA is much move involved, but work continues and may provide the only definitive means of ruling in or out potential children.
The case of Oliver Buell is an interesting one, since Fawn Brodie was insistent that he was Joseph's son. She based part of this argument on a photograph of Buell, which revealed a face which she claimed was "overwhelmingly on the side of Joseph's paternity."[61] A conception on this date would make Oliver two to three weeks overdue at birth, which makes Brodie's theory less plausible.[62]
Furthermore, prior the DNA results, Bachman and Compton pointed out that Brodie's timeline poses serious problems for her theory—Oliver's conception would have had to occurred between 16 April 1839 (when Joseph was allowed to escape during a transfer from Liberty Jail)[63] and 18 April, when the Huntingtons left Far West.[64] Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois to the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack, while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order in force.[65] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun's Mill, along Shoal Creek.[66] Yet, by 22 April Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by travel "off from the main road as much as possible"[67] "both by night and by day."[68] This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be meeting a woman, much less conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other Church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the prophet’s direction, who did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois.[69]
Brodie's inclusion of Oliver Buell is also inconsistent, since he was born prior to Joseph's sealing to Prescinda. By including Oliver as a child, Brodie wishes to paint Joseph as an indiscriminate womanizer. Yet, her theory of plural marriage argues that Joseph "had too much of the Puritan in him, and he could not rest until he had redefined the nature of sin and erected a stupendous theological edifice to support his new theories on marriage."[70] Thus, Brodie argues that Joseph created plural marriage to justify his immorality—yet, she then has him conceiving a child with Prescinda before being sealed to her. By her own argument, the paternity must therefore be seen as doubtful.[71]
Despite Brodie's enthusiasm, no other author has included Oliver on their list of possible children (see Table 1). And, DNA evidence has conclusively ruled him out. Oliver is an excellent example of Brodie's tendency to ignore and misread evidence which did not fit her preconceptions, and suggests that caution is warranted before one condemns Joseph for a pre-plural marriage "affair" or other improprieties. Since Brodie was not interested in giving Joseph the benefit of the doubt, or avoiding a rush to judgment, her decision is not surprising.
John Reed Hancock is another of Brodie's suggestions, though no other author has followed her. The evidence for Joseph having married Clarissa Reed Hancock is scant,[72] and as with Oliver Buell it is unlikely (even under Brodie's jaded theory of plural marriage as justification for adultery) that Joseph would have conceived a child with a woman to whom he was not polygamously married. DNA testing has since confirmed our justified scepticism of Brodie's claim.[73]
Bachman mentions a "seventh child" of Prescinda's, likely John Hyrum Buell, for whom the timeline would better accommodate conception by Joseph Smith. There is no other evidence for Joseph's paternity, however, save Ettie V. Smith's account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years Among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Prescinda said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hyrum's father.[74] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[75]
Besides being implausible, Ettie gets virtually every other detail wrong—she insists that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions, only to return and find their wives being courted by Joseph. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[76] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions, and their wives did not charge that Joseph had propositioned them. Jacobs had served missions, but was present during Joseph's sealing to his wife, and did not object (see Chapter 9). Jacobs was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[77] and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[78] as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[79]
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hyrum as a potential child (and carelessly misreads Ettie Smith's remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hyrum). No other historian has even mentioned this child, much less argued that Buell was not the father (see Table 1).
A few other possibilities should be mentioned, though the evidence surrounding them is tenuous. Sarah Elizabeth Holmes was born to Marietta Carter, though "No evidence links her with Joseph Smith."[80] The Dibble children suffer from chronology problems, and a lack of good evidence that Joseph and their mother was associated. Loren Dibble was, however, claimed by some Mormons as a child of Joseph’s when confronted with Joseph Smith III’s skepticism.[81]
Joseph Albert Smith was born to Esther Dutcher, but the available evidence supports her polyandrous sealing to Joseph as for eternity only. Carolyn Delight has no evidence at all of a connection to Joseph—the only source is a claim to Ugo Perego, a modern DNA researcher.[82] No textual or documentary evidence is known for her at all.
We have elsewhere seen the tenuous basis for many conclusions about the Fanny Alger marriage (see here and here). The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[83] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
A family tradition—repeated by anti-Mormon Wyl—holds that Eliza R. Snow was pregnant and shoved down the stairs by a jealous Emma before being required to leave the Smith home.[84] The tradition holds that Eliza, "heavy with child" subsequently miscarried. While Eliza was required to leave the home and Emma was likely upset with her, no contemporary evidence points to a pregnancy.[85] Eliza's diary says nothing about the loss of a child, which would be a strange omission given her love of children.[86] It seems unlikely that Eliza would have still been teaching school in an advanced state of pregnancy, especially given that her appearance as a pregnant "unwed mother" would have been scandalous in Nauvoo. Emma's biographers note that "Eliza continued to teach school for a month after her abrupt departure from the Smith household. Her own class attendance record shows that she did not miss a day during the months she taught the Smith children, which would be unlikely had she suffered a miscarriage."[87] Given Emma's treatment of the Partridge sisters, who were also required to leave the Smith household, Emma certainly needed no pregnancy to raise her ire against Joseph's plural wives.
Eliza repeatedly testified to the physical nature of her relationship with Joseph Smith (see Chapter 9), and was not shy about criticizing Emma on the subject of plural marriage.[88] Yet, she never reported having been pregnant, or used her failed pregnancy as evidence for the reality of plural marriage.
In the absence of further information, both of these reported pregnancies must be regarded as extremely speculative.
Sylvia was married to Windsor Lyon by Joseph Smith in Nauvoo. She was sealed to Joseph Smith at some point after she was married. Brian Hales notes that , "This marriage triangle is unique among all of the Prophet’s plural marriages because there is strong evidence that Sylvia bore children to both men. She became pregnant by Windsor Lyon in October of 1838, September of 1840, and April of 1842. Then a year later became pregnant with a daughter (named Josephine—born February 8, 1844) that was purportedly fathered by the Prophet." Sylvia's daughter, who had the intriguing name "Josephine," made the following statement:
Just prior to my mothers [Sylvia Sessions Lyon] death in 1882 she called me to her bedside and told me that her days on earth were about numbered and before she passed away from mortality she desired to tell me something which she had kept as an entire secret fro me and from others until no but which she now desired to communicate to me. She then told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith, she having been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon had was out of fellowship with the Church.
For many years, Josephine appeared to be the only viable candidate as a child of Joseph Smiths "polyandrous" sealings. However, DNA analysis ultimately disproved the paternity claim: Josephine was not a descendant of Joseph Smith, Jr.[89]
It appears, however, that Sylvia may have considered herself divorced from Windsor after he was excommunicated from the Church and left Nauvoo. Hales points out that "Currently, no documentation of a legal divorce between Windsor and Sylvia after his excommunication has been found. However, in the mid-nineteenth century, religious laws often trumped legal proceedings. Stanley B. Kimball observed: 'Some church leaders at that time considered civil marriage by non-Mormon clergymen to be as unbinding as their baptisms. Some previous marriages . . . were annulled simply by ignoring them.'" [90] The sealing to Joseph occurred after Windor's excommunication. Andrew Jenson, in his historical record, referred to Sylvia as a "formerly the wife of Windsor Lyons." [91] There is no known evidence that Windsor lived with Sylvia after he returned to Nauvoo, but Sylvia did "rejoin" Windsor after he was rebaptised in 1846. Hales states, "No details are available to clarify what authority was used to reconfirm the marriage relationship between Sylvia and Windsor after their previous marital separation. Most likely the couple consulted with Brigham Young or Heber C. Kimball, who authorized their rejoining. Whether a private religious marriage ceremony for time was performed or the couple resumed observing their legal marriage is unknown. Importantly, even with the renewed conjugality between Windsor and Sylvia after Joseph Smith’s death, no evidence has been found to support her involvement in sexual polyandry at any time." [92]
It is claimed that Prescindia Lathrop Huntington Buell admitted that she did not know who was the father of her child—Joseph Smith or her first husband. Sometimes Sarah Pratt (wife of apostle Orson Pratt) is mistakenly identified as the woman in this story. [93] Others sometimes mention Orson Hyde's wife as the source of this rumor. [94]
The source for this claim is a notoriously unreliable anti-Mormon work. It makes several errors of fact in the very paragraph in which the claim is made.
It is implausible that the supposed admission upon which the claim is based would be made. There are major historical problems of geography and timeline for Joseph to have even been a potential father of Buell's child.
The claim cannot be substantiated.
This book was written by Nelson Winch Green, who reported what estranged member Marry Ettie V. Coray Smith reportedly told him.
Even other anti-Mormon authors who had lived in Utah regarded it as nearly worthless. Fanny Stenhouse wrote:
Much has already been written on this subject much that is in accordance with facts, and much that is exaggerated and false. Hitherto, with but one exception [Mrs. Ettie V. Smith is noted in the footnote as the work referred to] that of a lady who wrote very many years ago, and who in her writings, so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where the one ended and the other began no woman who really was a Mormon and lived in Polygamy ever wrote the history of her own personal experience. Books have been published, and narratives have appeared in the magazines and journals, purporting to be written by Mormon wives; it is, however, perhaps, unnecessary for me to state that, notwithstanding such narratives may be imposed upon the Gentile world as genuine, that they were written by persons outside the Mormon faith would in a moment be detected by any intelligent Saint who took the trouble to peruse them. [95]
So, we must remember that this work is not regarded as generally reliable today, and it was not regarded as reliable even by the Church's enemies in the 19th century.
The source for this claim is an anti-Mormon book. The relevant passage reads:
The Prophet had sent some time before this, three men, Law, Foster and Jacobs, on missions, and they had just returned, and found their wives blushing under the prospective honors of spiritual wifeism; and another woman, Mrs. Buel [sic], had left her husband, a Gentile, to grace the Prophet's retinue, on horseback, when he reviewed the Nauvoo Legion. I heard the latter woman say afterwards in Utah, that she did not know whether Mr. Buel [sic] or the Prophet was the father of her son. These men [Law, Foster and Jacobs] established a press in Nauvoo, to expose his alleged vicious teachings and practices, which a revelation from Joseph destroyed. [96]
As might be expected, then, there are many claims in this passage that are in error. We know that the following are false:
Thus, in the single paragraph we have several basic errors of fact. Why should we believe the gossip of what Mrs. Buell is claimed to have said?
Furthermore, such an admission would be out of character for a believing Utah woman of the 19th century. As Todd Compton notes:
Talk of sexuality was avoided by the Victorian, puritanical Mormons; in diaries, the word 'pregnant' or 'expecting' is never or rarely used. Women are merely 'sick' until they have a child. Polyandry was rarely discussed openly by Mormon women. [97]
Fawn Brodie painted a fanciful scenario in which Joseph would have been able to potentially father a Buell child. However, she misread the historical information, and it is difficult, as Todd Compton has demonstrated, for Joseph to have even had contact with her at the proper time to conceive a child. [98] This would suggest that there were no grounds for Mrs. Buell—or a modern reader—to conclude that Joseph might have been the father.
Nauvoo Polygamy author George D. Smith tells his readers that "until decisive DNA testing of possible [Joseph] Smith descendants—daughters as well as sons—from plural wives can be accomplished, ascertaining whether Smith fathered children with any of his plural wives remains hypothetical" (pp. 228–29, cf. p. 473). This is true, but G. D. Smith fails to tell us that all those who have been definitively tested so far—Oliver Buell, Mosiah Hancock, Zebulon Jacobs, Moroni Pratt, and Orrison Smith—have been excluded. Would he have neglected, I wonder, to mention a positive DNA test?
The consequences of George D. Smith's less-than-rigorous approach to sources becomes clear in the case of Oliver Buell, son of Presendia.[99] Huntington Buell, one of Joseph’s polyandrous plural wives. Fawn Brodie was the first to suggest that Oliver Buell was Joseph’s son, and she was so convinced (based on photographic evidence)[100]Fawn Brodie to Dale Morgan, Letter, 24 March 1945, Dale Morgan papers, Marriott Library, University of Utah; cited by Todd Compton, "Fawn Brodie on Joseph Smith's Plural Wives and Polygamy: A Critical View," in Reconsidering No Man Knows My History: Fawn M. Brodie and Joseph Smith in Retrospect, ed. Newell G. Bringhurst (Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press, 1996), 166.</ref> In a footnote, G. D. Smith notes that Todd Compton "considers it improbable that Joseph and Presendia would have found time together during the brief window of opportunity after his release from prison in Missouri" (p. 80 n. 63).[101]
This slight nod toward an opposite point of view is inadequate, however. G. D. Smith does not mention and hence does not confront the strongest evidence. Compton’s argument against Joseph’s paternity does not rest just on a "narrow window" of opportunity but on the fact that Brodie seriously misread the geography required by that window. It is not merely a question of dates. Brodie would have Joseph travel west from his escape near Gallatin, Davies County, Missouri, to Far West in order to meet Lucinda, and then on to Illinois toward the east. This route would require Joseph and his companions to backtrack while fleeing from custody in the face of an active state extermination order.[102] Travel to Far West would also require them to travel near the virulently anti-Mormon area of Haun’s Mill, along Shoal Creek.[103] Yet by April 22 Joseph was in Illinois, having been slowed by traveling "off from the main road as much as possible"[104]:320-321 "both by night and by day."[104]:327 This seems an implausible time for Joseph to be conceiving a child. Furthermore, it is evident that Far West was evacuated by other church leaders, "the committee on removal," and not under the Prophet’s direction. Joseph did not regain the Saints until reaching Quincy, Illinois, contrary to Brodie’s misreading.[104]:315, 319, 322-23, 327 Timing is the least of the problems with G. D. Smith’s theory.
Despite Brodie’s enthusiasm, few other authors have included Oliver on their list of possible children.[105] With so many authors ranged against him, G. D. Smith ought not to act as if Compton’s analysis is merely about dates.
G. D. Smith also soft-pedals the most vital evidence—the DNA.[106] He makes no mention in the main text that Oliver’s paternity has been definitively ruled out by DNA testing. This admission is confined to a footnote, and its impact is minimized by its placement. After noting Compton’s disagreement with the main text’s suggestion that Oliver might be Joseph’s son, G. D. Smith writes, "There is no DNA connection," and cites a Deseret News article. He immediately follows this obtuse phrasing with a return to Compton, who finds it "‘unlikely, though not impossible, that Joseph Smith was the actual father of another Buell child,’ John Hiram, Presendia’s seventh child during her marriage to Buell and born in November 1843" (p. 80 n. 63). Thus the most salient fact—that Joseph is certainly not Oliver's father—is sandwiched between a vicarious discussion with Compton about whether Oliver or John could be Joseph’s sons. Since G. D. Smith knows there is definitive evidence against Joseph’s paternity in Oliver’s case, why mention the debate at all only to hide the answer in the midst of a long endnote? That Brodie is so resoundingly rebutted on textual, historical, and genetic grounds provides a cautionary lesson in presuming that her certainty counts for much.[107]
Two pages later, G. D. Smith again tells us of a Buell child being sealed to a proxy for Joseph with "wording [that] hints that it might have been Smith’s child." "It is not clear," he tells us, "which of her children it might have been" (p. 82). In fact, what is clear is that he has not assimilated the implications of the DNA data. John Hiram, the seventh child about whom Compton is skeptical, is the only other option. Yet the only evidence for this child belonging to Joseph is Ettie V. Smith’s account in the anti-Mormon Fifteen Years among the Mormons (1859), which claimed that Presendia said she did not know whether Joseph or her first husband was John Hiram’s father.[108] As Compton notes, such an admission is implausible, given the mores of the time.[109]
Besides being implausible, Ettie’s account gets virtually every other detail wrong—insisting that William Law, Robert Foster, and Henry Jacobs had all been sent on missions only to return to find Joseph preaching plural marriage. Ettie then has them establish the Expositor.[110] While Law and Foster were involved with the Expositor, they were not sent on missions. Jacobs had served missions but was a faithful Saint unconnected to the Expositor. He was also, contrary to Ettie’s claims, present when Joseph was sealed polyandrously to his (Jacobs’s) wife.
Even the anti-Mormon Fanny Stenhouse considered Ettie Smith to be a writer who "so mixed up fiction with what was true, that it was difficult to determine where one ended and the other began,"[111]:618 and a good example of how "the autobiographies of supposed Mormon women were [as] unreliable"[111]:x as other Gentile accounts, given her tendency to "mingl[e] facts and fiction" "in a startling and sensational manner."[111]:xi-xii
Brodie herself makes no mention of John Hiram as a potential child, going so far as to carelessly misread Ettie Smith’s remarks as referring to Oliver, not John Hiram. No other historian has argued that Buell was not the father.[112] There is no good evidence whatever that any of Presendia’s children were Joseph’s. It is not clear why G. D. Smith clings to the idea.
Few authors agree on which children should even be considered as Joseph's potential children. Candidates which some find overwhelmingly likely are dismissed—or even left unmentioned—by others. Recent scholars have included between one to four potential children as options. Of these, Josephine Lyon was the most persuasive, until her relationship to Joseph Smith was ultimately disproven through DNA testing. Orson W. Hyde died in infancy, and so can never be definitively excluded as a possible child, though the dates of conception argue against Joseph's paternity. Olive Gray Frost is mentioned in two sources as having a child by Joseph. Both she and the child died in Nauvoo, so no genetic evidence will ever be forthcoming.[113]
This table is in the same order as Table 1.
Notation:
Brodie;[114] Bachman;[115]; and Compton.[116]
As always, we are left where we began—with more suspicions and possibilities than certitudes. One's attitude toward Joseph and the Saints will influence, more than anything else, how these conflicting data are interpreted.
The uncertainty surrounding Joseph's offspring is even more astonishing when we appreciate how much such a child would have been valued. The Utah Church of the 19th century was anxious to prove that Joseph had practiced full plural marriage, and that their plural families merely continued what he started. Any child of Joseph's would have been treasured, and the family honoured. There was a firm expectation that even Joseph's sons by Emma would have an exalted place in the LDS hierarchy if they were to repent and return to the Church.[117] As Alma Allred noted, "Susa Young Gates indicated that [Brigham Young] wasn’t aware of such a child when she wrote that her father and the other apostles were especially grieved that Joseph did not have any issue in the Church."[118]
In 1884, George Q. Cannon bemoaned this lack of Joseph's posterity:
There may be faithful men who will have unfaithful sons, who may not be as faithful as they might be; but faithful posterity will come, just as I believe it will be the case with the Prophet Joseph's seed. To-day he has not a soul descended from him personally, in this Church. There is not a man bearing the Holy Priesthood, to stand before our God in the Church that Joseph was the means in the hands of God, of founding—not a man to-day of his own blood,—that is, by descent,—to stand before the Lord, and represent him among these Latter-day Saints.[119]
Brigham and Cannon, a member of the First Presidency, would have known of Joseph's offspring if any of the LDS leadership did. Yet, despite the religious and public relations value which such a child would have provided, they knew of none. It is possible that Joseph had children by his plural wives, but by no means certain. The data are surprisingly ephemeral.
Doctrine and Covenants 132꞉63 states,
But if one or either of the ten virgins, after she is espoused, shall be with another man, she has committed adultery, and shall be destroyed; for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men; for herein is the work of my Father continued, that he may be glorified.
Polygamy was not permitted only for the purpose of procreation. Joseph established the practice of plural marriage as part of the "restoration of all things," (D&C 132: 40, 45) and introduced it to a number of others within the Church. This alone may have been the purpose of Joseph's initiation of the practice. The establishment of the practice ultimately did have the effect of "raising up seed"...just not through Joseph Smith.
As Brian Hales writes:
Joseph Smith dictated what is now Doctrine and Covenant section 132 on July 12, 1843. This revelation, along with his other statements, provide several reasons why he believed plural marriage could be introduced among the Latter-day Saints.The earliest justification mentioned by the Prophet was as a part of the "restitution of all things" prophesied in Acts 3:19–21. Old Testament prophets practiced polygamy, so it could be a part of the restoration of "all things" (see D&C 132:40, 45).
Several members who knew Joseph Smith left accounts of him referring to a connection between the two during the Kirtland period.
Benjamin F. Johnson recalled in 1903: "In 1835 at Kirtland I learned from my Sisters Husband, Lyman R. Shirman,[120] who was close to the Prophet, and Received it from him. That the ancient order of plural marriage was again to be practiced by the Church."[121]
A few years later in 1841, Joseph Smith attempted to broach the topic publicly. Helen Mar Kimball remembered: "He [Joseph] astonished his hearers by preaching on the restoration of all things, and said that as it was anciently with Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, so it would be again, etc."[122] Joseph Smith was a prophet-restorer, which helps to explain why the command to practice plural marriage has been labeled a "restoration," even though it is not a salvific ordinance.[123]
Brian Hales addresses one aspect of D&C 132 that may be overlooked in casual readings:
The fourth reason Joseph Smith gave for the practice of plural marriage dwarfs the other three explanations in significance because it deals with eternity. The message of D&C 132:16–17 states that men and women who are not sealed in eternal marriages during this life (or vicariously later) "remain separately and singly, without exaltation, in their saved condition, to all eternity."In other words, "exaltation," the highest salvation, requires eternal marriage. No unmarried person can be exalted according to Joseph Smith’s teachings. Doctrine and Covenants section 132 seems to anticipate more worthy women than men as it approves a plurality of wives[124] and disallows a plurality of husbands.[125] Verse 63 states that a plurality of wives is "for their [the wives] exaltation in the eternal worlds." Section 132 supports that eternity was the primary focus of the Joseph’s marriage theology rather than plurality or sexuality. Eternal, rather than plural, marriage was his zenith doctrine. It appears that the crucial objective of polygamy on earth was to allow all worthy women to be eternally sealed to a husband and thus obtain all the ordinances needed for exaltation. According to these teachings, a plurality of wives in some form may be practiced in eternity, but not by all worthy men and women. We know that polygamy on earth is unequal and difficult, but we know nothing about how eternal marriage or eternal plural marriage might feel in eternity. Brigham Young acknowledged that eternal marriage (not plural marriage) is "the thread which runs from the beginning to the end" in God’s plan for His children:
The whole subject of the marriage [not plural marriage] relation is not in my reach, nor in any other man’s reach on this earth. It is without beginning of days or end of years; it is a hard matter to reach. We can tell some things with regard to it; it lays the foundation for worlds, for angels, and for the Gods; for intelligent beings to be crowned with glory, immortality, and eternal lives. In fact, it is the thread which runs from the beginning to the end of the holy Gospel of salvation—of the Gospel of the Son of God; it is from eternity to eternity.[126][127]
Another author commenting on this verse made a compelling case for this theology being put into D&C 132: 63:
Here is the text in its entirety, from verse 62: "for they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, and to fulfil the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world, and for their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men." [Emphasis added.] You want to get legalistic? Let’s get legalistic. Just for fun, let’s parse the living snot out of this.This clause begins with multiplying and replenishing as a primary justification. Then we get the word "and" thrown in there. You’re reading this as if it says "they are given unto him to multiply and replenish the earth, according to my commandment, in order to fulfil the promise…" But that’s not what it says.
"And" suggests we’re about to get a second reason, not a clarification of the first. In fact, a tight, strict-constructionist reading of this verse reveals three different and distinct reasons for plural marriage, not "only" the replenishment of the earth, [. . .]So let’s review the three reasons:
1. Multiply and replenish the earth.
[. . .] D&C 132 is unequivocal on this point, just as it is unequivocal on the two points that follow.
2. Fulfil [sic] "the promise which was given by my Father before the foundation of the world."
What promise? This seems to have reference to the "restitution of all things, which God hath spoken by the mouth of all his holy prophets since the world began." (Acts 3:21) Joseph cited the need to restore ancient practices to prepare for the Second Coming as a justification for polygamy, and this verse provides a credible scriptural context for him to do so. So just relying on this phrase – plural marriage is acceptable because it fulfills God’s promises – would be justification enough for the practice, at least according to D&C 132.
3. For "their exaltation in the eternal worlds, that they may bear the souls of men."
Oh, this one’s my favorite. Notice the emphasis I added on the "that." The word appears there to create a conditional clause. You claim the bearing of souls is the same thing as multiplying and replenishing the earth, but the actual text insists that the bearing of the souls of men will only be made possible by "exaltation in the eternal worlds." This is a promise of eternal increase, of bearing souls after the earth is no longer around to be replenished. Big, big difference.
And right here, with Reason #3, we have a clear rationale and justification for Joseph being sealed to women with whom he made no attempts to multiply and replenish the earth – i.e. no sex.[128]
Both modern and 19th century members of the Church have proposed a variety of explanations for the practice of plural marriage. Not all of these suggestions can be supported by the available data. |
|
Joseph identified four reasons for the restoration of plural marriage. |
|
Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. |
|
Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. |
Some wonder if sexual relations were included in Joseph Smith’s plural marriages. The answer is yes or no, depending upon the type of plural marriage. Those marriages, often called “sealings,” were of two types. Some were for this life and the next (called “time-and-eternity”) and could include sexuality on earth. Others were limited to the next life (called “eternity-only”) and did not allow intimacy in mortality. Overall, evidence indicates that less than half of Joseph Smith’s polygamous unions were consummated and sexual relations in the others occurred infrequently. |
|
It appears the Prophet experienced sexual relations with less than half of the women sealed to him. There is no credible evidence that Joseph had sex with three subgroups of his plural wives: (1) fourteen-year-old wives, (2) non-wives (or women to whom he was not married), and (3) legally married women who were experiencing conjugal relations with their civil husbands. |
|
No children are known to have been born to Joseph and his plural wives. |
Notes
When Joseph supposedly propositioned (or actually had sex with) fifteen year old Nancy Marinda Johnson, Dr. Dennison, with the encouragement of a neighborhood mob, nearly castrated him. Why would the mob try to castrate him? Castration is used as a penalty for sexual crimes only. The castration attempt is acknowledged by pro-LDS scholar Susan Easton, although she does not say why the Johnson brothers attempted to castrate Joseph.
Some critics believe that Joseph may have gotten some of his wives pregnant but had them get abortions. This is what Sarah Pratt, whom Joseph excommunicated for refusing to have sex with him, said to Smith's son.
FARMS reviewer Gregory L. Smith acknowledges, 71 pages into his 86-page review of George D. Smith's new book, Nauvoo Polygamy: "…but we called it celestial marriage" ("George D. Smith's Nauvoo Polygamy," FARMS Review 20:2, 2008), that Joseph Smith had "conjugal relations" with at least eight women in addition to his first wife, Emma.
If even the FARMS apologists, FAIR apologists and faithful LDS historians acknowledge that Joseph may have had sex with his polygamous wives (including the ones already married) then why should any LDS members dispute that Joseph likely did have sex with those wives?
The fact that these women continue to live with their earthly husbands and even have children by them indicates that the sealings to Joseph Smith were not marriages in the normal sense.
The relationship between these women and their husbands appear to have not changed even after they were sealed to Joseph Smith. Of the eight well-documented cases, five of the husbands were Latter-day Saints, and the other three were either not active in or not associated with the Church. In all cases, these women continued to live with their husbands, most of them doing so until their husbands died. These eternal marriages appear to have had little effect upon the lives of the women involved, with the exception that they would be sealed to Joseph in the afterlife rather than to their earthly husbands.
The available evidence also does not support the claim that Joseph had intimate relations with these married women. Fawn Brodie, who repeatedly stated her belief that Joseph had intimate relations with many of his plural wives, identified several individuals that she thought “might” be children of Joseph Smith, Jr. Yet, even Brodie noted that “it is astonishing that evidence of other children than these has never come to light.” Brodie postulated, in spite of a complete lack of evidence, that Joseph must have been able to successfully practice some sort of primitive birth control, or that abortions must have been routinely employed.To date, DNA analysis has ruled out Joseph Smith as the father of any of the children of the women to whom he was sealed who were married to other men.
In 1915, Sylvia Sessions Lyon's daughter, Josephine, signed a statement that in 1882 Sylvia "told me that I was the daughter of the Prophet Joseph Smith, she having been sealed to the Prophet at the time that her husband Mr. Lyon was out of fellowship with the Church." It is not known whether Sylvia was referring to her daughter as being a literal descendant of Joseph Smith, or if she was referring to the fact that she had been sealed to the prophet. In any case, in 2016 the daughter was shown by DNA testing to be definitively not the biological daughter of Joseph Smith.[1]
In an article published in Mormon Historical Studies, Brian C. Hales demonstrates that Sylvia considered herself divorced prior to marrying Joseph polygamously. [2]
It's often taught that concerning the marriage of Joseph to 14 year old Helen Mar Kimball, it was Helen's father that initiated and arranged the marriage. This is not true. Before Smith approached Heber to have 14 year-old Helen as his bride, Smith called on Heber to turn over his wife, Vilate, to be Smith's wife.....So after Joseph Smith went so far as to "test" Heber C. Kimball to see if he would turn over his wife, Smith then asked for his only daughter, 14 year-old Helen.
Editor Comments: Like many polygamous wives, Helen likely hated the very idea of polygamy when first introduced to it and for many years afterward as she said in many of her writings. The negative writings by Helen seem to greatly outweigh the positive writings. This is similar to Emma Smith, who at times accepted polygamy, but most of the time was bitterly opposed to the practice. As time went on Helen may have accepted it and even felt special by being known as one of the wives of the most revered prophet. Perhaps she decided to make the best of it as she had no choice at that point. No one but Helen herself can say for sure if she really enjoyed being a polygamous wife of Joseph Smith. However, one thing we can say with conviction is that a 14 year-old girl should never have been put in that position in the first place by Joseph and by her own parents.
Smith was killed 13 months after his sealing to Helen, so he simply may not have had the opportunity to consummate their relationship before his death. However, it's a virtual certainty that he would have if he had lived. The bottom line being that it's futile for Mormon apologists to argue that Smith's sealing to Helen was "dynastic" or "spiritual" only, in an effort to show that Smith's plural marriages to young girls were proper.
1844 Sermon given by Joseph. It is clear that on May 26, 1844 Joseph lied about practicing polygamy, despite claims to the contrary.Author's sources: Joseph Smith, History of the Church, Vol. 6, pp. 410-411
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [3]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[4]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[5]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[6]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[7] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[8] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[9] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[10]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[11]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[11]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[11]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[11]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[12]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[11]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[11]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[13]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[11]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
It is true that Joseph did not always tell others about plural marriage. One critic of the Church claims, "Joseph Smith publicly lied about his practice of polygamy, and lied to his own wife (Emma) about the practice." [1]
Joseph did, however, make an attempt to teach the doctrine to the Saints. When Joseph tried to teach the doctrine, it was rejected by many Saints, including Emma, his wife. Joseph then began to teach the doctrine privately to those who would obey. A contemporary journal describes the reaction to Joseph's attempt to teach this doctrine:
When the prophet "went to his dinner," [Joseph Lee] Robinson wrote, "as it might be expected several of the first women of the church collected at the Prophet’s house with his wife [and] said thus to the prophet Joseph O mister Smith you have done it now it will never do it is all but Blassphemy you must take back what you have said to day is it is outrageous it would ruin us as a people." So in the afternoon session Smith again took the stand, according to Robinson, and said "Brethren and Sisters I take back what we said this morning and leave it as though there had been nothing said."[2]
Keeping the doctrine private was also necessary because the enemies of the Church would have used it as another justification for their assault on the Saints. Orson Hyde looked back on the Nauvoo days and indicated what the consequences of disclosure would have been:
In olden times they might have passed through the same circumstances as some of the Latter-day Saints had to in Illinois. What would it have done for us, if they had known that many of us had more than one wife when we lived in Illinois? They would have broken us up, doubtless, worse than they did.[3]
It is thus important to realize that the public preaching of polygamy—or announcing it to the general Church membership, thereby informing the public by proxy—was simply not a feasible plan.
This statement refers to Joseph's well-known declaration on 26 May 1844 in his "Address of the Prophet—His Testimony Against the Dissenters at Nauvoo". Significantly, this address was given the day after the Laws sought to have Joseph indicted for adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence. (They also sought to indict him on a charge of perjury.)
Many have criticized or been concerned by the secrecy with which Joseph instituted plural marriage without appreciating the realities of the dangers involved. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Since Joseph was sealed to his plural wives for either eternity, or for time and eternity, he did not view these relationships as constituting adultery or fornication. Therefore, under Illinois law, as long as Joseph and his plural wives did not live in an "open," or "public," manner, they were not guilty of breaking any civil law then in force in Illinois. Furthermore, this reality explains some of Joseph's public denials, since he could be truthfully said to not be guilty of the charges leveled against him: he was not committing adultery or fornication.
History of The Church 6:410-411:
I had not been married scarcely five minutes, and made one proclamation of the Gospel, before it was reported that I had seven wives. I mean to live and proclaim the truth as long as I can.
This new holy prophet [William Law] has gone to Carthage and swore that I had told him that I was guilty of adultery. This spiritual wifeism! Why, a man dares not speak or wink, for fear of being accused of this.[4]....
A man asked me whether the commandment was given that a man may have seven wives; and now the new prophet has charged me with adultery. I never had any fuss with these men until that Female Relief Society brought out the paper against adulterers and adulteresses.
Dr. Goforth was invited into the Laws' clique, and Dr. Foster and the clique were dissatisfied with that document,[5] and they rush away and leave the Church, and conspire to take away my life; and because I will not countenance such wickedness,[6] they proclaim that I have been a true prophet, but that I am now a fallen prophet.
[Joseph H.] Jackson[7] has committed murder, robbery, and perjury; and I can prove it by half-a-dozen witnesses. Jackson got up and said—"By God, he is innocent," and now swears that I am guilty. He threatened my life.
There is another Law, not the prophet, who was cashiered for dishonesty and robbing the government. Wilson Law also swears that I told him I was guilty of adultery. Brother Jonathan Dunham can swear to the contrary. I have been chained. I have rattled chains before in a dungeon for the truth's sake. I am innocent of all these charges, and you can bear witness of my innocence, for you know me yourselves.
When I love the poor, I ask no favors of the rich. I can go to the cross—I can lay down my life; but don't forsake me. I want the friendship of my brethren.—Let us teach the things of Jesus Christ. Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a downfall.
Be meek and lowly, upright and pure; render good for evil. If you bring on yourselves your own destruction, I will complain. It is not right for a man to bare down his neck to the oppressor always. Be humble and patient in all circumstances of life; we shall then triumph more gloriously. What a thing it is for a man to be accused of committing adultery, and having seven wives, when I can only find one.
I am the same man, and as innocent as I was fourteen years ago; and I can prove them all perjurers. I labored with these apostates myself until I was out of all manner of patience; and then I sent my brother Hyrum, whom they virtually kicked out of doors.[8]
Note the rejection of the term "spiritual wifeism". Note that "spiritual wifeism" likely refers to John C. Bennett's pattern of seduction and sexual license, which the Saints were always at pains to deny.
In light of the circumstances under which they were spoken, Joseph's words were carefully chosen. Joseph was not merely bluffing, nor was he lying—he literally could prove that the Laws were perjuring themselves on this point in the charges brought only the day before.
Bradshaw cites a portion of Joseph's above statement, and then concludes:
A review of Joseph's remarks in light of the circumstances under which they were spoken shows that Joseph's words were carefully chosen. In this speech, Joseph was specifically reacting to the indictments for perjury and adultery that were presented by the grand jury the day earlier. Thus, when Joseph affirmed during the same speech: "I am innocent of all these charges," he was in particular refuting a claim that he and Maria [Lawrence] had openly and notoriously cohabitated, thus committing the statutory offense of adultery. He was also refuting the perjury charge. While the overall tone of Joseph's remarks may seem misleading, it is understandable that Joseph would have taken pains to dodge the plural marriage issue. By keeping his plural marriages in Nauvoo secret, Joseph effectively kept them legal, at least under the Illinois adultery statute.[9]:413
Joseph Smith was, in fact, once charged with adultery under Illinois Law. This occurred shortly before his death, when Robert Foster, William Law (Joseph's former counselor in the First Presidency) and Law's brother Wilson charged Joseph with adultery in the case of Maria Lawrence.[9]:403,414 Joseph took an aggressive stance in the defense of himself and Maria, which would be surprising if Illinois law was as detrimental to his case as many have assumed.
For example, as soon as Joseph was charged, two days later he and his supporters "rode to Carthage, intent on having" the charge "'investigated.'"[9]:404
It is vital to understand, however, that:
Joseph Smith could not have been properly convicted of adultery under the law of Illinois in 1844. Illinois law only criminalized adultery or fornication if it was "open". Had Joseph lived to face trial on this charge, he would have had good reason to expect acquittal because his relationships with his plural wives were not open, but were kept confidential and known by a relative few. Given a fair trial on this indictment, Joseph could have relied on several legal defenses.[9]:402
The same author emphasized:
The term "open" in [the Illinois Criminal Code of the day[10]] is a key element of this crime. The meaning of this term was then and still today is generally understood in law to cover conduct that is "notorious," "exposed to public view," or "visible," and which is "not clandestine." Joseph's relationships with his plural wives did not meet this definition.[9]:408
Two cases decided after Joseph's death but under the same legal regime likewise demonstrate that there was nothing about Maria and Joseph's relationship (regardless of whether or not they had sexual relations) which would have permitted conviction under the Illinois adultery statute. Additionally, Stephen R. Douglas (the famed Illinois judge and later candidate for the presidency of the United States) and Thomas Ford (the governor of Illinois at the time of Joseph's murder) prosecuted adultery cases during their legal careers and both were definitive that an "open" and "notorious" aspect to the cohabitation had to be proven under the statute.[9]:408-411
By contrast, had Joseph been charged by his wife Emma with adultery, this could have served as grounds for divorce, and did not require the stringent requirements of being "open" or "notorious."[11]
Even Joseph's near-contemporaries would later realize that Illinois law would probably support the practice of Latter-day Saint plural marriage, perhaps even if done so openly.
Recognizing the breadth of [the] state constitutional provision [for religious freedom] as it stood in 1844, Illinois adopted a new constitution in 1869 that introduced a number of changes in the clause governing religious liberty, including wording specifically intended to give the state authority to prohibit Mormon polygamy or other religiously-based practices that might be deemed offensive. Comments by certain delegates to the 1869 Illinois Constitutional Convention show taht there was a concern that the Mormon practice of plural marriage could be protected under the state constitution....
Several delegates expressed support for changes in the wording of the Illinois constitution in order to protect the state from what they viewed as extreme forms of worship, including Mormon polygamy. These delegates feared that the more liberal wording of the earlier constitution (in force in Joseph's day) might actually protected practices such as polygamy. One such delegate was Thomas J. Turner...[who] stated:"...Mormonism is a form of religion 'grant it, a false religion' nevertheless, it claims to be the true Christian religion...[d]o we desire that the Mormons shall return to our State, and bring with them polygamy?"[9]:416, 416n45
Critics charge that Joseph Smith and his successors made repeated public statements in which they hid or frankly denied the practice of polygamy, despite knowledge to the contrary. It is argued that this dishonesty is morally dubious and inconsistent with the Church’s purported principles.But, as we have seen, the practice of polygamy must be viewed in its moral context as an act of religious devotion which the Saints were unwilling to forego simply because the state or society disapproved.
The concept of “civil disobedience” is essential to understanding those occasions in which Joseph Smith or other Church members were not forthright about the practice of polygamy.
Like obedience to civil law, honesty and integrity are foundational values to the Church of Jesus Christ. Indeed, the success which critics have in troubling members of the Church with tales of polygamy and its deceptive circumstances is, in a way, a compliment to the Church. If the Church as an institution typically taught its members to have a casual disregard for the truth, a discovery that Joseph Smith had deceived others about polygamy would not be troubling to most. But, because the Church (contrary to the suggestions of some critics) really does teach its members to aspire to live elevated lives of moral rectitude, the discovery that deception was involved with polygamy can come as something of a shock. Disillusionment can ensue if we follow the critics in assuming that because Joseph occasionally misled others in this specific context, he must therefore have lied about everything else, and been absolutely unworthy of trust.
Summary: Sometime in 1840 Joseph Smith first broached the topic of plural marriage privately to trusted friends. Most of the apostles were in England and thus were unavailable for an introduction to the practice.
Notes
The Church continued to practice polygamy after 1890
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
At first, the performance of new plural marriages after the Manifesto was largely unknown to people outside the Church. When discovered, these marriages troubled many Americans, especially after President George Q. Cannon stated in an 1899 interview with the New York Herald that new plural marriages might be performed in Canada and Mexico.40 After the election of B. H. Roberts, a member of the First Council of the Seventy, to the U.S. Congress, it became known that Roberts had three wives, one of whom he married after the Manifesto. A petition of 7 million signatures demanded that Roberts not be seated. Congress complied, and Roberts was barred from his office.41
The exclusion of B. H. Roberts opened Mormon marital practices to renewed scrutiny. Church President Lorenzo Snow issued a statement clarifying that new plural marriages had ceased in the Church and that the Manifesto extended to all parts of the world, counsel he repeated in private. Even so, a small number of new plural marriages continued to be performed, probably without President Snow’s knowledge or approval. After Joseph F. Smith became Church President in 1901, a small number of new plural marriages were also performed during the early years of his administration.[1]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Church’s role in these marriages became a subject of intense debate after Reed Smoot, an Apostle, was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1903. Although Smoot was a monogamist, his apostleship put his loyalty to the country under scrutiny. How could Smoot both uphold the laws of the Church, some of whose officers had performed, consented to, or participated in new plural marriages, and uphold the laws of the land, which made plural marriage illegal? For four years legislators debated this question in lengthy public hearings.[2]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Senate called on many witnesses to testify. Church President Joseph F. Smith took the stand in the Senate chamber in March 1904. When asked, he defended his family relationships, telling the committee that he had cohabited with his wives and fathered children with them since 1890. He said it would be dishonorable of him to break the sacred covenants he had made with his wives and with God. When questioned about new plural marriages performed since 1890, President Smith carefully distinguished between actions sanctioned by the Church and ratified in Church councils and conferences, and the actions undertaken by individual members of the Church. "There never has been a plural marriage by the consent or sanction or knowledge or approval of the church since the manifesto," he testified.43
In this legal setting, President Smith sought to protect the Church while stating the truth. His testimony conveyed a distinction Church leaders had long understood: the Manifesto removed the divine command for the Church collectively to sustain and defend plural marriage; it had not, up to this time, prohibited individuals from continuing to practice or perform plural marriage as a matter of religious conscience.[3]—(Click here to continue)
We note again that the Church and its members were in an impossible position–the government showed no concern for the women and children who would be left without support if government policies were obeyed. Members and leaders again had agonizing choices to make, in which all their moral duties simply could not be honored. Joseph F. Smith wrote to a member who faced just this dilemma, “The whole thing in a nut shell is this, you should keep your covenants with your family and you should also not violate the law. Now if you can comprehend it–you will grasp the situation.”President Woodruff continued similar tactics throughout the remainder of his administration. By July 1892 he had granted a few recommends for plural marriages in Mexico, and in June 1897 marriages sanctioned by the First Presidency were performed at sea, on the Great Lakes, and in Mexico. There is circumstantial evidence that President Woodruff himself married a plural wife at sea in September 1897. At times, President Woodruff seems to have maintained some “plausible deniability” by declining to personally approve a polygamous marriage, while referring the potential polygamists to his counselor, George Q. Cannon, for a recommend.
The situation–which critics and many modern members have not grasped–is that it was impossible to do both. A choice had to be made, the Saints chose whatever was most important, and most seem to have chosen support for families over being straightforward with the government.
After the Manifesto, monogamy was advocated in the Church both over the pulpit and through the press. On an exceptional basis, some new plural marriages were performed between 1890 and 1904, especially in Mexico and Canada, outside the jurisdiction of U.S. law; a small number of plural marriages were performed within the United States during those years. In 1904, the Church strictly prohibited new plural marriages. Today, any person who practices plural marriage cannot become or remain a member of the Church.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
At first, the performance of new plural marriages after the Manifesto was largely unknown to people outside the Church. When discovered, these marriages troubled many Americans, especially after President George Q. Cannon stated in an 1899 interview with the New York Herald that new plural marriages might be performed in Canada and Mexico.40 After the election of B. H. Roberts, a member of the First Council of the Seventy, to the U.S. Congress, it became known that Roberts had three wives, one of whom he married after the Manifesto. A petition of 7 million signatures demanded that Roberts not be seated. Congress complied, and Roberts was barred from his office.41
The exclusion of B. H. Roberts opened Mormon marital practices to renewed scrutiny. Church President Lorenzo Snow issued a statement clarifying that new plural marriages had ceased in the Church and that the Manifesto extended to all parts of the world, counsel he repeated in private. Even so, a small number of new plural marriages continued to be performed, probably without President Snow’s knowledge or approval. After Joseph F. Smith became Church President in 1901, a small number of new plural marriages were also performed during the early years of his administration.[1]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Church’s role in these marriages became a subject of intense debate after Reed Smoot, an Apostle, was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1903. Although Smoot was a monogamist, his apostleship put his loyalty to the country under scrutiny. How could Smoot both uphold the laws of the Church, some of whose officers had performed, consented to, or participated in new plural marriages, and uphold the laws of the land, which made plural marriage illegal? For four years legislators debated this question in lengthy public hearings.[2]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Senate called on many witnesses to testify. Church President Joseph F. Smith took the stand in the Senate chamber in March 1904. When asked, he defended his family relationships, telling the committee that he had cohabited with his wives and fathered children with them since 1890. He said it would be dishonorable of him to break the sacred covenants he had made with his wives and with God. When questioned about new plural marriages performed since 1890, President Smith carefully distinguished between actions sanctioned by the Church and ratified in Church councils and conferences, and the actions undertaken by individual members of the Church. "There never has been a plural marriage by the consent or sanction or knowledge or approval of the church since the manifesto," he testified.43
In this legal setting, President Smith sought to protect the Church while stating the truth. His testimony conveyed a distinction Church leaders had long understood: the Manifesto removed the divine command for the Church collectively to sustain and defend plural marriage; it had not, up to this time, prohibited individuals from continuing to practice or perform plural marriage as a matter of religious conscience.[3]—(Click here to continue)
We note again that the Church and its members were in an impossible position–the government showed no concern for the women and children who would be left without support if government policies were obeyed. Members and leaders again had agonizing choices to make, in which all their moral duties simply could not be honored. Joseph F. Smith wrote to a member who faced just this dilemma, “The whole thing in a nut shell is this, you should keep your covenants with your family and you should also not violate the law. Now if you can comprehend it–you will grasp the situation.”President Woodruff continued similar tactics throughout the remainder of his administration. By July 1892 he had granted a few recommends for plural marriages in Mexico, and in June 1897 marriages sanctioned by the First Presidency were performed at sea, on the Great Lakes, and in Mexico. There is circumstantial evidence that President Woodruff himself married a plural wife at sea in September 1897. At times, President Woodruff seems to have maintained some “plausible deniability” by declining to personally approve a polygamous marriage, while referring the potential polygamists to his counselor, George Q. Cannon, for a recommend.
The situation–which critics and many modern members have not grasped–is that it was impossible to do both. A choice had to be made, the Saints chose whatever was most important, and most seem to have chosen support for families over being straightforward with the government.
After the Manifesto, monogamy was advocated in the Church both over the pulpit and through the press. On an exceptional basis, some new plural marriages were performed between 1890 and 1904, especially in Mexico and Canada, outside the jurisdiction of U.S. law; a small number of plural marriages were performed within the United States during those years. In 1904, the Church strictly prohibited new plural marriages. Today, any person who practices plural marriage cannot become or remain a member of the Church.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
At first, the performance of new plural marriages after the Manifesto was largely unknown to people outside the Church. When discovered, these marriages troubled many Americans, especially after President George Q. Cannon stated in an 1899 interview with the New York Herald that new plural marriages might be performed in Canada and Mexico.40 After the election of B. H. Roberts, a member of the First Council of the Seventy, to the U.S. Congress, it became known that Roberts had three wives, one of whom he married after the Manifesto. A petition of 7 million signatures demanded that Roberts not be seated. Congress complied, and Roberts was barred from his office.41
The exclusion of B. H. Roberts opened Mormon marital practices to renewed scrutiny. Church President Lorenzo Snow issued a statement clarifying that new plural marriages had ceased in the Church and that the Manifesto extended to all parts of the world, counsel he repeated in private. Even so, a small number of new plural marriages continued to be performed, probably without President Snow’s knowledge or approval. After Joseph F. Smith became Church President in 1901, a small number of new plural marriages were also performed during the early years of his administration.[1]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Church’s role in these marriages became a subject of intense debate after Reed Smoot, an Apostle, was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1903. Although Smoot was a monogamist, his apostleship put his loyalty to the country under scrutiny. How could Smoot both uphold the laws of the Church, some of whose officers had performed, consented to, or participated in new plural marriages, and uphold the laws of the land, which made plural marriage illegal? For four years legislators debated this question in lengthy public hearings.[2]—(Click here to continue)
"The Manifesto and the End of Plural Marriage," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
The Senate called on many witnesses to testify. Church President Joseph F. Smith took the stand in the Senate chamber in March 1904. When asked, he defended his family relationships, telling the committee that he had cohabited with his wives and fathered children with them since 1890. He said it would be dishonorable of him to break the sacred covenants he had made with his wives and with God. When questioned about new plural marriages performed since 1890, President Smith carefully distinguished between actions sanctioned by the Church and ratified in Church councils and conferences, and the actions undertaken by individual members of the Church. "There never has been a plural marriage by the consent or sanction or knowledge or approval of the church since the manifesto," he testified.43
In this legal setting, President Smith sought to protect the Church while stating the truth. His testimony conveyed a distinction Church leaders had long understood: the Manifesto removed the divine command for the Church collectively to sustain and defend plural marriage; it had not, up to this time, prohibited individuals from continuing to practice or perform plural marriage as a matter of religious conscience.[3]—(Click here to continue)
We note again that the Church and its members were in an impossible position–the government showed no concern for the women and children who would be left without support if government policies were obeyed. Members and leaders again had agonizing choices to make, in which all their moral duties simply could not be honored. Joseph F. Smith wrote to a member who faced just this dilemma, “The whole thing in a nut shell is this, you should keep your covenants with your family and you should also not violate the law. Now if you can comprehend it–you will grasp the situation.”President Woodruff continued similar tactics throughout the remainder of his administration. By July 1892 he had granted a few recommends for plural marriages in Mexico, and in June 1897 marriages sanctioned by the First Presidency were performed at sea, on the Great Lakes, and in Mexico. There is circumstantial evidence that President Woodruff himself married a plural wife at sea in September 1897. At times, President Woodruff seems to have maintained some “plausible deniability” by declining to personally approve a polygamous marriage, while referring the potential polygamists to his counselor, George Q. Cannon, for a recommend.
The situation–which critics and many modern members have not grasped–is that it was impossible to do both. A choice had to be made, the Saints chose whatever was most important, and most seem to have chosen support for families over being straightforward with the government.
After the Manifesto, monogamy was advocated in the Church both over the pulpit and through the press. On an exceptional basis, some new plural marriages were performed between 1890 and 1904, especially in Mexico and Canada, outside the jurisdiction of U.S. law; a small number of plural marriages were performed within the United States during those years. In 1904, the Church strictly prohibited new plural marriages. Today, any person who practices plural marriage cannot become or remain a member of the Church.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Critics of Mormonism allege that the Manifesto ending the practice of polygamy, printed as Official Declaration 1 in the LDS scriptures, was not the product of revelation but rather of legal pressure from the U.S. government, or alternately, of a compromise to achieve statehood. Critics also point to some marriages contracted after the Manifesto as evidence for their claims.
There was great political, legal, and even military pressure brought against the Saints because of plural marriage. The members endured great privations for their faith.[1]
Wilford Woodruff was clear that the Lord had made it his "duty" to issue the Manifesto. It is impossible to know what President Woodruff "really" thought about what he was doing. But, he insisted and the other Church leaders insisted that he had been guided by the Lord in the decisions made during this difficult period.
His decision also has clear Biblical parallels for peoples in similarly oppressive political circumstances.
This event has a parallel in the book of Jeremiah. The Torah instructs the Israelites to remain an independent people and to not make contracts or treaties with the surrounding nations. Many Jews in Jeremiah's day likely saw that instruction as further reason to rebel against their vassal-state condition as a subject of Babylon.[citation needed] Jeremiah, however, told them they should submit to their present political condition. He particularly warned them that if they disobeyed, they would lose their freedom and the temple. Choosing to heed their own interpretation of a dead prophet's word rather than obey the living prophet, the Jews did not submit to Babylonian rule and lost their lands, possessions, and access to the holy temple.
This outcome is very similar to what Wilford Woodruff saw in vision.
The Lord showed me by vision and revelation exactly what would take place if we did not stop this practice. If we had not stopped it, you would have had no use for . . . any of the men in this temple at Logan; for all ordinances would be stopped throughout the land of Zion. Confusion would reign throughout Israel, and many men would be made prisoners. This trouble would have come upon the whole Church, and we should have been compelled to stop the practice. Now, the question is, whether it should be stopped in this manner, or in the way the Lord has manifested to us, and leave our Prophets and Apostles and fathers free men, and the temples in the hands of the people, so that the dead may be redeemed. . . . I say to you that that is exactly the condition we as a people would have been in had we not taken the course we have. OD—1 off-site
The Edmunds-Tucker Act granted the federal government unprecedented powers in prosecuting Mormon polygamists, and prosecutors took these powers to cruel and illegal extremes:
In the Edmunds-Tucker Act, [Congress] provided that a wife was a competent witness in polygamy, bigamy, and cohabitation trials and required that records be kept of weddings in the territories. These provisions still retained one restraint on spousal testimony, however; they provided only that a willing wife would be allowed to testify. The act specifically forbade attempts by the judiciary to compel wives to testify against their husbands. Utah’s judges did not always follow the law, however. A number of Mormon women were required to testify against their husbands or face contempt charges. The power of contempt could be a fearful weapon. On the basis of the most sketchy or nonexistent hearings, Mormon wives who refused to testify against their husbands could be sent to prison for indefinite periods. In 1888 Representative Burnes read to the House of Representatives a report by a visitor to Utah’s prison:
"I found in one cell (meaning a cell of the penitentiary in Utah) 10 by 13 1/2 feet, without a floor, six women, three of whom had babies under six months of age, who were incarcerated for contempt of court in refusing to acknowledge the paternity of their children. When I plead with them to answer the court and be released, they said: "If we do, there are many wives and children to suffer the loss of a father."[2]
The most reprehensible aspect of this treatment of the women is that it was completely unnecessary. With the evisceration of evidentiary standards, the courts were practically assured of convictions without the testimony of Mormon wives:
In retrospect it is difficult to offer any explanation for this judicial conduct toward Mormon wives other than a spirit of vindictiveness. The polygamy laws, which were being vigorously enforced in the latter part of the 1880s, imposed ample punishment for the women who stubbornly clung to polygamy. The imposition of contempt sentences on wives who refused to testify introduced a sort of random sexual equality in the federal punishment of polygamy that was being imposed on Utah’s Mormons. Courts had reduced the quantum of evidence required to establish polygamy or cohabitation to such a low level that in almost any case ample alternate sources of proof must have been available. So Utah’s courts could not have believed that they needed to compel Mormon women to testify in order to convict their polygamous husbands. The cohabitation cases produced heartrending stories of suffering and pathos. Men were forbidden to associate with their children or provide for their former wives. Women were denied care and association with former husbands. Moreover, the law, not limited to prohibiting future polygamous marriages, fell with all its severity upon people whose relationships had most often been established when the law did not unambiguously forbid them.[3]
Legal challenges brought against Edmunds-Tucker failed, removing the final obstacle to those who sought to use the law to not simply stop polygamy, but to destroy the Church:
Congress, the Presidency, and the Supreme Court combined to generate repressive legislation and distortions of Constitutional jurisprudence which to this day are unequalled in the degree to which they destroyed individual and institutional rights, freedoms, and privileges. Politicians so successfully exploited the situation that at times the nation was prepared to accept the destruction of the Church and its members.[4]
President Woodruff attended a council meeting on 24 September 1890, and presented a statement which he had written, declaring: "I have been struggling all night with the Lord about what should be done under the existing circumstances of the Church. And here is the result."[5]
This document was to become the Manifesto. After the Manifesto was revised by the First Presidency, three members of the Quorum of the Twelve, and a few others, it was sent to the media.
Of the process, George Q. Cannon wrote:
This whole matter has been at President Woodruff’s own instance. He has felt strongly impelled to do what he has, and he has spoken with great plainness to the brethren in regard to the necessity of something of this kind being done. He has stated that the Lord had made it plain to him that this was his duty, and he felt perfectly clear in his mind that it was the right thing.[6]
President Cannon also spoke soon after the Manifesto's publication, and indicated that President Woodruff’s writing of the Manifesto had been done "under the influence of the ‘Spirit’" and promised that "when God speaks and…makes known His mind and will, I hope that I and all Latter-day Saints will bow in submission to it."[7] Thus, the Manifesto was considered to be a divinely mandated and inspired step by leaders at the time.
Some wonder whether or not Wilford Woodruff was actually inspired to end polygamy.
Woodruff wrote in his journal on September 25, 1890 that "I have arived at a point in the History of my life as the President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints whare I am under the necessity of acting for the Temporal Salvation of the Church. The United State Governmet has taken a stand & passed Laws to destroy the Latter day Saints upon the subject of poligamy or Patriarchal order of Marriage. And after Praying to the Lord & feeling inspired by his spirit I have issued the following Proclamation which is sustaind by My Councillors and the 12 Apostles."
Thus, anyone denying that Woodruff had a revelation must either not believe in God, not believe in the Latter-day Saint God, or just believe that Woodruff was lying in the case of fundamentalists.
Some of these marriages were apparently sanctioned by some in positions of Church leadership.
Some Church members unfamiliar with the history behind the aggressive Federal anti-polygamy movement have been troubled by critics who try to portray Church members’ and leaders’ choices as dishonest and improper. It is important to realize that this is a point on which modern enemies of the Church would be impossible to satisfy. If the Church had acquiesced to government pressure and stopped polygamy completely in 1890, the Church would then be charged with having "revelations on demand," or with abandoning something they claimed was divine under government pressure. In fact, prior to the Manifesto, the attorney prosecuting Elder Lorenzo Snow for polygamy "predicted that if Snow and others were found guilty and sent to prison church leaders would find it convenient to have a revelation setting aside the commandment on polygamy."[8]
If they were to comply with the law, they would (in the eyes of some) be admitting that revelation came "on demand" and in response to secular pressure or "convenience." Their enemies would "win" no matter what they did.
But, this did not happen—the leaders and members of the Church were literally willing to do anything they were commanded to do, in order to obey the Lord, until they were told otherwise. Impressively, the Church and its leaders took the only possible course which would preserve its revelatory integrity: only when they literally had no further choice besides dissolution was the plural marriage commandment completely rescinded.
It should be remembered, finally, that a key doctrine of the Church is that no one should have to take anyone else’s word for something—"that man should not council his fellow man, neither trust in the arm of flesh—but that every man might speak in the name of God the Lord, even the savior of the world."(D&C 1꞉19-20.) This doesn’t apply to polygamy alone; every discussion of testimony includes it. Joseph Smith made numerous other claims that might make us skeptical: appearances of God and Jesus, angels, gold plates, and everything else. Said he:
Search the scriptures—search the revelations which we publish, and ask your Heavenly Father, in the name of His Son Jesus Christ, to manifest the truth unto you, and if you do it with an eye single to His glory nothing doubting, He will answer you by the power of His Holy Spirit. You will then know for yourselves and not for another. You will not then be dependent on man for the knowledge of God; nor will there be any room for speculation.[9]
As President Cannon explained, the leaders of the Church were not exempt from the rigors of receiving revelation:
Yet, though [Church doctrines] shocked the prejudices of mankind, and perhaps startled us as Latter-day Saints, when we sought God for a testimony concerning them, He never failed to give unto us His Holy Spirit, which witnessed unto our spirits that they were from God, and not of man. So it will be to the end. The Presidency of the Church have to walk just as you walk. They have to take steps just as you take steps. They have to depend upon the revelations of God as they come to them. They cannot see the end from the beginning, as the Lord does. They have their faith tested as you have your faith tested. So with the Twelve Apostles. All that we can do is to seek the mind and will of God, and when that comes to us, though it may come in contact [conflict?] with every feeling that we have previously entertained, we have no option but to take the step that God points out, and to trust to Him…[10]
The Doctrine and Covenants clearly indicates that the First Presidency and Quorum of the Twelve are of equal authority[11] and that every decision should be done in unanimity in order to make such decisions binding upon the Church[12]: to make them "official," as it were. Clearly, President Woodruff did not follow this practice—which would be very strange if he expected the Manifesto to be read as a formal revelation insisting that all polygamous practices immediately cease: only three of the apostles even saw the Manifesto prior to its publication. The leaders were agreed that President Woodruff had been right to issue it, and acknowledged his action of the Lord; the full implications of the Manifesto, however, were still the subject of discussion and debate.
President Woodruff did not frame the matter as a declaration from the First Presidency and the Twelve (which would be required for any official change in doctrine or practice). Rather, he spoke of the Manifesto as a "duty" on his part, which the Lord required. Even the wording of the Manifesto reflects this—it does not speak of "we the First Presidency and Council of the Twelve," but simply of Wilford Woodruff in the first person singular. The wording is careful and precise: "I hereby declare my intention to submit to those laws, and to use my influence with the members of the Church over which I preside to have them do likewise… And I now publicly declare that my advice to the Latter-day Saints is to refrain from contracting any marriage forbidden by the law of the land."(OD-1) Thus, President Woodruff announces a personal course of action, but does not commit other general authorities or the Church—he even issues "advice," rather than a "command" or "instruction." No other signatures or authorities are given, other than his own.
A useful comparison can be made with Official Declaration 2, which follows the prescribed pattern for Church government:
…the First Presidency announced that a revelation had been received by President Spencer W. Kimball…[who] has asked that I advise the conference that after he had received this revelation…he presented it to his counselors, who accepted it and approved it. It was then presented to the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles, who unanimously approved it, and was subsequently presented to all other General Authorities, who likewise approved it unanimously.(OD-2)
Even at this meeting their intent was clear, since they debated whether the Church as a whole should sustain the Manifesto, since "some felt that the assent of the Presidency and Twelve to the matter was sufficient without committing the people by their votes to a policy which they might in the future wish to discard."[13]
It is evident that these united quorums did not consider the Manifesto to be a revelation forbidding all plural marriage in 1890: for, why would they then contemplate the Church wanting to "disregard" it? The leaders were doubtless still hoping that they might be able to gain some reprieve, and continue to practice their religion without civil or criminal penalty.
Perhaps most convincingly, an editorial in the Church’s Deseret News responded to the government’s Utah Commission, which had argued that President Woodruff needed to "have a revelation suspending polygamy." The editorial advised that "[w]hen President Woodruff receives anything from a Divine source for the Church over which he presides he will be sure to deliver the message."[14] This was written five days after the publication of the Manifesto. It seems clear that President Woodruff considered his action inspired and divinely directed; however, he and the Church did not believe that God had, by the Manifesto, told them to cease all plural marriage.
George Q. Cannon said,
But the nation has interposed and said, "Stop," and we shall bow in submission, leaving the consequences with God. We shall do the best we can; but when it comes in contact with constituted authorities, and the highest tribunals in the land say "Stop," there is no other course for Latter-day Saints, in accordance with the revelations that God has given to us telling us to respect constituted authority, than to bow in submission thereto and leave the consequences with the Lord.[15]
The Manifesto thus strove to walk this difficult line–conceding sufficient to "constitutional authority" to prevent the Church’s destruction, maintaining the restrictions on plural marriage, and refraining from teaching the doctrine. Yet, significantly President Cannon says that the Saints "shall do the best we can" (emphasis added). That is, they will continue to practice their faith to the extent possible without threatening the Church’s existence. This would later include a limited continuation of plural marriage.
The Church leaders’ united understanding was that the Manifesto was a revelation. However, they did not understand it as universally forbidding all plural marriage at that time, though for the Church’s survival it was necessary that the government so interpret it.
The leaders and Saints would understand the meaning and application of the Manifesto differently in time. An altered understanding—via revelation—of a revelation is not unprecedented: Jesus commanded the apostles to "teach all nations," but the apostles continued to interpret this command in a more limited way until later revelation expanded the Christian gospel beyond those who had first embraced the rites of Judaism. A modern example involves the Word of Wisdom, which was not declared to be universally binding for more than a century, though the revelation in section 89 did not "change."[16]
It is estimated that fewer than two hundred plural marriages were sanctioned between 1890 and 1904.[17] These were often performed in areas outside the reach of U.S. law, such as on the seas or in Mexico.
Elder Dallin H. Oaks spoke at BYU about the difficulties of this period:
Some have suggested that it is morally permissible to lie to promote a good cause. For example, some Mormons have taught or implied that lying is okay if you are lying for the Lord… As far as concerns our own church and culture, the most common allegations of lying for the Lord swirl around the initiation, practice, and discontinuance of polygamy. The whole experience with polygamy was a fertile field for deception. It is not difficult for historians to quote LDS leaders and members in statements justifying, denying, or deploring deception in furtherance of this religious practice.
Elder Oaks then reaches the key point—there will be times when moral imperatives clash:
My heart breaks when I read of circumstances in which wives and children were presented with the terrible choice of lying about the whereabouts or existence of a husband or father on the one hand or telling the truth and seeing him go to jail on the other. These were not academic dilemmas. A father in jail took food off the table and fuel from the hearth. Those hard choices involved collisions between such fundamental emotions and needs as a commitment to the truth versus the need for loving companionship and relief from cold and hunger.
My heart also goes out to the Church leaders who were squeezed between their devotion to the truth and their devotion to their wives and children and to one another. To tell the truth could mean to betray a confidence or a cause or to send a brother to prison. There is no academic exercise in that choice!
It is also clear that polygamy did not end suddenly with the 1890 Manifesto. Polygamous relationships sealed before that revelation was announced continued for a generation. The performance of polygamous marriages also continued for a time outside the United States, where the application of the Manifesto was uncertain for a season. It appears that polygamous marriages also continued for about a decade in some other areas among leaders and members who took license from the ambiguities and pressures created by this high-level collision between resented laws and reverenced doctrines.
I do not know what to think of all of this, except I am glad I was not faced with the pressures those good people faced. My heart goes out to them for their bravery and their sacrifices, of which I am a direct beneficiary. I will not judge them. That judgment belongs to the Lord, who knows all of the circumstances and the hearts of the actors, a level of comprehension and wisdom not approached by even the most knowledgeable historians.[18]
Note: This article was adapted from a longer paper which examines these historical matters in much more detail. Interested readers are strongly encouraged to consult it for a much more thorough analysis of the basic concepts sketched in this wiki article. FAIR link PDF link
Notes
Critics' Comment: Today's church leaders assert that the mainstream Mormon church has nothing whatsoever to do with fundamentalist polygamists. There's no contradiction in the fact that a sitting apostle in the 1950s had a polygamous Father-in-law living in full fellowship in the church and was a temple worker, more than half a century after church leaders claimed to have abandoned polygamy???
The website notes the following from an interview with Larry King on September 8, 1998:Larry King: You condemn it (polygamy)?
Gordon B. Hinckley: I condemn it, yes, as a practice, because I think it is not doctrinal. It is not legal. And this church takes the position that we will abide by the law. We believe in being subject to kings, presidents, rulers, magistrates in honoring, obeying and sustaining the law.The site then responds with the following "Critic's comments":
Why did the prophet of the church just lie and say that polygamy was not doctrinal? It is still in our scriptural canon, D&C 132. Hinckley makes it sound as if it was either a mistake or practiced for reasons unrelated to religion. Surely he knows why it was practiced. Also he makes an issue that polygamy is not legal today (as practiced by the fundamentalists). That's correct but it was not legal when the LDS practiced it in the 1800s either. He wants everyone to believe that polygamy was legal when the Latter-day Saints practiced it in the 1800s but is illegal now as practiced by the fundamentalists. As shown above, this is completely untrue. It was always illegal - from Joseph's first plural wife in 1833 through the 2nd manifesto in 1904.
The April 2007 Ensign had a lengthy article on the amazing life of Parley P. Pratt, one of the prominent apostles of the restoration. In the article they actually made a brief mention of a second wife. At they end of the article it says that Brother Pratt was murdered. That's all that was said. Other LDS books we've read merely say Parley was killed by a foe. What most LDS people don't know is why he was murdered. Parley had 12 polygamous wives. The last one was already married to another man, and he wasn't very happy that Parley added his wife and his children to his harem.
and
While in San Francisco, Pratt induced the wife of Hector H. McLean, the former Elenor J. McComb, to accept the Mormon faith and to elope with him to Utah as his 12th wife.
and concludes with this sarcastic response:
Critic's note:The Church Almanac lists Parley P Pratt as assassinated while on a mission but he was really murdered by the irate existing husband of his latest fancy. Technically therefore, she was polyandrous also. Practically, she was adulterous and then when she married Parley, bigamous. She was never divorced from her first husband. She had just abducted one of her children. Her husband took the child back after a court hearing and then killed Parley. I don't think he was ever tried for the murder which was in Arkansas. The Mountain Meadows Massacre was one later result of the ensuing hatred by Brigham et al of people from that area. The brethren did not recognize any marriage they did not perform as being legal, so they took whom they pleased. Missions were often wife gathering expeditions. Moral of the story: Better be careful whose family you try to steal...you might just get yourself killed!
Pratt’s last wife, Eleanor, “was sealed to him without divorcing her legal husband, who fatally shot Parley near Van Buren, Arkansas” (p. 333). There is, however, much that we are not told. Eleanor’s husband was a heavy drinker, which in 1844 resulted in separation. The couple was reconciled, and the family moved to San Francisco. While in California, Eleanor discovered the church. Her husband forbade her to join and “purchased a sword cane and threatened to kill her and the minister who baptized her if she became a Mormon.” [1]
It is therefore claimed by critics of Mormonism that Parley P. Pratt's practice of polygamy was responsible for his murder, partly because he married a woman who hadn't been divorced from her first husband.
Eleanor attended LDS meetings, and one Sunday at home, “while Eleanor was singing from a Mormon hymn book she had purchased, Hector tore the book from her hands, threw it into the fire, beat her, cast her out into the street, and locked the door.” [2]
Eleanor lodged a complaint of assault and battery against Hector and planned to leave him until prevailed upon by local church members and her physician. At that point, said Eleanor, “I presume McLean himself would not deny that I then declared that I would no more be his wife however many years I might be compelled to appear as such for the sake of my children". [3]
Eleanor was not baptized until 1854, and she had the written permission of her husband to do so. However, he forbade her to read church literature or to sing church hymns at home. It is not clear, then, why G. D. Smith feels Eleanor owed an observance of all the twentieth-century legal niceties to a violent, abusive, tyrannical drunkard. Through it all, as a church leader, Parley Pratt had tried to help the couple reconcile.
Eleanor had her children baptized, and Hector responded by filing a charge of insanity against his wife so he could have her committed to an asylum. Hector sent her children by steamer to their maternal grandparents’ home, confined Eleanor to the house, and again threatened to have her committed for insanity. Eleanor eventually found her children at her parents’ home, but they refused to let her take them. [4] Eleanor went to Salt Lake City and married Pratt on 14 November 1855. As we have seen, she considered herself divorced from Hector from the time he violently threw her from their home in San Francisco. They never received a civil divorce, however.
It is assumed that nineteenth century marriages always ended in a formal divorce. They did not--this was often impossible. From which authority, exactly, would G. D. Smith prefer that Eleanor receive a divorce? She was in Utah; Hector was in San Francisco. He had abused, beaten, confined, and threatened to institutionalize her. As we have seen, notions of divorce were also more fluid in the mid-nineteenth century, especially on the frontier. It is unlikely that most contemporaries would have insisted that Eleanor required a formal divorce.
Pratt was arrested on trumped-up charges, freed by a non-Mormon judge, and pursued by Hector, who shot the unarmed apostle six times and stabbed him twice. He was left to bleed to death over the course of two hours. [5] In G. D. Smith’s worldview, are men like Hector entitled to hold women emotionally or martially hostage, civil divorce or no? One suspects not. But in his zeal to condemn the church, he does not provide his readers with the facts necessary to understand the Pratts’ choices.
"Plural Marriage and Families in Early Utah," Gospel Topics on LDS.org:
Church leaders recognized that plural marriages could be particularly difficult for women. Divorce was therefore available to women who were unhappy in their marriages; remarriage was also readily available.[6]
Some members of the Church remarried without obtaining a formal legal divorce. Was this adultery? Remarriage without a formal, legal divorce was the norm for the period, especially on the frontier and among the poor. These were the legal realities faced by nineteenth century Americans.
"Presentism" is an analytical fallacy in which past behavior is evaluated by modern standards or mores. Even worse than a historian's presentism is a historian exploiting the presentism of his readers. Critics do this repeatedly when they speak about legal issues. "Presentism," observed American Historical Association president Lynn Hunt, "at its worst, encourages a kind of moral complacency and self-congratulation. Interpreting the past in terms of present concerns usually leads us to find ourselves morally superior. . . . Our forbears constantly fail to measure up to our present-day standards." [7]
Louisa Rising married Edwin Woolley "without first divorcing her legal husband," the dust jacket of George D. Smith's Nauvoo Polygamy teases. We are reminded later that "though she was not divorced from her legal husband, she agreed to marry" (p. 345). Eleanor McLean also married Parley Pratt without divorcing her first husband. It appears that G. D. Smith hopes to capitalize on ignorance about nineteenth-century laws and practices regarding marriage and divorce. "From the standpoint of the legal historian," wrote one expert who is not a Latter-day Saint, "it is perhaps surprising that anyone prosecuted bigamy at all. Given the confusion over conflicting state laws on marriage, there were many ways to escape notice, if not conviction." [8] To remarry without a formal divorce was not an unusual thing in antebellum America.
Bigamy or, rather, serial monogamy (without divorce or death) was a common social experience in early America. Much of the time, serial monogamists were poor and transient people, for whom the property rights that came with a recognized marriage would not have been much of a concern, people whose lives only rarely intersected with the law of marriage. [9]
The Saints were often poor and spent most of their time on the frontier, where the legal apparatus of the state was particularly feeble. Women who had joined the church and traveled to Zion without their husbands were particularly likely to be poor, and also unlikely to be worried about property rights. Nor, not incidentally, were their husbands available for a formal divorce.
Does this mean that marriage in America was a free-for-all? Hardly, notes Nancy Cott:
When couples married informally, or reversed the order of divorce and remarriage, they were not simply acting privately, taking the law into their own hands. . . . A couple about to join or leave an intimate relationship looked for communal sanction. The surrounding local community provided the public oversight necessary. Without resort to the state apparatus, local informal policing by the community affirmed that marriage was a well-defined public institution as well as a contract made by consent. Carrying out the standard obligations of the marriage bargain—cohabitation, husband's support, wife's service—seems to have been much more central to the approbation of local communities at this time than how or when the marriage took place, and whether one of the partners had been married elsewhere before. [10]
It also should be remembered that because Joseph Smith, Brigham Young, and other Latter-day Saint leaders exercised exclusive jurisdiction over celestial or plural marriages, marriages conducted under their supervision had as much (or more) formal oversight as many traditional marriages in America during the first half of the nineteenth century. Critics of the Church offer us none of this information or perspective—with the result that some readers might be horrified by the "loose" marriage practices of the Saints.
Some critics of Mormonism like to emphasize that some LDS members did not receive civil divorces before remarrying—either monogamously or polygamously. They either state or imply that this shows the Saints' cavalier attitude toward the law.
The Saints were often poor and spent most of their time on the frontier, where the legal apparatus of the state was particularly feeble. Women who had joined the church and traveled to Zion without their husbands were particularly likely to be poor, and also unlikely to be worried about property rights. Critics usually tell us nothing of all this—with the result that some credulous readers might be horrified by the "loose" marriage practices of the Saints. It also should be remembered that because Joseph Smith, Brigham Young, and other Latter-day Saint leaders exercised exclusive jurisdiction over celestial or plural marriages, marriages conducted under their supervision had as much (or more) formal oversight as many traditional marriages in America during the first half of the nineteenth century.
"From the standpoint of the legal historian," wrote one expert who is not a Latter-day Saint, "it is perhaps surprising that anyone prosecuted bigamy at all. Given the confusion over conflicting state laws on marriage, there were many ways to escape notice, if not conviction." [11]
Bigamy or, rather, serial monogamy (without divorce or death) was a common social experience in early America. Much of the time, serial monogamists were poor and transient people, for whom the property rights that came with a recognized marriage would not have been much of a concern, people whose lives only rarely intersected with the law of marriage. [12]
Nor, not incidentally, were their husbands available for a formal divorce.
Does this mean that marriage in America was a free-for-all? Hardly, notes Nancy Cott:
When couples married informally, or reversed the order of divorce and remarriage, they were not simply acting privately, taking the law into their own hands. . . . A couple about to join or leave an intimate relationship looked for communal sanction. The surrounding local community provided the public oversight necessary. Without resort to the state apparatus, local informal policing by the community affirmed that marriage was a well-defined public institution as well as a contract made by consent. Carrying out the standard obligations of the marriage bargain—cohabitation, husband’s support, wife’s service—seems to have been much more central to the approbation of local communities at this time than how or when the marriage took place, and whether one of the partners had been married elsewhere before. [13]
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Many LDS are under the impression that shortly before Joseph Smith was killed, he was put in jail unjustly by anti-Mormons using trumped-up charges. In reality, the circumstances surrounding Joseph's assassination was a result of the actions he took to prevent his being exposed as a polygamist.Author's sources: From the "neutral" site wikipedia (from June 2008)
Editor comment: The concept of a Heavenly Mother can be a bit strange for some people to accept but the idea of Heavenly Mothers (plural) is very unnerving. Logically, if God has multiple wives then although everyone has the same Father-in-Heaven, most people would have different 'Mothers-in-Heaven'. Perhaps that's one reason we're told not to pray to our Mother-in-Heaven as we wouldn't know which one.
We have to wonder why an angel didn't appear to Emma to convince her that polygamy was commanded by God. The Bible talks of Mary being visited by the angel Gabriel. Mary's soon-to-be husband Joseph was going to put her away until he had a visit in a dream explaining the virgin birth. Wouldn't it make sense that Emma would have been given the same information from God as Joseph did about polygamy, so that Emma would have gone along and not fought Joseph as she did? This is another reason to think that perhaps polygamy may have originated with Joseph Smith rather than from God or an angel.
With the statements that these justifications for polygamy are simply not true, by such LDS leaders as apostle John A. Widtsoe and FAIR Chairman John Lynch, we must turn to the only possible remaining answer - God commanded the early saints to take multiple wives for some reason. But we can't think of any earthly reason for practicing polygamy. Why would God command this? Even if there were women that needed help, why would the men have to marry the women in order to help them. We certainly don't advocate marrying a homeless person to help them financially or otherwise. And why have polygamy at all since it could only be practiced by maybe 30% of its members?
And although polygamy was practiced somewhat in Old Testament times, it was more of a social custom and not a religious commandment....Yes, polygamy was practiced in the OT, but God never commanded it to be practiced. The model was Adam and Eve, not Adam and Eve and Jane and Sally .... God seems to have accepted their practicing it for cultural reasons.
With the authority of the Bible behind them, early Mormons argued for 'plural marriage,' and some Mormon fundamentalist sects continue to practice polygyny. They were and are right: if the Bible provides authoritative models, then a man should be allowed to have more than one wife, as did Abraham, Jacob, David, and other biblical heroes, with no hint of divine disapproval.
—Michael Coogan, God and Sex: What the Bible Really Says (New York, N.Y.: Twelve, 2010), 78–79.
While sometimes forced to admit that some Old Testament figures practiced polygamy, some Christians insist that there was no biblical mandate or command to practice plural marriage.
This claim is false; levirate marriage was mandated by the law of Moses (Deuteronomy 25:5-6).
Even if true, this claim is immaterial. God did not condemn the practice of plural marriage in the Bible. If it was everywhere and always forbidden, God could and would have done so. Early Christian authors understood this.
The details of this practice are outlined in Deuteronomy 25:5-6, which the Sadducees quote in asking the question to Jesus. The practice of levirate marriage did not make any conditions on whether or not the brother-in-law was married. There was a way for the brother-in-law to avoid this marriage, through a ceremony called halitza, which was a mark of shame on the brother-in-law for refusing to continue his brother's name, thus declaring that his brother was irrevocably dead. This secondary option however, has become much more relevant to the modern practice of Judaism than it was to ancient Israel. Additionally, the practice makes no distinction to whether or not the brother was already married. It is the only instance in the Old Testament where polygamy was mandated under certain circumstances. Finally, the widow with no children, upon the death of her husband, was automatically considered to be betrothed, or engaged, to the next brother in the family of her now-deceased husband.
This practice was changed somewhat in Talmudic law where we find more than a hundred clarifications and expansions on the practice. Among these was a shift towards the practice of halitza being preferable to levirate marriage. This became a ban that was established by religious law in modern Israel in 1957. Because of this, there was an interesting case reported in 1998 in the Spring Newsletter of the International Council of Jewish Women. It describes the unusual case of a married woman, living in Israel, who had a single daughter. In 1991, the family was involved in a serious automobile accident, and the daughter died immediately. The husband died hours later. According to Jewish law, the woman (who was childless at the time of her husband's death) was immediately placed in the role of the childless widow. Before she could remarry, she needed to go through the halitza ceremony with the only living brother of her late husband, who lived in Paris. This case was of significance because the brother-in-law refused to perform the ceremony. At first the Jewish courts simply ordered the brother-in-law to either perform the ceremony, or to pay the woman a thousand dollars a month for maintenance. He refused to do either. It took the woman six years to get the brother-in-law to perform the ceremony, and he also ended up paying her thousands of dollars as ordered by the religious courts.
This practice was not just a custom, but an integral part of the religious law at the time of Jesus. While the above story happened only recently, ancient Israel was just as fervent in their keeping the Law of Moses, even in cases such as this. While a hypothetical situation was proposed to Jesus, it was a hypothetical situation that could actually happen, and the statements provided by the authors do not represent correctly this practice.
Some Christians claim that plural marriage has no Biblical precedents—they point to condemnation of King David and King Solomon as evidence that polygamy is always forbidden by God. Some claim that Abraham's polygamy "portrays his acceptance of plural marriage as a mark of disobedience to, and a lack of faith in, God." It is claimed that since the Bible didn't allow a man to marry two sisters, this proves that LDS plural marriage was "unbiblical" because some Mormons did so.
The Bible does not forbid plural marriage. In fact, many of the most noble Biblical figures (e.g., Abraham) had more than one wife. Furthermore, Biblical laws quoted by critics forbid kings from being led astray by plural spouses, or entering relationships not sanctioned by God's authority. However, the same Biblical laws provide guidelines for legitimate plural relationships.
This problem was mentioned in Deuteronomy:
15 Thou shalt in any wise set him king over thee, whom the LORD thy God shall choose: one from among thy brethren shalt thou set king over thee: thou mayest not set a stranger over thee, which is not thy brother...17 Neither shall he multiply wives to himself, that his heart turn not away... (Deuteronomy 17:15,17
Critics ignore the fact that only four chapters later, the Lord gives instructions on how to treat equitably plural wives and children. (See Deuteronomy 21:15-17.) Why does He not simply forbid plural marriage, if that is the intent of chapter 17? Why does He instruct the Israelites on how to conduct themselves in plural households, if all such households are forbidden?
So, rather than opposing plural marriage, the command to kings is that they:
David and Solomon are excellent examples of violating one or more of these Biblical principles, as described below.
David is well-known for his sin with Bathsheba and Uriah (see 2 Samuel 12:1-27. Nathan the prophet arrived to condemn David's behavior, and told the king:
7 ¶ And Nathan said to David...Thus saith the LORD God of Israel, I anointed thee king over Israel, and I delivered thee out of the hand of Saul;
8 And I gave thee thy master's house, and thy master's wives into thy bosom, and gave thee the house of Israel and of Judah; and if that had been too little, I would moreover have given unto thee such and such things.
9 Wherefore hast thou despised the commandment of the LORD, to do evil in his sight? thou hast killed Uriah the Hittite with the sword, and hast taken his wife to be thy wife, and hast slain him with the sword of the children of Ammon.
10 Now therefore the sword shall never depart from thine house; because thou hast despised me, and hast taken the wife of Uriah the Hittite to be thy wife. (2 Samuel 12:7-10)
Nathan here tells David that the Lord "gave thee...thy master's wives." And, the Lord says, through His prophet, that He would have given even more than He has already given of political power, wives, and wealth.
But, David sinned and did evil in the matter of Uriah. If plural marriage is always a sin to God, then why did Nathan not take the opportunity to condemn David for it now? Or, why did the prophet not come earlier?
Solomon's problem is described:
1 BUT king Solomon loved many strange women, together with the daughter of Pharaoh, women of the Moabites, Ammonites, Edomites, Zidonians, and Hittites;
2 Of the nations concerning which the LORD said unto the children of Israel, Ye shall not go in to them, neither shall they come in unto you: for surely they will turn away your heart after their gods: Solomon clave unto these in love...
7 Then did Solomon build an high place for Chemosh, the abomination of Moab, in the hill that is before Jerusalem, and for Molech, the abomination of the children of Ammon.
8 And likewise did he for all his strange wives, which burnt incense and sacrificed unto their gods. (1 Kings 11:1-8
Solomon's wives turned his heart away from the Lord, as Deuteronomy cautioned. Nothing is said against the plurality of wives, but merely of wives taken without authority that turn his heart away from the Lord.
David and Solomon do not prove the critics' point, but in fact demonstrate that plural marriage may, on occasion, be sanctioned (as in David's case certainly).
But, we need not rely on these examples only to demonstrate that plural marriage was practiced by righteous followers of God in the Bible. Other cases include:
and also possibly:
As noted above, Deuteronomy 21:15 provides rules governing Israelites who have plural wives. Further instructions are also given in Exodus 21:10. Why did God not ban plural marriage through Moses if it is always an immoral act?
Latter-day Saint plural marriage did not rely on biblical authority or interpretation (though they used biblical parallels to explain and understand the command which they believed they had received from God via a modern prophet.)
Marrying two sisters was quite frequent, possibly because sisters had already learned to get along together, which made for more harmonious plural families. One researcher noted:
Marriage to the wife's sister, defined as incest only by Anglican canon law, is the only form of polygamous marriage of the [potentially 'incestuous] categories...that occurs in significant numbers. [2]
The Saints did not claim to be restoring Mosaic plural marriage—they only used Moses' example as precedent for the fact that God could and had commanded plural marriage in the past. The specific structure, rules, and restrictions varied from time to time as guided by prophets.
D&C 132 tells Joseph and others to "do the works of Abraham." What are the "works of Abraham" and how does this relate to plural marriage?
The "works of Abraham" are fundamentally about obedience to God's laws, obedience to any commandment given, and willingness to sacrifice. For Joseph and the early Saints, a prominent part of such works was plural marriage, but this was (in a sense) incidental—the great work was obedience to covenant and law; plural marriage was simply their burden and trial.
It is often casually assumed that "the works of Abraham" refer mainly to plural marriage.[3] A consideration of both the phrase's orgins, and its use in D&C 132, may suggest that a broader meaning is intended.
The phrase has its origins in the gospel of John. Jesus rebuked unrighteous Jews, saying:
...Verily, verily, I say unto you, Whosoever committeth sin is the servant of sin. And the servant abideth not in the house for ever: but the Son abideth ever. If the Son therefore shall make you free, ye shall be free indeed. I know that ye are Abraham's seed; but ye seek to kill me, because my word hath no place in you. I speak that which I have seen with my Father: and ye do that which ye have seen with your father (John 8:34-38).
Stung, the Jews replied, "Abraham is our father." Jesus answered:
If ye were Abraham's children, ye would do the works of Abraham. But now ye seek to kill me, a man that hath told you the truth, which I have heard of God: this did not Abraham (John 8:39-40).
Even before the abolition of plural marriage, leaders of the Church understood this,[4] though many also used obedience to the command to practice plural marriage as a pre-eminent example.[5]
Yet, it is not simply as a polygamist that Abraham is appealed to:
29 Abraham received all things, whatsoever he received, by revelation and commandment, by my word, saith the Lord, and hath entered into his exaltation and sitteth upon his throne.
30 Abraham received promises concerning his seed, and of the fruit of his loins—from whose loins ye are, namely, my servant Joseph—which were to continue so long as they were in the world; and as touching Abraham and his seed, out of the world they should continue; both in the world and out of the world should they continue as innumerable as the stars; or, if ye were to count the sand upon the seashore ye could not number them.
31 This promise is yours also, because ye are of Abraham, and the promise was made unto Abraham; and by this law is the continuation of the works of my Father, wherein he glorifieth himself.
32 Go ye, therefore, and do the works of Abraham; enter ye into my law and ye shall be saved.
33 But if ye enter not into my law ye cannot receive the promise of my Father, which he made unto Abraham.
The works of Abraham, we remember, were obedience and service to God. Joseph and others were to "enter into [God's] law," which has been explained earlier in the section as the law of sealing as part of the new and everlasting covenant (D&C 132꞉7; see here for a more extensive discussion of the new and everlasting covenant).
34 God commanded Abraham, and Sarah gave Hagar to Abraham to wife. And why did she do it? Because this was the law; and from Hagar sprang many people. This, therefore, was fulfilling, among other things, the promises.
35 Was Abraham, therefore, under condemnation? Verily I say unto you, Nay; for I, the Lord, commanded it.
We must not confuse "the law" to which verse 34 refers with "the law" described in verse 7: "The conditions of this law are these: All covenants, contracts, bonds, obligations, oaths, vows, performances, connections, associations, or expectations, that are not made and entered into and sealed by the Holy Spirit of promise...are of no efficacy, virtue, or force in and after the resurrection from the dead; for all contracts that are not made unto this end have an end when men are dead."
"The law" which Sarah obeys or follows is later (v. 64-65) referred to as "the law of Sarah"—this law seems to imply that a man who will practice plural marriage must first give his wife the opportunity to approve and endorse the new wife. Thus, the rhetorical question and answer is not
But, rather:
We here recall that this revelation was written to persuade Emma Smith to endorse plural marriage; this argument, then, is especially directed at her (see verses 51-56).
We note also that Abraham was not condemned—but not because plural marriage was "the law" and he practiced it, but because he was commanded and then acted. And, it was this fundamental obedience to any and every commandment that made Abraham great, as the next verse makes clear:
36 Abraham was commanded to offer his son Isaac; nevertheless, it was written: Thou shalt not kill. Abraham, however, did not refuse, and it was accounted unto him for righteousness.
If taking a plural wife was "the law," which Abraham was bound by, then this analogy makes little sense—for it is surely not a law to murder. Indeed, the Lord acknowledges that the "default setting" for the law is not to kill. But, Abraham was commanded to sacrifice Isaac. Abraham took a plural wife not because it was the law, but because he was commanded (just as Joseph had been):
37 Abraham received concubines, and they bore him children; and it was accounted unto him for righteousness, because they were given unto him, and he abode in my law; as Isaac also and Jacob did none other things than that which they were commanded; and because they did none other things than that which they were commanded, they have entered into their exaltation, according to the promises, and sit upon thrones, and are not angels but are gods.
Abraham kept "the law"—the sealing power and conditions detailed earlier. He, Isaac, and Jacob were justified because they "did the works of Abraham"—they did "none other things than that which they were commanded."
The Lord returns to Abraham later in the section:
49 For I am the Lord thy God, and will be with thee even unto the end of the world, and through all eternity; for verily I seal upon you your exaltation, and prepare a throne for you in the kingdom of my Father, with Abraham your father.
50 Behold, I have seen your sacrifices, and will forgive all your sins; I have seen your sacrifices in obedience to that which I have told you. Go, therefore, and I make a way for your escape, as I accepted the offering of Abraham of his son Isaac.
The same themes recur—Joseph has been obedient, and thus will join Abraham. He has sacrificed (as with Isaac, notably, rather than as with Hagar) in obedience.
The criticism that polygamy is irreligious appeals to western sensibilities which favor monogamy, and argues that polygamy is inconsistent with biblical Christianity or (ironically) the Book of Mormon itself.Even were there no such precedents, LDS theology has no problem accepting and implementing novel commandments, since the Saints believe in continuing revelation. I will not belabor the matter here, since ample resources are available.
This is a weak attack at best, and replies–devotional, apologetic, and scholarly–have been made to the claim. There is extensive, unequivocal evidence that polygamous relationships were condoned under various circumstances by biblical prophets, despite how uncomfortable this might make a modern Christian. Elder Orson Pratt was widely viewed as the victor in a three-day debate on this very point with Reverend John P. Newman, Chaplain of the U.S. Senate, in 1870.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Joseph's plural marriages were not known until Joseph was caught with Fanny Alger. Oliver Cowdery referred to it as a 'dirty, nasty, filthy affair'. Now suppose for just a minute, that this really was an affair as reported by Brother Cowdery, an apostle and one of the three witnesses to the Book of Mormon. Why would Joseph make up the preposterous story that an angel with a sword commanded him to practice polygamy (before the sealing power was even restored no less)? Why, because he could. People believed him. They believed his earlier story about an angel, so why not another one? Perhaps the entire practice of polygamy by the saints was inspired by Joseph's efforts to cover up an affair? If he was truly in an affair, he would have a hard time justifying his adultery, and he may have lost many, many followers. But he came up with the only excuse that could be justified - God commanded him to. It was so successful that he continued to take more and more women as wives.
Question: Did Joseph Smith institute polygamy because he had a "voracious sexual appetite"? Source:Webb:BYUS:2011:18:Joseph Smith's doctrine and character demand our amazement
Template:IndexClaimItemShort Question: Was Heber C. Kimball concerned that missionaries would "take all the best" convert women as plural wives before they returned to Salt Lake City?
Template:Endnotes sources
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now